Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat blocked or narrowed blood vessels, often caused by conditions like coronary artery disease. It helps restore blood flow to the heart, reducing symptoms such as chest pain and preventing severe complications like heart attacks. Patients often wonder whether angioplasty with or without a stent is the better option for their condition.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Choosing between angioplasty with or without a stent depends on factors like the severity of the blockage, patient health, and long-term outcomes. Both approaches have their benefits and risks, making it essential for patients to understand the differences. This article explores these options to help you make an informed decision about your cardiac care.
What Is Angioplasty and How Does It Work?
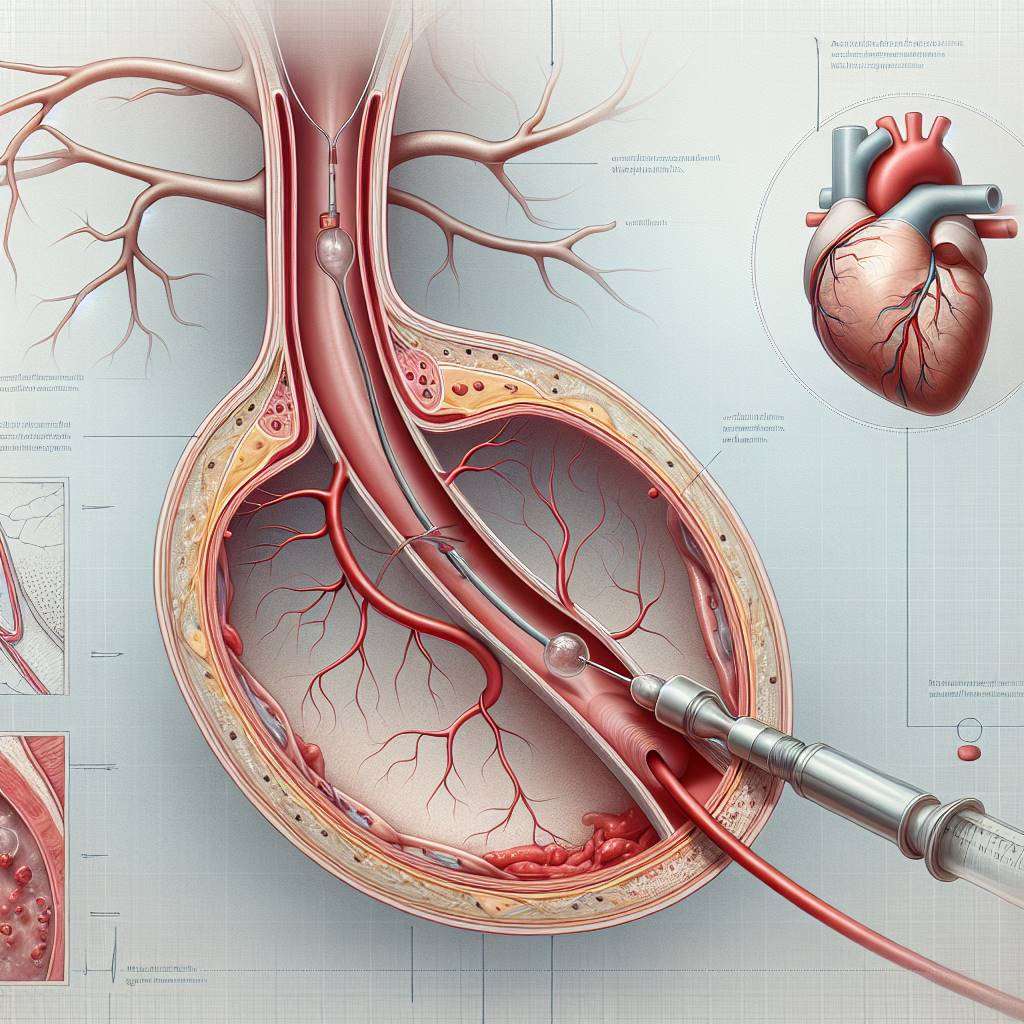
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure designed to open blocked or narrowed arteries. It involves inserting a thin tube called a catheter into the blood vessel, usually through the groin or wrist. A small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow.
This procedure is commonly used to treat atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up in the arteries. Angioplasty is often performed as an emergency treatment during a heart attack or as a planned procedure for patients with chronic chest pain (angina). It is a safe and effective way to restore blood flow and reduce symptoms.
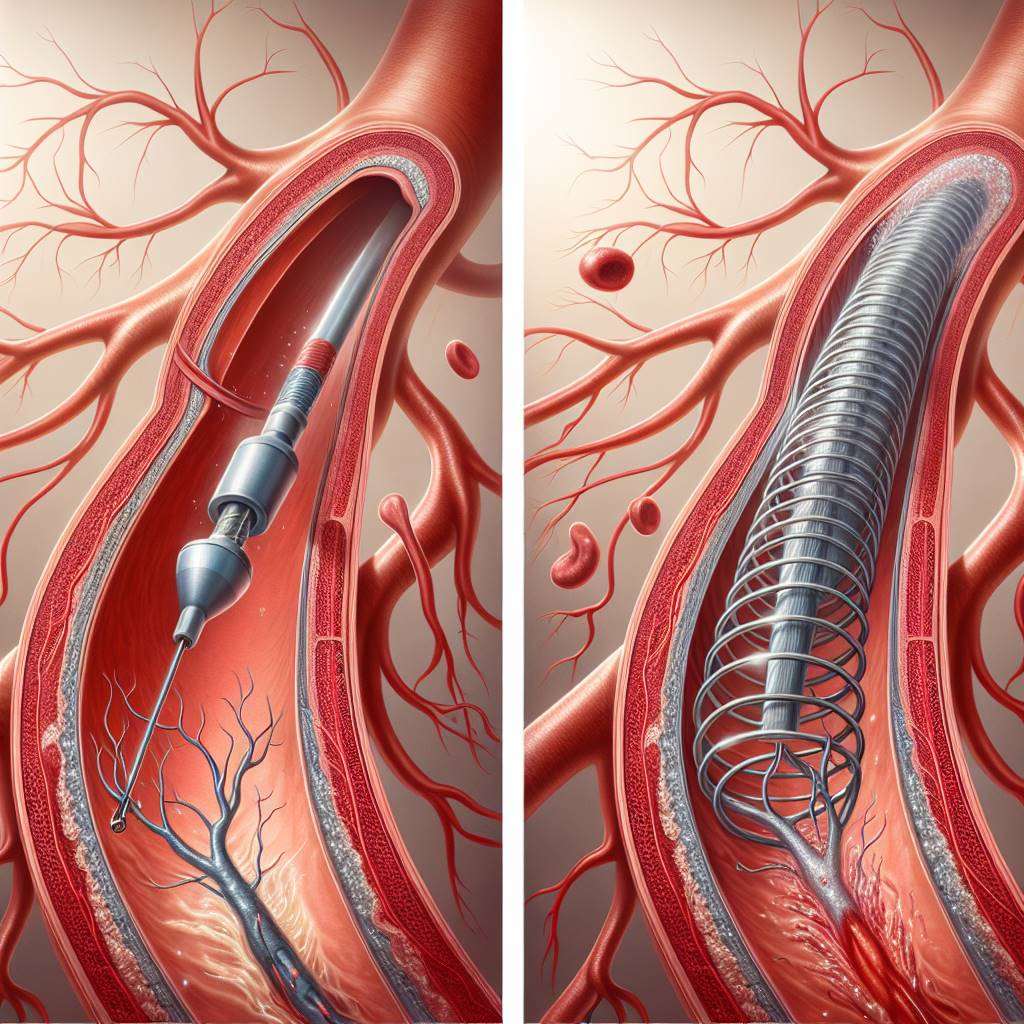
In some cases, a stent—a small mesh tube—is placed in the artery to keep it open after the balloon is deflated and removed. This helps prevent the artery from narrowing again, a condition known as restenosis.
Understanding the Role of Stents in Angioplasty
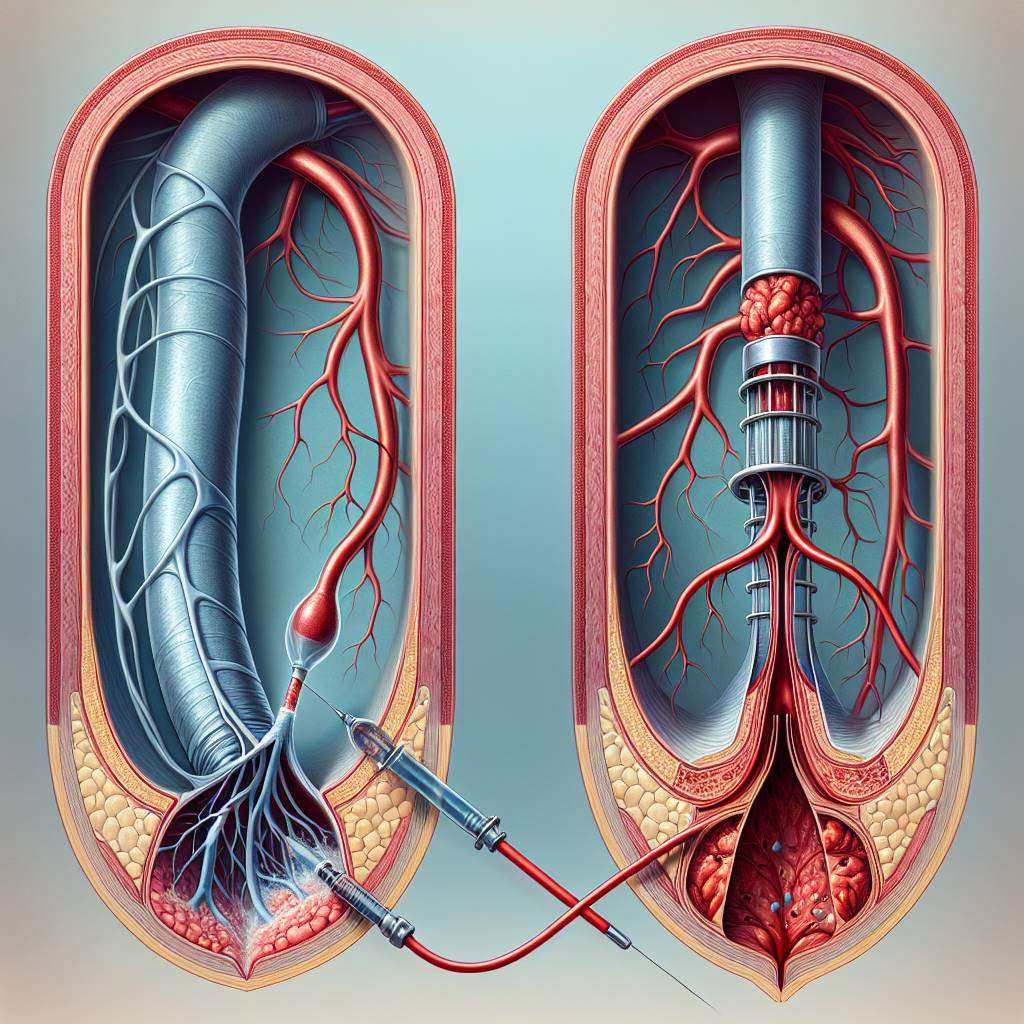
A stent is a tiny, expandable mesh tube that is placed in an artery during angioplasty to keep it open. Stents are particularly useful in cases where the artery is at high risk of collapsing or becoming blocked again. There are two main types of stents: bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents. Drug-eluting stents are coated with medication that helps prevent scar tissue from forming inside the artery.
Stents have revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease by significantly reducing the risk of restenosis. However, they also come with potential risks, such as blood clots forming around the stent, which may require long-term use of blood-thinning medications. Understanding the role of stents is crucial for patients considering angioplasty as a treatment option.
Angioplasty Without Stent: Pros and Cons Explained
Angioplasty without a stent, also known as balloon angioplasty, is a procedure where only the balloon is used to widen the artery. This approach may be suitable for patients with minimal or short-term blockages. One advantage of this method is that it eliminates the need for a permanent implant, reducing the risk of complications like stent thrombosis.
However, the main drawback of angioplasty without a stent is the higher likelihood of restenosis. Without a stent to support the artery, there is a greater chance that the artery will narrow again over time. Patients undergoing this procedure may require close monitoring and additional treatments if restenosis occurs.
- Pros: No permanent implant, lower risk of stent-related complications.
- Cons: Higher risk of restenosis, may require repeat procedures.
When Is Angioplasty With a Stent Recommended?
Angioplasty with a stent is often recommended for patients with severe or long-term blockages in their arteries. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like acute coronary syndrome or those who have experienced a heart attack. Stents provide structural support to the artery, reducing the risk of restenosis and improving long-term outcomes.
This approach is also preferred in cases where the blockage is located in a critical area of the artery or when the artery is prone to collapse. Drug-eluting stents are commonly used in such cases to minimize the risk of scar tissue formation. Patients should discuss their specific condition with their doctor to determine if a stent is the right choice.
Comparing Risks: Angioplasty With vs Without Stent
Both angioplasty with and without a stent have their own set of risks and benefits. While stents reduce the risk of restenosis, they can increase the likelihood of complications like stent thrombosis or the need for long-term blood-thinning medications. On the other hand, angioplasty without a stent avoids these risks but has a higher chance of the artery narrowing again.
The table below highlights the key differences between the two approaches:
| Aspect |
With Stent |
Without Stent |
| Risk of Restenosis |
Lower |
Higher |
| Need for Blood Thinners |
Yes |
No |
| Long-Term Outcomes |
Better |
Varies |
Patients should weigh these factors carefully and consult their doctor to choose the most suitable treatment option based on their medical history and condition.
Cost Differences Between Angioplasty With and Without Stent
The cost of an angioplasty procedure can vary significantly depending on whether a stent is used. Angioplasty without a stent is generally less expensive because it involves fewer materials and a shorter procedure time. However, in many cases, a stent is necessary to keep the artery open and prevent future blockages.
In India, the cost of angioplasty with a stent can range from ₹1.5 lakh to ₹3.5 lakh, depending on the type of stent used (e.g., drug-eluting stents are more expensive than bare-metal stents). On the other hand, angioplasty without a stent may cost between ₹80,000 and ₹1.5 lakh. Patients should also consider additional costs like hospital stay, medications, and follow-up care.
Which Is Safer: Angioplasty With or Without Stent?
When it comes to safety, both types of angioplasty have their own benefits and risks. Angioplasty with a stent is often considered safer for patients with severe blockages or recurring coronary artery disease (CAD). The stent helps keep the artery open, reducing the risk of re-narrowing (restenosis).
However, angioplasty without a stent may be safer for patients with minimal blockages or those at higher risk of complications from stent placement, such as blood clots. In such cases, the procedure focuses on widening the artery without leaving a foreign object behind.
- Angioplasty with stent: Lower risk of restenosis but requires long-term antiplatelet therapy.
- Angioplasty without stent: Fewer complications but higher risk of artery narrowing again.
Recovery Time: Angioplasty With Stent vs Without
Recovery time after an angioplasty depends on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s overall health. Generally, patients who undergo angioplasty with a stent may require a slightly longer recovery period due to the need for close monitoring of the stent's placement and function.
Most patients can resume light activities within a week after the procedure, whether or not a stent is used. However, those with a stent may need to follow stricter guidelines for medication adherence and lifestyle changes to prevent complications like blood clots or restenosis.
It is essential to attend follow-up appointments and adhere to prescribed medications, such as blood thinners, to ensure a smooth recovery.
Long-Term Outcomes of Angioplasty With and Without Stent
The long-term outcomes of angioplasty depend on factors like the severity of the blockage, the patient’s adherence to treatment, and whether a stent was used. Angioplasty with a stent generally offers better long-term results by reducing the risk of restenosis. Drug-eluting stents, in particular, are effective at preventing the re-narrowing of arteries.
On the other hand, angioplasty without a stent may be sufficient for patients with minor blockages. However, these patients may face a higher likelihood of needing repeat procedures if the artery narrows again. Lifestyle changes, such as a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, play a crucial role in improving long-term outcomes for both types of procedures.
| Factor |
With Stent |
Without Stent |
| Risk of Restenosis |
Low |
Moderate to High |
| Need for Repeat Procedure |
Rare |
Possible |
| Medication Requirement |
Long-term |
Short-term |
How to Decide Between Angioplasty With or Without Stent
Deciding between angioplasty with or without a stent depends on several factors, including the severity of the blockage, the patient’s medical history, and the advice of the treating cardiologist. Patients with significant blockages or recurring chest pain (angina) may benefit more from a stent to ensure long-term artery patency.
For patients with minimal blockages or those at higher risk of complications from stent placement, angioplasty without a stent may be a viable option. It is crucial to discuss the risks, benefits, and costs of each approach with your doctor to make an informed decision.
Ultimately, the choice should be tailored to the patient’s individual needs, ensuring the best possible outcome for their heart health.
Angioplasty Success Rates: With Stent vs Without Stent
Angioplasty is a common procedure to treat blocked arteries. It can be performed with or without a stent. A stent is a small mesh tube inserted into the artery to keep it open after the blockage is cleared. Studies show that angioplasty with stents generally has higher success rates in preventing re-narrowing of arteries.
However, not all patients require a stent. Angioplasty without a stent may be effective in cases where the blockage is minimal or in smaller arteries. The choice depends on factors like the severity of the blockage, patient health, and the risk of complications. Discussing these options with your doctor is crucial for the best outcome.
Do All Patients Need a Stent During Angioplasty?
Not all patients undergoing angioplasty require a stent. The decision depends on the type and location of the arterial blockage. For example, stable angina or minor blockages may not need stenting, while severe blockages often do.
Doctors use advanced imaging techniques like angiography to assess the need for a stent. In some cases, medications and lifestyle changes may be sufficient to manage the condition without a stent. However, for patients with high-risk blockages, stents can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and improve blood flow.
It’s essential to consult a cardiologist to understand whether a stent is necessary for your specific condition and how it impacts long-term outcomes.
Angioplasty Without Stent: Who Is It Suitable For?
Angioplasty without a stent, also known as plain balloon angioplasty, is suitable for certain patients. It is often recommended for individuals with small blockages or those who cannot tolerate stents due to allergies or other medical conditions.
This procedure involves using a balloon to widen the blocked artery without leaving a stent behind. While it can be effective, there is a higher risk of the artery narrowing again, a condition called restenosis. For this reason, it is typically reserved for specific cases where stenting is not ideal.
Patients considering this option should discuss the risks and benefits with their doctor to ensure it aligns with their health needs and lifestyle.
Benefits of Stents in Treating Blocked Arteries
Stents offer several benefits in treating blocked arteries. They help maintain blood flow by keeping the artery open after angioplasty. This reduces the risk of restenosis and improves long-term outcomes for patients with severe blockages.
There are two main types of stents: bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents. Drug-eluting stents release medication to prevent scar tissue formation, further lowering the risk of re-narrowing. Stents are particularly beneficial for patients with multiple or complex blockages.
| Type of Stent |
Key Benefit |
| Bare-Metal Stent |
Provides immediate artery support |
| Drug-Eluting Stent |
Reduces risk of restenosis |
Discussing the type of stent with your doctor can help you make an informed decision.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Angioplasty Options
Before undergoing angioplasty, it’s important to ask your doctor the right questions to understand your treatment options. Here are some key questions to consider:
- Do I need a stent, or is angioplasty without a stent sufficient?
- What are the risks and benefits of each option?
- What type of stent is best for my condition?
- How long will recovery take, and what lifestyle changes are necessary?
- Are there alternative treatments to angioplasty?
By addressing these questions, you can make a well-informed decision about your treatment and ensure the best possible outcome for your heart health.
Best Coronary Angioplasty Doctors in India
Two reputed doctors specializing in Angioplasty in India are Dr. Naresh Trehan, Chairman of Medanta - The Medicity, Gurugram, with over 50 years of experience and international recognition in cardiovascular surgery, and Dr. Ashok Seth, Chairman of Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Delhi, with over 35 years of experience and expertise in interventional cardiology. Both are globally acclaimed for their medical excellence and contributions.
Learn more on best coronary angioplasty doctors in india
Best Coronary Angioplasty Hospitals in India
Leading hospitals for Angioplasty in India include Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Delhi, known for its advanced interventional cardiology and NABH accreditation, and Medanta - The Medicity, Gurugram, offering multidisciplinary care and robotic-assisted procedures. Both hospitals provide international patient services and have a track record of high success rates in cardiovascular treatments.
Find more best coronary angioplasty hospitals in india
Coronary Angioplasty Cost in India
The cost of Angioplasty in India typically ranges from INR 1,50,000 to INR 3,50,000 (approximately USD 1,800 to USD 4,200), depending on factors like the doctor’s expertise, hospital type, and procedure complexity. The average hospital stay is 1-3 days. India offers a significant cost advantage compared to Western countries, with options for medical insurance and third-party financing.
Learn coronary angioplasty cost in india
Coronary Angioplasty Treatment in India
Angioplasty in India involves inserting a catheter with a balloon to open blocked arteries, often followed by stent placement. Advanced technologies like drug-eluting stents and intravascular imaging are commonly used. Recovery typically takes 1-2 weeks. Top hospitals in India adhere to global medical protocols and adopt innovations like robotic-assisted angioplasty for precision and better outcomes.
Learn on Coronary Angioplasty Treatment in India
FAQs
What is the difference between angioplasty with and without a stent?
Angioplasty without a stent involves using a balloon to open a blocked artery, while angioplasty with a stent includes placing a stent (a small mesh tube) to keep the artery open and reduce the risk of re-narrowing.
Is angioplasty with a stent more effective?
In most cases, angioplasty with a stent is more effective as it helps maintain long-term artery patency, especially in patients with severe blockages or high risk of restenosis.
What are the risks of angioplasty?
Risks of angioplasty include bleeding, infection, artery damage, or restenosis. However, these risks are minimal when performed by experienced cardiologists in advanced facilities.
How long does it take to recover from angioplasty?
Recovery from angioplasty typically takes 1-2 weeks. Patients are advised to follow a heart-healthy lifestyle and attend follow-up appointments for optimal recovery.
Is angioplasty a permanent solution for heart blockages?
While angioplasty can effectively treat blockages, it is not a permanent solution. Lifestyle changes and medications are essential to prevent future blockages.
Can angioplasty be repeated if needed?
Yes, angioplasty can be repeated if necessary, especially in cases of restenosis or new blockages. However, the decision depends on the patient’s overall health and medical history.
Are there alternatives to angioplasty?
Alternatives to angioplasty include medications, lifestyle changes, or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) for severe cases. The choice depends on the severity of the condition.
How do I choose between angioplasty with or without a stent?
The choice depends on the severity of the blockage, patient health, and risk of restenosis. Your cardiologist will recommend the best option based on your condition.
Is angioplasty covered by insurance in India?
Yes, most health insurance policies in India cover angioplasty. It is advisable to check with your insurer for specific coverage details and pre-authorization requirements.
How do I prepare for an angioplasty procedure?
Preparation for angioplasty includes fasting for a few hours, stopping certain medications as advised, and undergoing pre-procedure tests like blood work and imaging studies.
Understanding Angioplasty and Its Alternatives
Angioplasty is a common procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, particularly in the heart. However, the decision to recommend angioplasty over bypass surgery often depends on various factors, including the severity of the blockage and the overall health of the patient. For a detailed exploration of when doctors prefer angioplasty instead of bypass surgery, check out this insightful article on angioplasty recommendations.
While angioplasty can be effective, there are instances where the procedure may not achieve the desired results. In such cases, understanding the next steps is crucial for patients. If you’re curious about what happens when angioplasty fails, this comprehensive guide on angioplasty failures provides valuable insights into alternative treatments and management strategies.
By staying informed about these procedures and their outcomes, patients can make better decisions regarding their heart health and treatment options.
Explore the Best Heart Care Resources in India
Find some of the top cardiologist, surgeons and the best heart hospitals in India
Best Heart Hospitals in India
Choosing the right hospital is crucial for successful heart treatments. If you want to explore trusted options, check the list of Best Heart Hospitals in India offering world-class facilities, advanced cardiac care units, and experienced teams for both simple and complex procedures.
Best Cardiologists in India
Finding the right cardiologist can make a huge difference in early diagnosis and long-term heart health. If you are looking for the Best Cardiologists in India, see this curated list of experts who specialize in preventive care, interventional cardiology, and complex heart disease management. Check the full list Best Cardiologists in India.
Best Cardiac Surgeons in India
If you are planning for heart surgery and need top-level expertise, we recommend exploring the Best Cardiac Surgeons in India. These surgeons have a proven record in performing bypass surgeries, valve replacements, and minimally invasive heart operations with excellent outcomes.
Get more indepth information on Cardiology treatments and their costs.
Conclusion
Your cardiology health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top cardiac hospitals and cardiac surgeons in India.
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in angioplasty by providing detailed visuals of the arteries, helping guide the procedure, and ensuring optimal outcomes. Techniques like X-ray fluoroscopy, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), and optical coherence tomography (OCT) are commonly used. These methods allow for precise placement of stents, accurate assessment of blockages, and real-time monitoring during the procedure. By using advanced imaging, healthcare providers can better identify the true extent of arterial disease, improve stent deployment, and reduce the risk of complications such as restenosis and thrombosis. Understanding the Role of Imaging Techniques in Angioplasty
Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program designed to improve cardiovascular health after angioplasty. It typically includes exercise training, education on heart-healthy living, and counseling to reduce stress. The goal is to help patients recover, improve their fitness and confidence, and make necessary lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of future heart issues. This comprehensive approach supports physical, emotional, and psychological well-being, enhancing the overall quality of life for heart patients. The Role of Cardiac Rehabilitation After Angioplasty
Angioplasty often employs various stents to keep arteries open after clearing blockages. Bare-metal stents (BMS) provide permanent support but can lead to scar tissue. Drug-eluting stents (DES) release medication to prevent blockages and are suited for complex cases. Bioabsorbable stents dissolve over time and are ideal for younger patients. The choice depends on the blockage severity, patient’s age, and medical history. Understanding the Different Types of Stents Used in Angioplasty