Cardiovascular health is a critical aspect of patient management following a liver transplant. Patients who have undergone this procedure may experience changes in their cardiovascular system due to factors such as immunosuppressive therapy, alterations in metabolism, and pre-existing conditions. The liver plays a significant role in regulating various metabolic processes, and its absence can lead to complications that affect cardiovascular function. Therefore, it is essential to monitor and manage cardiovascular health proactively to ensure long-term success and quality of life.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Importance of Monitoring Cardiovascular Health
Monitoring cardiovascular health after a liver transplant is paramount. Transplant recipients are at increased risk for developing cardiovascular diseases due to factors like hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, which may be exacerbated by medications. Regular assessments, including blood pressure checks, lipid profiles, and echocardiograms, are essential to detect potential issues early. By maintaining vigilant monitoring, healthcare providers can implement timely interventions, thereby reducing the risk of serious complications such as heart attacks or strokes.
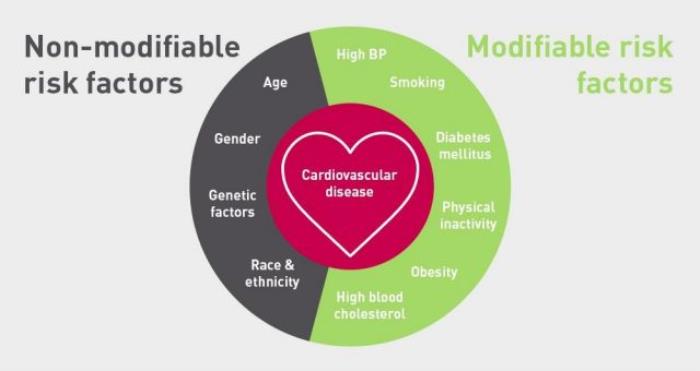
Understanding Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
Several risk factors contribute to cardiovascular disease in liver transplant recipients. These include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and the side effects of immunosuppressive medications. Additionally, pre-existing conditions such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus can further increase the risk. It is crucial for healthcare providers to identify these risk factors in each patient to tailor an appropriate management plan aimed at mitigating cardiovascular risks effectively.
Role of Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy is vital for preventing organ rejection in liver transplant patients. However, these medications can have adverse effects on cardiovascular health, including weight gain, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Common immunosuppressive agents such as tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil may contribute to these risks. Healthcare professionals must balance the need for effective immunosuppression while monitoring and managing potential cardiovascular side effects to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Dietary Considerations for Cardiovascular Health
A heart-healthy diet is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health after a liver transplant. Patients should focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, sugars, and sodium. Incorporating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, can also be beneficial. Moreover, staying hydrated and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is crucial for both liver and cardiovascular health. A registered dietitian can assist in creating personalized dietary plans tailored to individual needs.
Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations
Regular physical activity is vital for improving cardiovascular health and overall well-being in liver transplant recipients. Engaging in moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help manage weight, reduce blood pressure, and improve lipid profiles. Patients should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by health authorities. Before starting any exercise regimen, it is essential to consult healthcare providers to develop a safe and effective plan that accommodates individual health status and recovery progress.
Managing Hypertension After Transplant
Hypertension is a common complication following a liver transplant, often exacerbated by immunosuppressive medications and lifestyle factors. Effective management of hypertension is crucial to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. This may include lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, regular exercise, and weight management, alongside pharmacological interventions when necessary. Patients should regularly monitor their blood pressure and maintain open communication with their healthcare team to optimize hypertension management strategies.
Diabetes Management in Post-Transplant Patients
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is a significant concern for liver transplant recipients, often linked to the use of immunosuppressive medications. Managing blood glucose levels is essential for preventing cardiovascular complications. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to monitor their blood sugar levels and adopt lifestyle changes that promote glycemic control, including dietary adjustments and physical activity. In some cases, medication may be required to manage diabetes effectively.
Dyslipidemia and Its Implications
Dyslipidemia, characterized by abnormal lipid levels, is a prevalent issue among liver transplant recipients and poses a significant risk for cardiovascular disease. Regular lipid profile assessments are essential for early detection and management. Patients may be advised to adopt dietary changes and, if necessary, initiate pharmacological treatment to achieve target lipid levels. Monitoring and managing dyslipidemia can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, thus enhancing overall health outcomes.
Importance of Regular Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are critical for monitoring cardiovascular health in liver transplant recipients. These visits allow healthcare providers to assess the patient's overall health, including cardiovascular risk factors, medication adherence, and lifestyle changes. During these appointments, healthcare teams can also educate patients about the importance of self-monitoring and provide tailored recommendations to address specific health concerns. Consistent follow-up is key to preventing complications and ensuring long-term success after transplantation.
Psychological Impact on Cardiovascular Health
The psychological well-being of liver transplant recipients can significantly affect their cardiovascular health. Stress, anxiety, and depression are common among patients post-transplant and can lead to poor lifestyle choices, such as unhealthy eating and inactivity. Addressing psychological health through counseling, support groups, and stress management techniques is essential for improving overall health outcomes. A holistic approach that includes mental health support can contribute to better cardiovascular management.
Smoking Cessation and Cardiovascular Health
Smoking is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease and can adversely affect transplant outcomes. For liver transplant recipients, quitting smoking is crucial for improving cardiovascular health and enhancing the success of the transplant. Various cessation programs, including counseling and pharmacotherapy, can assist individuals in overcoming nicotine addiction. Healthcare providers should actively encourage and support smoking cessation efforts to mitigate cardiovascular risks and promote overall well-being.
Impact of Alcohol Consumption on Health
Alcohol consumption poses unique challenges for liver transplant recipients. While moderate alcohol intake may be acceptable for some individuals, it can significantly impact cardiovascular health and liver function. Patients should be educated about the risks associated with alcohol consumption and encouraged to limit or abstain from alcohol altogether. Healthcare providers must assess each patient's situation and provide personalized recommendations to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Role of Family Support in Recovery
Family support plays a vital role in the recovery and management of cardiovascular health in liver transplant recipients. Emotional and practical support from family members can encourage adherence to treatment plans, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-ups. Families can also help monitor health behaviors, such as diet and exercise, thereby contributing to the patient’s overall well-being. Engaging family members in the care process fosters a supportive environment that enhances recovery and health management.
Utilizing Technology for Health Management
Advancements in technology offer valuable tools for managing cardiovascular health after a liver transplant. Mobile health applications and wearable devices can help patients track their physical activity, monitor dietary intake, and manage medication schedules. Telehealth services allow for easier communication with healthcare providers, enabling timely interventions and support. By leveraging technology, patients can take an active role in their health management, ultimately leading to improved outcomes.
Understanding the Signs of Cardiovascular Issues
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular issues is crucial for liver transplant recipients. Patients should be educated about potential warning signs, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, and swelling in the legs. Prompt reporting of these symptoms to healthcare providers can facilitate early intervention and prevent serious complications. Education on self-monitoring and awareness of cardiovascular health is essential for empowering patients in their recovery journey.
Collaborative Care Approach
A collaborative care approach involving a multidisciplinary team is essential for managing cardiovascular health in liver transplant recipients. This team may include transplant surgeons, hepatologists, cardiologists, dietitians, and mental health professionals. By working together, they can develop comprehensive care plans that address the unique needs of each patient, ensuring holistic management of both liver and cardiovascular health. This collaborative model fosters effective communication and improves patient outcomes.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups Post Liver Transplant
Understand why regular medical check-ups are crucial after a liver transplant. Learn about the benefits of ongoing monitoring for long-term success.
How Bile Duct Issues Are Managed After Liver Transplant Surgery
Learn how bile duct complications are addressed post-surgery. This blog delves into treatments and techniques for managing these issues effectively.
Long-Term Prognosis and Health Maintenance
The long-term prognosis for liver transplant recipients can be significantly improved through effective cardiovascular health management. By addressing risk factors, adhering to treatment regimens, and maintaining healthy lifestyle choices, patients can enhance their quality of life and reduce the likelihood of cardiovascular complications. Regular monitoring and proactive management strategies are essential for sustaining health and achieving optimal long-term outcomes post-transplant.
Best Liver Transplant in India
The Best Liver Transplant in India provides life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage liver disease, offering advanced surgical techniques and comprehensive post-transplant care for successful recovery.
Best Liver Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Liver Transplant Hospitals in India are equipped with cutting-edge technology and expert medical teams, ensuring top-notch care and optimal recovery for liver transplant patients.
Liver Transplant Cost in India
The Liver Transplant Cost in India offers an affordable solution for patients needing liver transplantation, ensuring access to world-class care at competitive pricing.
Best Liver Transplant Surgeons in India
The Best Liver Transplant Surgeons in India are highly skilled in performing liver transplants, providing precise surgeries and personalized care to ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
FAQs
What are the common cardiovascular risks after a liver transplant?
Post-liver transplant patients may face several cardiovascular risks, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and increased risk of diabetes. These conditions can be exacerbated by immunosuppressive medications and lifestyle factors.
How can I monitor my cardiovascular health after a liver transplant?
Monitoring cardiovascular health involves regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, tracking blood pressure, and lipid levels, and being vigilant about any symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
What lifestyle changes can help improve cardiovascular health post-transplant?
Key lifestyle changes include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress effectively.
What role does medication play in managing cardiovascular health?
Medications may be prescribed to manage hypertension, dyslipidemia, or diabetes. It is crucial to adhere to prescribed medication regimens and consult healthcare providers about any concerns.
When should I seek medical attention for cardiovascular symptoms?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe chest pain, persistent shortness of breath, or sudden swelling in your legs, as these may indicate serious cardiovascular issues.
Living liver donation is a life-saving act with manageable risks and generally positive health outcomes for donors. The Impact of Living Liver Donation on Donors’ Health
Stem cell therapy presents a promising, less invasive alternative to liver transplants, potentially transforming liver disease treatment. Is Stem Cell Therapy a Future Alternative to Liver Transplants?
Explore the risks and prevention of liver transplant scams and illegal organ trafficking, ensuring patient safety and ethical practices. Understanding Liver Transplant Scams and Illegal Organ Trafficking