Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect involving four key anatomical abnormalities that significantly impact heart function, especially the right ventricle. The condition alters the normal flow of blood through the heart, resulting in decreased oxygenation and impaired circulation. The right ventricle, in particular, plays a crucial role in the clinical manifestations of TOF, as the defects associated with the condition directly affect its function, leading to complications such as right ventricular hypertrophy and obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract. Understanding these effects is essential in managing and treating the condition.
The Anatomy of the Right Ventricle and Its Role in Circulation
The right ventricle is one of the heart’s four chambers and plays a pivotal role in pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation. It receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which transports it to the lungs. The right ventricle is structured to handle relatively low-pressure blood flow. Its ability to efficiently pump blood to the lungs is crucial for maintaining normal circulation and ensuring that oxygen-rich blood is then delivered to the rest of the body. However, in the case of TOF, the normal function of the right ventricle is disrupted by several structural defects.
How Tetralogy of Fallot Affects the Right Ventricle’s Function
In Tetralogy of Fallot, the right ventricle is affected by several key defects, including the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and pulmonary stenosis. The VSD creates an abnormal opening between the two ventricles, allowing oxygen-poor blood from the right side of the heart to mix with oxygen-rich blood from the left side. This can lead to reduced oxygen delivery to the body. Pulmonary stenosis, or narrowing of the pulmonary valve and right ventricular outflow tract, forces the right ventricle to work harder to push blood through the lungs. As a result, the right ventricle is under increased pressure, which can impair its ability to pump blood efficiently.
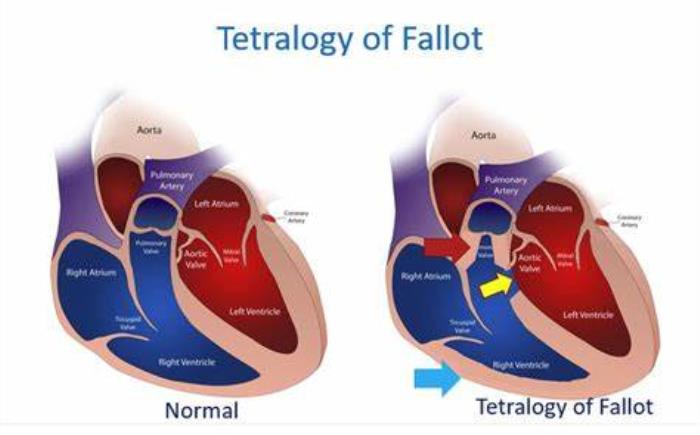
The Role of Right Ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot’s Clinical Manifestations
The right ventricle is at the center of many of the clinical signs and symptoms of Tetralogy of Fallot. The right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (RVOTO) caused by pulmonary stenosis is one of the most important factors contributing to cyanosis, or a bluish tint to the skin. This occurs because the obstruction limits the amount of blood reaching the lungs for oxygenation, leading to a lower oxygen saturation in the bloodstream. Over time, this condition can also lead to right ventricular hypertrophy (enlargement), as the heart muscle works harder to overcome the obstruction, leading to further deterioration of the right ventricle’s function.
Understanding the Pressure Load on the Right Ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot
One of the most significant effects of Tetralogy of Fallot on the right ventricle is the increased pressure load. The narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the RVOTO force the right ventricle to generate higher pressures in order to pump blood into the lungs. This additional strain on the right ventricle can lead to right ventricular hypertrophy, where the muscle thickens in an attempt to compensate for the increased workload. Over time, this hypertrophy can lead to reduced efficiency and further complications, such as arrhythmias or even heart failure if not properly managed.
The Effect of Right Ventricle Hypertrophy in Tetralogy of Fallot
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a common consequence of Tetralogy of Fallot, especially if the pulmonary stenosis is severe. The thickening of the right ventricular wall occurs as the heart works harder to pump blood through the narrowed pulmonary valve. While RVH may initially help compensate for the increased workload, it eventually causes the right ventricle to lose its ability to relax and expand, leading to further complications. Over time, the hypertrophied right ventricle becomes less efficient, which can exacerbate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and cyanosis. Surgical intervention, such as repair of the pulmonary stenosis and VSD, is often necessary to reduce the strain on the right ventricle and improve heart function.
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction A Key Feature of Tetralogy of Fallot
Right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (RVOTO) is one of the hallmark features of Tetralogy of Fallot. This obstruction occurs when the pulmonary valve or the muscular area below the valve is narrowed, making it difficult for the right ventricle to pump blood into the pulmonary artery. RVOTO increases the pressure within the right ventricle and causes the blood flow to the lungs to be restricted. As a result, oxygen-poor blood is not efficiently oxygenated, leading to cyanosis. In severe cases, the obstruction can be life-threatening if not surgically corrected. Management of RVOTO typically involves surgical repair or valve replacement to restore normal blood flow and reduce the burden on the right ventricle.
How Pulmonary Stenosis Complicates Right Ventricular Function in Tetralogy of Fallot
Pulmonary stenosis, a narrowing of the pulmonary valve or the pulmonary artery, is one of the four key components of Tetralogy of Fallot. This condition creates an obstruction to the flow of blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, leading to increased pressure within the right ventricle. Over time, this pressure overload can cause the right ventricle to work harder, leading to hypertrophy (thickening) of the right ventricle muscle. If left untreated, this strain can worsen the heart's ability to pump blood efficiently, resulting in further complications in heart function.
The Impact of Tetralogy of Fallot on Blood Oxygen Levels and the Right Ventricle
In Tetralogy of Fallot, the combination of pulmonary stenosis, a ventricular septal defect, an overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy leads to an inadequate flow of oxygenated blood to the body. The right ventricle is forced to pump deoxygenated blood through the aorta, which causes a drop in blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia). The right ventricle must compensate for this by working harder, which can cause long-term damage to its function and lead to symptoms like cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin) and respiratory distress in severe cases.
Right Ventricle Dilatation in Tetralogy of Fallot: What Does It Mean?
Right ventricular dilatation refers to the enlargement of the right ventricle due to chronic pressure overload, a common consequence of pulmonary stenosis in Tetralogy of Fallot. This dilatation can result from the right ventricle being forced to pump blood against high pressure for prolonged periods. Over time, this can weaken the muscle and reduce the efficiency of the heart's pumping function, which can lead to heart failure if not addressed. Surgical correction of the defect often helps to reduce this strain and prevent further dilatation.
How Tetralogy of Fallot Alters Blood Flow Between the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Artery
In Tetralogy of Fallot, the abnormal narrowing of the pulmonary valve or artery (pulmonary stenosis) obstructs blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs. This alteration in blood flow means that less blood reaches the lungs for oxygenation, and more blood is diverted through the overriding aorta, mixing oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich blood. This inefficient circulation leads to reduced oxygen levels in the blood and places additional strain on the right ventricle as it tries to pump blood through the restricted pulmonary arteries.
The Long-Term Effects of Tetralogy of Fallot on Right Ventricular Health
Long-term effects on the right ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot may include chronic right ventricular hypertrophy (thickening of the muscle), dilatation, and eventual dysfunction. As the right ventricle continues to pump blood against the resistance caused by pulmonary stenosis, the muscle becomes overworked and less efficient. Over time, this can lead to right heart failure, arrhythmias, and other complications. Early surgical intervention and proper postoperative care are crucial to preserving right ventricular health and preventing long-term damage.
Management of Right Ventricle Dysfunction in Tetralogy of Fallot Patients
Managing right ventricular dysfunction in Tetralogy of Fallot typically involves a combination of surgical correction, medications, and close monitoring. Surgery to repair the pulmonary stenosis and close the ventricular septal defect (VSD) is the primary treatment. Post-surgery, medications such as beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors may be used to reduce the workload on the right ventricle and manage heart function. Additionally, regular monitoring through echocardiograms and other imaging techniques is essential to assess the function of the right ventricle and detect any early signs of dysfunction.
The Role of Surgical Correction in Improving Right Ventricular Function in Tetralogy of Fallot
Surgical correction plays a vital role in improving right ventricular function in Tetralogy of Fallot patients. The primary goals of surgery are to relieve the obstruction caused by pulmonary stenosis, close the ventricular septal defect, and address the abnormal positioning of the aorta. By improving blood flow to the lungs and reducing the pressure on the right ventricle, surgery can prevent further hypertrophy and dilatation, restoring more normal function to the right ventricle and improving overall cardiac performance.
Monitoring Right Ventricular Function Post-Tetralogy of Fallot Repair
After Tetralogy of Fallot surgery, ongoing monitoring of right ventricular function is essential to detect any potential complications early. This may include routine echocardiograms, MRI scans, and sometimes heart catheterization, to assess the size, shape, and efficiency of the right ventricle. Monitoring also includes tracking the patient’s symptoms, such as shortness of breath or fatigue, which may indicate changes in heart function. Regular follow-up visits with a pediatric cardiologist or adult congenital heart specialist are crucial for managing long-term health.
Understanding the Relationship Between the Right Ventricle and Other Heart Chambers in Tetralogy of Fallot
In Tetralogy of Fallot, the right ventricle plays a central role in overall heart function. The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated by the lungs. However, due to pulmonary stenosis, this flow is obstructed, causing the right ventricle to work harder to overcome the resistance. This leads to hypertrophy and dilation of the right ventricle, which can eventually affect the left ventricle and overall circulatory dynamics. The interplay between these chambers can complicate the repair and recovery process, highlighting the importance of addressing the pulmonary stenosis and other defects during surgery.
How Right Ventricular Function Impacts Overall Cardiac Health in Tetralogy of Fallot
The function of the right ventricle is crucial for overall cardiac health in Tetralogy of Fallot. When the right ventricle is not functioning properly due to pressure overload from pulmonary stenosis, it can lead to poor oxygenation of the blood and compromised circulation throughout the body. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, cyanosis, and decreased exercise tolerance. Over time, if the right ventricle becomes too damaged, it can affect the left ventricle and other parts of the circulatory system, further compromising heart health.
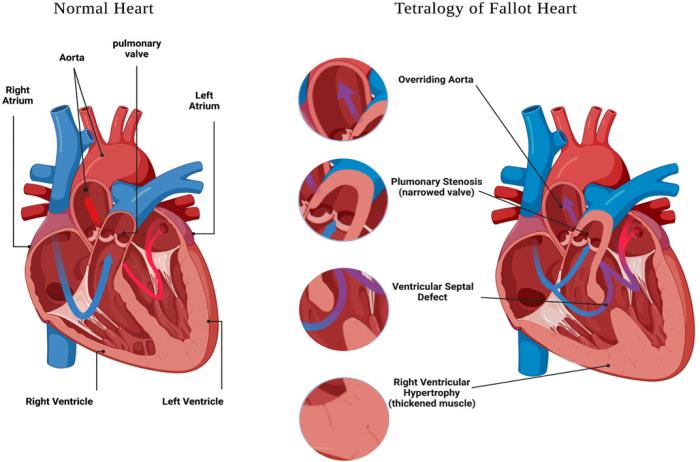
Advances in Imaging Techniques for Assessing Right Ventricular Health in Tetralogy of Fallot
Recent advances in imaging techniques, such as cardiac MRI and 3D echocardiography, have greatly improved the ability to assess right ventricular health in Tetralogy of Fallot patients. These techniques provide detailed images of the right ventricle’s size, function, and any structural abnormalities. By closely monitoring the right ventricle over time, doctors can identify issues like dilatation or reduced function early, allowing for timely interventions to prevent further damage and improve long-term outcomes.
The Importance of Early Intervention to Protect the Right Ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot
Early intervention in Tetralogy of Fallot is crucial to protect the right ventricle from long-term damage. Surgery to repair the defect early in life helps prevent the development of right ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation, which can occur when the heart is forced to work against elevated pressure. Timely correction of pulmonary stenosis and other abnormalities reduces the strain on the right ventricle and improves overall heart function, significantly enhancing long-term health and quality of life for patients.
Advances in Cardiac Imaging for Tetralogy of Fallot Diagnosis
Discover the latest advances in cardiac imaging for diagnosing Tetralogy of Fallot, enabling more accurate and detailed assessments to guide treatment and surgical decisions.
Conclusion: Improving Right Ventricle Function and Outcomes in Tetralogy of Fallot
Improving right ventricular function in Tetralogy of Fallot requires timely and effective intervention, including surgical repair, proper postoperative care, and continuous monitoring. By addressing the underlying defects early in life and managing right ventricular health throughout the patient’s life, it is possible to significantly improve heart function and overall health outcomes. Advances in imaging, surgical techniques, and medical management all contribute to better long-term outcomes for patients with Tetralogy of Fallot.
Best Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery in India
The Best Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery in India offers a comprehensive surgical solution for children and adults with TOF, helping correct heart defects and improve oxygenation and quality of life.
Best TOF Surgery Surgeons in India
The Best TOF Surgery Surgeons in India are experts in treating complex congenital heart defects, providing patient-focused care and skilled surgical expertise for successful TOF correction.
FAQ
How does Tetralogy of Fallot affect the right ventricle?
Tetralogy of Fallot causes increased pressure in the right ventricle due to pulmonary stenosis, leading to hypertrophy (thickening) and possible dilatation of the ventricle. Over time, this can impair the right ventricle’s ability to pump blood effectively.
What is the role of the right ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot?
The right ventricle is responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation. In Tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis restricts blood flow, causing the right ventricle to work harder and leading to long-term damage if left untreated.
How does pulmonary stenosis impact the right ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot?
Pulmonary stenosis obstructs blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs, causing increased pressure in the right ventricle. This pressure overload can lead to hypertrophy and eventually dysfunction of the right ventricle.
Why is early intervention important to protect the right ventricle in Tetralogy of Fallot?
Early intervention with surgery to repair the defects can prevent long-term damage to the right ventricle, such as hypertrophy and dilatation, which can lead to right heart failure and other complications.
How is right ventricular function monitored after Tetralogy of Fallot repair?
Right ventricular function is monitored through routine imaging tests such as echocardiograms, MRI scans, and clinical assessments of symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath. Regular follow-up with a pediatric or adult congenital heart specialist is essential for ongoing evaluation.