Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect that encompasses four key abnormalities, each of which disrupts the normal flow of blood through the heart and lungs. This condition leads to significant challenges in oxygen delivery throughout the body, often resulting in cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin) and other symptoms related to insufficient oxygen levels. The four defects work together to hinder proper circulation, making it essential for timely diagnosis and intervention to prevent long-term complications.
The Four Key Defects of Tetralogy of Fallot and Their Effects on Heart Function
Tetralogy of Fallot involves four key heart defects: pulmonary stenosis, a ventricular septal defect (VSD), overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy. Each of these defects impairs the heart's ability to efficiently pump oxygenated blood to the body. Pulmonary stenosis narrows the pathway to the lungs, making it difficult for the heart to send blood to the lungs for oxygenation. The VSD allows oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to mix with oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle, further compromising oxygen delivery to the body.
How Tetralogy of Fallot Disrupts Normal Blood Flow in the Heart
In a healthy heart, oxygen-poor blood is sent from the right side of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation, while oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart to be pumped throughout the body. However, in Tetralogy of Fallot, the combination of pulmonary stenosis, VSD, and overriding aorta disrupts this orderly circulation. The right ventricle struggles to pump blood into the lungs due to the obstruction created by the pulmonary stenosis. As a result, oxygen-poor blood mixes with oxygen-rich blood, reducing the amount of oxygen available for the body.
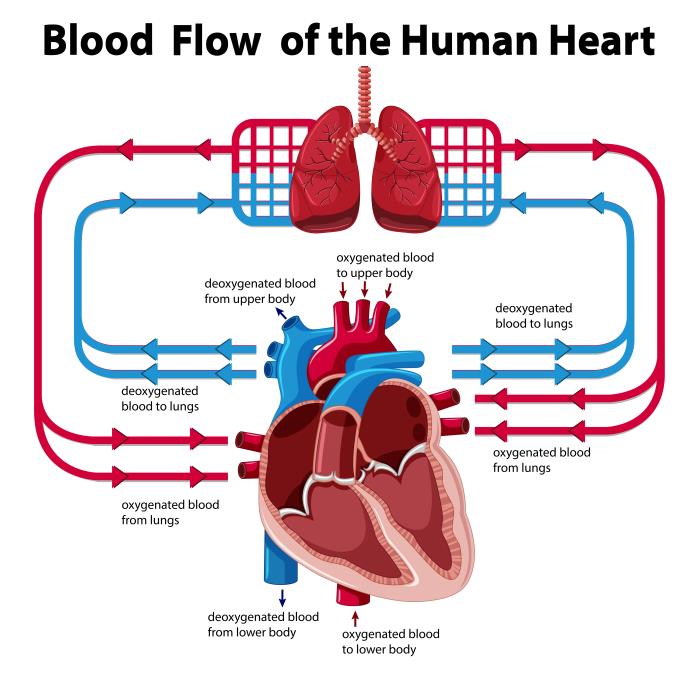
The Role of the Pulmonary Stenosis in Restricting Blood Flow to the Lungs
Pulmonary stenosis is a narrowing of the pulmonary valve or the pathway leading to the lungs, and it is one of the most significant contributors to the disruption of blood flow in Tetralogy of Fallot. This narrowing makes it harder for the right ventricle to pump blood into the pulmonary artery, reducing the amount of blood flowing to the lungs for oxygenation. As a result, the heart is forced to work harder, and the body receives less oxygen-rich blood.
The Ventricular Septal Defect: Creating Abnormal Blood Flow Between Heart Chambers
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a hole between the left and right ventricles of the heart. In the case of Tetralogy of Fallot, this defect allows oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to mix with oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle. This abnormal mixing of blood leads to the delivery of less oxygen to the body and can result in cyanosis. The VSD contributes to the inefficiency of the heart by allowing the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix, preventing the body from receiving the full benefit of the oxygen-rich blood that should be delivered to the systemic circulation.
Overriding Aorta: How It Compromises Oxygen Delivery to the Body
The overriding aorta is another key feature of Tetralogy of Fallot, where the aorta is positioned directly over the VSD rather than arising from the left ventricle alone. As a result, the aorta receives blood from both the left and right ventricles. Since the right ventricle is pumping blood that is low in oxygen due to the VSD, the overriding aorta contributes to the circulation of oxygen-poor blood throughout the body. This condition further limits the amount of oxygenated blood available for the body’s tissues and organs, leading to the characteristic symptoms of cyanosis and respiratory distress.
The Role of Right Ventricular Hypertrophy in Tetralogy of Fallot
Right ventricular hypertrophy occurs as a compensatory response to the increased workload placed on the right ventricle by pulmonary stenosis. As the right ventricle struggles to pump blood through the narrowed pulmonary valve, it thickens and enlarges in an attempt to overcome the obstruction. While this hypertrophy can temporarily help the right ventricle maintain blood flow, it ultimately weakens the heart muscle and further compromises heart function. Over time, the strain on the right ventricle can lead to heart failure if not addressed with surgical intervention.
How Blood Mixing Leads to Decreased Oxygen Levels in the Body
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect that causes blood mixing between the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart. The four components of TOF (ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy) lead to abnormal blood flow. As a result, oxygen-poor blood from the right side of the heart is pumped into the body alongside oxygen-rich blood from the left side, leading to decreased oxygen levels throughout the body. This is a critical issue, as oxygen is essential for all organ functions, especially in growing infants.
The Impact of Reduced Oxygen Supply on Organ Function and Growth
Low oxygen levels (hypoxemia) can affect the function of major organs, including the brain, heart, and lungs. In infants and children with TOF, chronic oxygen deprivation can result in poor growth, developmental delays, and difficulty with physical activities. The brain is particularly sensitive to reduced oxygen, which can cause cognitive and motor skill delays. Prolonged hypoxemia can also strain the heart, leading to heart failure if left untreated.
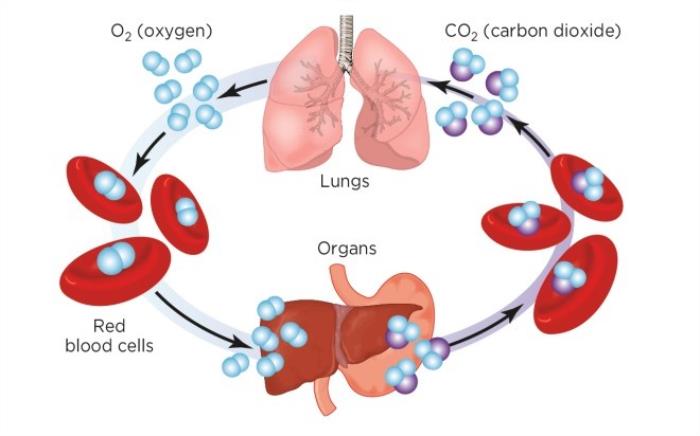
Symptoms of Low Oxygen Levels in Tetralogy of Fallot Patients
Patients with TOF may exhibit various symptoms of low oxygen levels, such as:
- Cyanosis (bluish skin, lips, or nails)
- Fatigue and low energy
- Shortness of breath during activity
- Poor weight gain or slow growth in infants
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded, especially during physical activity
How Cyanosis (Bluish Skin) Relates to Oxygen Deprivation in Tetralogy of Fallot
Cyanosis is one of the hallmark signs of TOF and occurs when the blood circulating through the body has a low oxygen content. Oxygen-deprived blood leads to a bluish tint in the skin, lips, and nail beds. Cyanosis is particularly noticeable during physical activity or in situations where oxygen demand increases, as the body struggles to supply enough oxygen to the tissues.
The Role of Surgical Repair in Restoring Normal Blood Flow and Oxygenation
Surgical repair of TOF involves addressing the defects that cause blood mixing, such as closing the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and relieving the pulmonary stenosis. This restores normal blood flow, allowing oxygenated blood from the lungs to flow properly to the body, improving oxygenation levels. The surgery helps correct the abnormal circulation, reducing cyanosis and allowing the heart and lungs to function more effectively.
How Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery Improves Oxygenation and Blood Flow in the Heart
Surgical repair for TOF typically involves patching the VSD and widening the narrowed pulmonary artery (pulmonary stenosis). These corrective measures improve the blood flow through the heart, ensuring that oxygenated blood is pumped into the systemic circulation. The surgery significantly enhances the efficiency of the heart and lungs, improving oxygenation and reducing symptoms associated with low oxygen levels, such as fatigue and cyanosis.
Post-Surgery: Managing Oxygen Levels and Monitoring Blood Flow Recovery
After TOF surgery, it is important to closely monitor oxygen levels to ensure proper oxygenation as the heart and circulatory system recover. This may include regular oxygen saturation checks with pulse oximetry, and sometimes, blood gas tests to assess how well the lungs and heart are exchanging gases. Monitoring the heart’s function through echocardiograms and ECGs is also essential to ensure that blood flow remains optimal and to detect any potential complications.
The Long-Term Impact of Tetralogy of Fallot on Circulation and Oxygenation
While surgery significantly improves circulation and oxygenation, some patients may experience long-term effects due to previous low oxygen levels. This can include developmental delays, reduced exercise capacity, or an increased risk of arrhythmias later in life. Regular follow-up care is necessary to monitor heart function, lung health, and growth, ensuring that any issues are addressed early to maintain optimal health.
How Blood Flow and Oxygen Levels Affect Development in Infants with Tetralogy of Fallot
Infants with TOF often struggle with poor growth and delayed development due to chronic oxygen deprivation. Oxygen is critical for the growth of tissues, organs, and the brain. Infants with TOF may have difficulty feeding and gaining weight, leading to failure to thrive. Surgical correction helps improve growth and developmental outcomes by restoring proper oxygen levels.
The Connection Between Tetralogy of Fallot and Respiratory Health
Because TOF affects the flow of oxygenated blood through the body, it can also impact lung function. Chronic oxygen deprivation can strain the lungs, leading to conditions like pulmonary hypertension, which is high blood pressure in the lungs. Over time, this can lead to further respiratory problems. Surgery helps alleviate this strain, improving the oxygenation of blood and overall respiratory health.
Addressing the Effects of Tetralogy of Fallot on Exercise and Physical Activity
Children and adults with untreated TOF often experience limited exercise tolerance due to the reduced oxygen supply. After surgery, most patients experience significant improvement in exercise capacity and stamina. However, they may still face some limitations, particularly if there are residual heart issues. Physical therapy and gradual increases in activity levels can help maximize recovery and build strength.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Oxygen Levels in Tetralogy of Fallot Patients
Regular monitoring of blood oxygen levels, especially post-surgery, is essential for tracking recovery and ensuring that the heart is functioning properly. Pulse oximetry is often used to monitor oxygen saturation levels non-invasively. This helps healthcare providers determine if the patient needs supplemental oxygen or if further interventions are required. For infants and children, monitoring oxygen levels at home can also provide reassurance to parents and caregivers.
Conclusion: How Surgical Correction of Tetralogy of Fallot Restores Normal Circulation and Oxygen Flow
Surgical repair of Tetralogy of Fallot significantly improves blood flow and oxygenation, addressing the issues of blood mixing that lead to low oxygen levels. By correcting the defects in the heart, the surgery restores normal circulation, leading to improved oxygen levels, better growth, and enhanced quality of life. However, long-term monitoring and care are essential to address any residual effects and maintain good health.
Best Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery in India
The Best Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery in India offers a comprehensive surgical solution for children and adults with TOF, helping correct heart defects and improve oxygenation and quality of life.
Best TOF Surgery Surgeons in India
The Best TOF Surgery Surgeons in India are experts in treating complex congenital heart defects, providing patient-focused care and skilled surgical expertise for successful TOF correction.
FAQ
How does Tetralogy of Fallot affect oxygen levels in the body?
TOF causes a mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart, reducing the oxygen supply to the body. This leads to low oxygen levels, which can affect organ function and growth.
What are the common symptoms of low oxygen levels in children with Tetralogy of Fallot?
Common symptoms include cyanosis (bluish skin, lips, or nails), fatigue, shortness of breath, poor feeding, and slow growth. These symptoms are due to the body not receiving enough oxygen.
How does surgery help restore normal blood flow in Tetralogy of Fallot patients?
Surgery repairs the heart defects causing blood mixing, such as closing the ventricular septal defect and relieving the pulmonary stenosis. This restores normal blood flow, improving oxygen levels throughout the body.
What are the long-term effects of Tetralogy of Fallot on oxygenation and blood flow?
Even after surgery, patients may experience long-term effects such as developmental delays, exercise intolerance, or increased risk of arrhythmias. Regular follow-up care is crucial to address these issues early.
Why is it important to monitor oxygen levels in Tetralogy of Fallot patients after surgery?
Monitoring oxygen levels ensures that the heart and lungs are functioning properly after surgery and helps detect any potential complications, such as low oxygen levels or impaired circulation, that may require intervention.