Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, originates in the large intestine (colon) or rectum. It is a significant health concern globally, particularly in India, where the incidence is rising. Several risk factors contribute to the development of colon cancer, including age, gender, genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and dietary habits. Understanding these factors is crucial for prevention and early detection strategies. This article focuses specifically on how age and gender influence the risk of developing colon cancer.
The Role of Age in Colon Cancer Risk
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for colon cancer. The majority of cases occur in individuals over the age of 50. As people age, the likelihood of developing mutations in the cells of the colon increases, leading to potential tumor formation. Regular screenings, such as colonoscopies, are recommended starting at age 45, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Additionally, the risk continues to rise with advancing age, making it imperative for older adults to be vigilant about their gastrointestinal health.
Gender Differences in Colon Cancer Incidence
Research indicates that gender plays a critical role in the incidence of colon cancer. Men are generally at a higher risk compared to women. Several studies have shown that men are 30% more likely to develop colon cancer than their female counterparts. This disparity may be attributed to various factors, including hormonal differences, lifestyle choices, and the prevalence of certain risk factors like smoking and obesity, which are often more common in men.
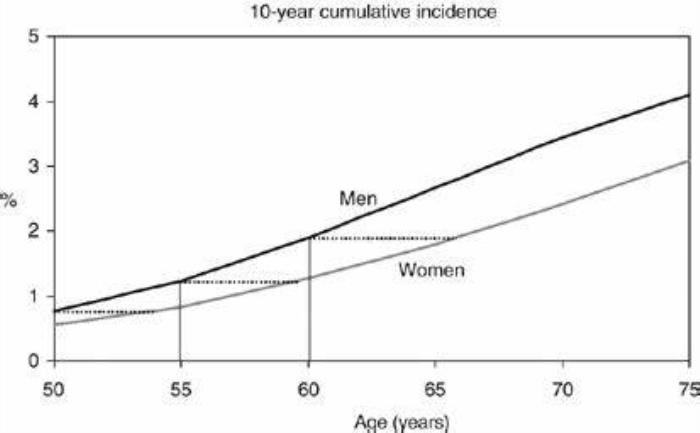
The Impact of Hormonal Differences on Colon Cancer Risk
Hormonal differences between men and women may influence colon cancer risk. Estrogen, a hormone prevalent in females, has been suggested to have a protective effect against the development of colon cancer. Some studies indicate that postmenopausal women who use hormone replacement therapy may have a reduced risk of colon cancer. In contrast, the absence of estrogen in men may contribute to a higher susceptibility to the disease, highlighting the importance of understanding hormonal influences in cancer risk assessments.
Genetic Predisposition and Family History
Both age and gender are closely linked to genetic predispositions that affect colon cancer risk. Individuals with a family history of colon cancer or genetic conditions such as Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) or Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC) are at an elevated risk. This risk is compounded by age, as the likelihood of developing these genetic mutations increases over time. Regular screening and genetic counseling are recommended for individuals with a family history of colon cancer to facilitate early detection and preventive measures.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Colon Cancer Risk by Age and Gender
Lifestyle choices significantly impact colon cancer risk, with variations observed between genders and age groups. Factors such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption play a crucial role. For instance, a diet high in red and processed meats is associated with an increased risk of colon cancer, particularly in men. Conversely, women may benefit from a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Engaging in regular physical activity can also mitigate risk, emphasizing the importance of healthy lifestyle choices across all age groups.
Screening Recommendations Based on Age and Gender
Screening for colon cancer is vital for early detection and improved outcomes. Guidelines recommend that individuals at average risk begin screening at age 45. However, those with a family history or other risk factors may need to start earlier. Men are often encouraged to adhere strictly to screening schedules due to their higher risk. Various screening methods, including colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and stool tests, are available, and healthcare providers should tailor recommendations based on individual risk factors, age, and gender.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer to Watch For by Age and Gender
Awareness of colon cancer symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss. While these symptoms can occur at any age, older adults should be particularly vigilant, as symptoms may be overlooked or attributed to other health issues. Gender-specific symptoms may also arise; for instance, men may experience more pronounced abdominal pain, while women might report changes in menstrual cycles alongside gastrointestinal symptoms.
The Importance of Early Detection in Colon Cancer
Early detection of colon cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. Regular screenings and awareness of symptoms are crucial, especially for individuals over the age of 50 or those at higher risk due to family history or genetic factors. Early-stage colon cancer may not present noticeable symptoms, making routine screenings essential. Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating patients about the importance of early detection and encouraging adherence to screening guidelines based on age and gender.
Advancements in Colon Cancer Research Related to Age and Gender
Recent advancements in colon cancer research have shed light on the complex interplay between age, gender, and cancer risk. Studies are increasingly focusing on understanding the molecular and genetic factors that contribute to differences in colon cancer incidence among genders and age groups. Ongoing research aims to develop targeted therapies and personalized treatment plans that consider these differences, ultimately improving outcomes for all patients. Staying informed about the latest research is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Management and Treatment Options for Colon Cancer
Management and treatment of colon cancer typically involve a multidisciplinary approach, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Treatment plans are often tailored based on the stage of cancer, age, and overall health of the patient. Younger patients may have different treatment tolerances compared to older adults, influencing the choice of therapy. Gender may also play a role in treatment response and side effects, necessitating individualized care plans that consider these factors for optimal outcomes.
Psychosocial Factors Affecting Patients with Colon Cancer
The diagnosis of colon cancer can significantly impact the psychological well-being of patients. Age and gender can influence how individuals cope with the diagnosis and treatment. Younger patients may face unique challenges, such as concerns about fertility and family planning, while older patients may experience anxiety related to comorbidities. Gender differences in coping mechanisms also exist, with women often seeking social support more readily than men. Understanding these psychosocial factors is crucial for providing comprehensive care to colon cancer patients.
Support Systems for Colon Cancer Patients Across Different Ages
Support systems are vital for patients undergoing treatment for colon cancer, and these systems may vary depending on age and gender. Younger patients may benefit from support groups focused on issues unique to their demographic, such as fertility preservation and family dynamics. In contrast, older patients may require assistance with managing comorbidities and navigating healthcare systems. Gender-specific support networks can also enhance coping strategies, emphasizing the need for tailored support systems to address the diverse needs of colon cancer patients.
Nutrition and Diet for Colon Cancer Prevention by Age and Gender
Nutrition plays a critical role in the prevention and management of colon cancer. Dietary recommendations may vary based on age and gender. For instance, older adults may require diets rich in fiber to promote bowel health, while younger individuals may focus on maintaining a balanced diet to support overall health. Women may benefit from diets high in calcium and vitamin D, which have been linked to lower colon cancer risk. Understanding these dietary nuances is essential for both prevention and recovery from colon cancer.
Community Awareness and Education on Colon Cancer
Community awareness and education are crucial in combating colon cancer, particularly in India, where awareness levels are still low. Educational initiatives should focus on informing the public about the importance of screenings, recognizing symptoms, and understanding risk factors associated with age and gender. Engaging community leaders and healthcare providers in awareness campaigns can help disseminate vital information and encourage proactive health measures among different demographics, ultimately aiming to reduce the incidence of colon cancer.
Future Directions in Colon Cancer Research Related to Demographics
Future research in colon cancer must continue to explore the demographic factors of age and gender to better understand their impact on disease risk, progression, and treatment response. Longitudinal studies that follow diverse populations can provide insights into how these factors influence cancer biology and patient outcomes. Additionally, research focused on developing targeted therapies that consider age and gender differences will be essential in improving treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects for colon cancer patients.
Role of Precision Medicine in Advanced Colon Cancer Care
Learn about the transformative impact of precision medicine in advanced colon cancer care. By tailoring treatments to the unique genetic profile of a patient’s cancer, precision medicine enhances effectiveness and minimizes side effects. Discover how this approach is reshaping the future of colon cancer treatment.
Role of PET Scans in Colon Cancer Staging and Monitoring
Discover the significance of PET scans in colon cancer staging and monitoring. These advanced imaging techniques provide detailed insights into cancer spread and treatment response, playing a crucial role in personalized care plans for colon cancer patients.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Age and Gender in Colon Cancer Risk
In summary, both age and gender significantly influence the risk of developing colon cancer. Understanding these factors allows for improved screening, prevention, and treatment strategies tailored to individual needs. As research continues to evolve, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in educating patients about their risks and the importance of early detection. By addressing the unique challenges posed by age and gender, we can enhance outcomes for all individuals affected by colon cancer.
Best Colon Cancer Treatment in India
The Best Colon Cancer Treatment in India includes advanced procedures such as minimally invasive surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies to achieve the best outcomes for patients.
Colon Cancer Treatment Cost in India
The colon cancer treatment cost in india is competitive, providing patients with affordable access to high-quality care and innovative treatment options.
Best Colon Cancer Specialists in India
The Best Colon Cancer Specialists in India bring years of expertise in diagnosing and treating colon cancer, ensuring personalized treatment plans and compassionate care for every patient.
FAQs About Colon Cancer Risk Related to Age and Gender
What is the average age for colon cancer diagnosis?
The average age for colon cancer diagnosis is typically over 50, with recommendations for screening beginning at age 45 for average-risk individuals. Early detection is crucial for improving outcomes.
Are women less likely to develop colon cancer than men?
Yes, studies indicate that men are approximately 30% more likely to develop colon cancer than women, although women still face significant risk, particularly after menopause.
How can lifestyle changes impact colon cancer risk?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can significantly reduce colon cancer risk for individuals of all ages and genders.
What screening methods are available for colon cancer?
Common screening methods for colon cancer include colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and stool-based tests. The choice of screening method may depend on individual risk factors and preferences.
Is genetic testing recommended for individuals with a family history of colon cancer?
Yes, genetic testing is often recommended for individuals with a family history of colon cancer or related genetic syndromes to assess their risk and inform screening strategies.
Discover the Best Oncologists and Cancer Hospitals in India
When it comes to cancer treatment, finding the right specialist and hospital can make a significant difference in the outcome. In this blog, we have compiled a list of the top oncologists and cancer hospitals across major cities in India, ensuring that you have access to the best care available.
Top Oncologists in Major Cities
For those seeking expert oncologists, we have identified the best specialists in key cities:
Leading Cancer Hospitals
In addition to finding the right specialist, choosing the right hospital is crucial for comprehensive cancer care. Here are the top hospitals in major cities:
Get more indepth information on Cancer treatments and their costs
Conclusion
Finding the right oncologist and hospital is the first step in your cancer treatment journey. Explore the links above to learn more about the top specialists and hospitals in your area.