The intragastric balloon is designed to aid weight loss by occupying space in the stomach, which reduces the amount of food it can hold. This process can affect overall digestive health by altering gastric function, including how food moves through the digestive tract and how hunger signals are regulated. Patients may experience changes in digestion and appetite as a result of the balloon's presence.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
How the Intragastric Balloon Affects Gastric Function Over Time
Over time, the presence of the intragastric balloon can influence gastric function by reducing the stomach's capacity to store food, which leads to a feeling of fullness with smaller meals. Additionally, the balloon may cause temporary changes in gastric motility, or the rate at which food moves through the digestive system, as it puts pressure on the stomach walls and intestines. These changes are generally reversible after balloon removal.
Potential Changes in Digestion After Balloon Placement
The intragastric balloon can slow down the digestive process initially, allowing patients to feel fuller for longer periods. This effect helps reduce food intake, but it may also lead to some discomforts like bloating, indigestion, or mild nausea, especially during the early phase after placement. As the digestive system adjusts, these symptoms typically decrease.
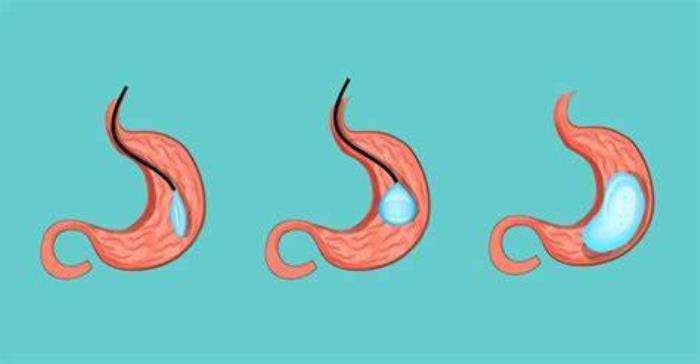
The Role of the Intragastric Balloon in Slowing Down Gastric Emptying
One of the key functions of the intragastric balloon is to slow gastric emptying, which can help with weight loss by prolonging the feeling of fullness after eating. By occupying space in the stomach, the balloon delays the passage of food into the small intestine, making patients feel satiated sooner and reducing the amount of food they consume during meals.
How the Intragastric Balloon Influences Appetite and Satiety
The balloon works by affecting appetite-regulating hormones, particularly ghrelin, which is responsible for stimulating hunger. With the balloon in place, there is often a reduction in ghrelin production, which can lead to a decrease in appetite and an increase in satiety, making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet. This hormonal change contributes significantly to the balloon's effectiveness in promoting weight loss.
The Risk of Gastric Irritation and Ulcers Post-Treatment
Gastric irritation is a potential side effect of intragastric balloon treatment. The presence of the balloon can cause irritation to the stomach lining, increasing the risk of developing gastric ulcers or discomfort. In some cases, medications or changes in diet may be recommended to manage these issues. Regular follow-up care ensures that any signs of irritation are addressed promptly.
Managing Acid Reflux and Heartburn After Balloon Placement
Acid reflux and heartburn are common digestive complaints after intragastric balloon placement, especially during the initial adjustment period. The balloon's pressure on the stomach can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, increasing the likelihood of stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus. Managing acid reflux may involve lifestyle changes, including avoiding certain foods, eating smaller meals, and taking antacid medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
The Long-Term Impact on Nutrient Absorption
The intragastric balloon can reduce the stomach's capacity, which may impact nutrient absorption by limiting the amount of food and fluids that can be consumed at one time. Over time, this can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, particularly if a balanced diet and supplements are not carefully managed.
How the Intragastric Balloon Affects Bowel Movements and Constipation
After balloon placement, constipation can be a common issue due to changes in eating habits, reduced food intake, and dehydration. The balloon can slow down gastric emptying, leading to discomfort and difficulty in passing stools. Adequate hydration, fiber intake, and regular exercise can help manage this issue.
Potential Risks of Gastric Stasis or Delayed Digestion
The balloon can cause gastric stasis or delayed digestion, where food remains in the stomach longer than usual. This can lead to bloating, nausea, and discomfort, especially if the balloon is overinflated or if there are underlying gastric issues. These symptoms are typically temporary, but management through diet and follow-up care is essential.
The Role of the Balloon in Altering Gastric pH and Enzyme Activity
The intragastric balloon can alter gastric pH levels due to changes in food intake and the balloon's physical presence in the stomach. This alteration may impact the activity of digestive enzymes, potentially affecting the digestion of food and nutrient absorption. It's important to monitor digestive health and address any issues as they arise.
How to Prevent and Manage Digestive Discomfort After Balloon Removal
After the balloon is removed, digestive discomfort may persist as the stomach adjusts to its previous size and function. To prevent discomfort, a gradual reintroduction to normal food intake, staying hydrated, and avoiding large meals can help ease the transition. If discomfort continues, consultation with a healthcare provider is necessary.
The Risk of Intestinal Obstruction Due to Balloon Migration
While rare, there is a risk of the balloon migrating into the intestines, which could cause a blockage or obstruction. If this occurs, medical intervention is required to remove the balloon. Regular monitoring and early detection through imaging or endoscopic procedures can help mitigate this risk.
Long-Term Effects on Gastrointestinal Motility and Function
In some cases, the presence of the balloon may have a temporary impact on gastrointestinal motility, resulting in slower digestion and transit time. After balloon removal, most individuals experience a return to normal motility, but some may have long-term adjustments in digestion. A balanced diet, hydration, and exercise are essential for maintaining healthy motility.
How the Balloon Affects the Stomach Lining and Mucosa
The intragastric balloon may irritate the stomach lining and mucosa, especially if left in place for an extended period. Inflammation, ulcers, or mucosal damage could occur, though these are rare. Regular follow-up care and endoscopic evaluation can help identify any damage early on.
The Importance of a Healthy Diet to Support Digestive Health Post-Treatment
Maintaining a nutrient-rich diet is crucial to support digestive health after balloon treatment. This includes adequate hydration, balanced meals with fiber, and avoiding highly processed foods. A healthy diet can prevent complications like constipation, nutrient deficiencies, and digestive discomfort.
Managing Digestive Complications During the Adjustment Period
During the adjustment period after the balloon placement, individuals may experience digestive issues such as bloating, nausea, and constipation. These can often be managed with dietary changes, increased fluid intake, and small, frequent meals. It's important to work with healthcare professionals for tailored advice during this phase.
The Role of Post-Treatment Follow-Up in Assessing Digestive Health
Post-treatment follow-up care is essential to assess and manage any digestive health issues that may arise after balloon placement or removal. Regular check-ups help detect complications such as obstruction, ulcers, or nutrient deficiencies, and allow for adjustments in diet or treatment.
Can Intragastric Balloon Treatment Lead to Long-Term Gastric Damage?
Long-term gastric damage from intragastric balloon treatment is rare but possible, particularly if complications such as ulceration, excessive pressure, or balloon migration occur. Regular monitoring, proper balloon removal, and adherence to medical guidelines can minimize this risk.
The Role of Physical Activity in Enhancing Intragastric Balloon Results
Understand how physical activity enhances intragastric balloon results. This article highlights the importance of incorporating regular exercise into your routine to boost weight loss and improve overall health during and after the treatment.
Exploring the Potential for Reversal of Digestive Effects After Balloon Removal
In most cases, any digestive effects caused by the intragastric balloon, such as gastric stasis or mild discomfort, are reversible after the balloon is removed. However, some individuals may experience lingering symptoms, and ongoing support from healthcare providers may be necessary to manage these effects.
Best Intragastric Balloon Treatment in India
The Best Intragastric Balloon Treatment in India offers a non-surgical weight-loss solution by placing a balloon in the stomach to reduce hunger and promote healthy eating habits.
Best Intragastric Balloon Hospitals in India
The Best Intragastric Balloon Hospitals in India are equipped with advanced endoscopy technology and skilled medical teams, providing safe and effective weight-loss treatments.
Intragastric Balloon Treatment Cost in India
The Intragastric Balloon Treatment Cost in India is cost-effective, offering patients an affordable and efficient option for achieving significant weight loss under expert care.
Best Intragastric Balloon Specialists in India
The Best Intragastric Balloon Specialists in India are experienced in performing this procedure, providing personalized guidance and comprehensive support to ensure successful weight-loss outcomes.
FAQ Section
1. How does the intragastric balloon impact digestion over the long term?
The balloon can temporarily slow digestion and may affect nutrient absorption due to reduced stomach capacity. Long-term effects are typically minimal if proper follow-up care and nutrition are maintained.
2. What digestive issues can arise after the balloon is placed?
Common issues include nausea, bloating, constipation, and delayed gastric emptying. These symptoms generally subside as the body adjusts to the balloon.
3. Can the intragastric balloon cause acid reflux or heartburn?
In some cases, the balloon can cause acid reflux or heartburn, particularly if the stomach is overfilled or the balloon is not properly positioned. Medication or adjustments may be needed to manage these symptoms.
4. How does the balloon affect nutrient absorption in the stomach?
The balloon reduces the stomach’s capacity, which can impact the absorption of nutrients by limiting food intake. It's important to monitor vitamin and mineral levels to avoid deficiencies.
5. Is it common to experience constipation after the balloon is placed?
Yes, constipation is a common issue due to changes in food intake, hydration, and digestion. This can typically be managed with increased fiber, water, and physical activity.
Updated for 2025 – Learn about the top hospitals in India for intragastric balloon treatment, including advanced techniques, cost, and success rates. Intragastric Balloon Treatment Cost in India
Learn about the top hospitals in India for intragastric balloon treatment, including advanced techniques, cost, and success rates. Intragastric Balloon Treatment in India
Discover the science behind the intragastric balloon, a revolutionary non-surgical weight loss solution designed to help control appetite and promote healthier eating habits. This comprehensive guide delves into how the intragastric balloon works, its benefits, and what to expect during the procedure. Learn how this innovative approach can aid in achieving sustainable weight loss and improving overall health. Perfect for those considering weight loss options or seeking to understand the latest advancements in appetite control. How the Intragastric Balloon Works to Control Appetite