What is VP Shunt Surgery, and Why is it Performed?
VP (Ventriculoperitoneal) shunt surgery is a medical procedure primarily performed to treat conditions involving the build-up of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain, such as hydrocephalus. The procedure involves the insertion of a shunt, which is a flexible tube, into the ventricles of the brain to drain excess CSF to another part of the body, typically the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen, where it can be absorbed. The primary goal of the surgery is to reduce intracranial pressure, alleviate symptoms like headaches and vomiting, and prevent further brain damage. This surgery is critical for individuals who experience chronic or acute hydrocephalus due to various causes, including congenital abnormalities, infections, or brain trauma.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
How Common Are Complications After VP Shunt Surgery?
While VP shunt surgery is generally safe, complications can occur in a small percentage of patients. Studies suggest that around 30-40% of patients experience some form of complication during the first year after surgery. The likelihood of complications depends on several factors, such as the patient's age, underlying condition, and the skill of the surgical team. Although most complications can be managed effectively, some may require additional interventions or revisions to the shunt. Early detection and proper post-operative care significantly reduce the risks of complications, making routine monitoring essential.
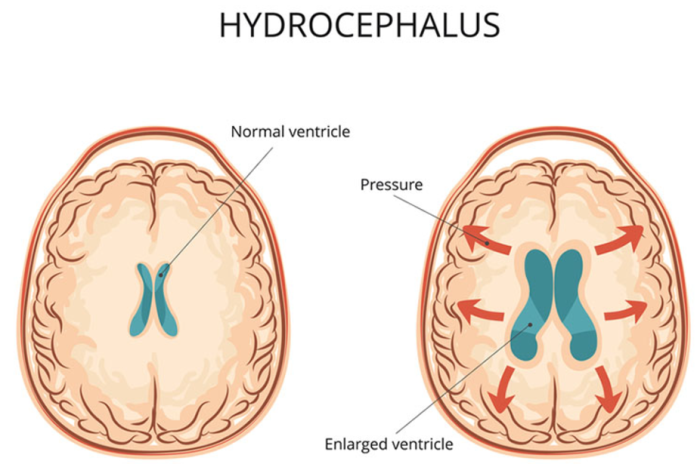
What Are the Immediate Risks of VP Shunt Surgery?
The immediate risks of VP shunt surgery are primarily associated with the surgical procedure itself. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissues. Bleeding can occur during the insertion of the shunt, particularly in areas like the brain or surrounding blood vessels. Infection at the surgical site or within the shunt itself is another concern, as it can lead to serious complications requiring the removal or replacement of the shunt. Additionally, there is the risk of anesthesia-related complications, especially in older adults or those with pre-existing health conditions. It is essential for the surgical team to monitor patients closely in the immediate post-operative period to manage these risks effectively.
Can Infection Occur After VP Shunt Surgery?
Yes, infection is one of the most common complications following VP shunt surgery. The risk of infection is typically higher during the first few weeks to months post-surgery. Infection can occur at the surgical site or within the shunt system itself. Symptoms of infection include fever, redness or swelling at the incision site, and discomfort. If an infection is suspected, prompt medical attention is required to prevent further complications, such as meningitis or sepsis. In some cases, the infected shunt must be removed or replaced, and the patient may require a course of antibiotics to resolve the infection. Ensuring proper hygiene and following post-operative care instructions can help reduce the risk.
How Does a VP Shunt Surgery Lead to Shunt Malfunction?
Shunt malfunction can occur due to several factors, most commonly blockage or dislodgement of the shunt. Blockages may develop when debris, blood clots, or tissue obstruct the shunt tubing, preventing the proper flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Dislodgement, where the shunt moves from its intended position, can occur due to physical trauma or gradual movement of the shunt within the body. A malfunction can lead to a recurrence of symptoms such as headaches, vomiting, and cognitive issues, signifying that the shunt is not draining CSF effectively. Shunt malfunctions typically require revision surgery to restore proper function and prevent further complications.
What is the Risk of Bleeding During or After VP Shunt Surgery?
Bleeding is a known risk during VP shunt surgery, particularly during the insertion of the catheter into the brain's ventricles. Though rare, significant bleeding can lead to complications such as hematomas (blood clots) or increased intracranial pressure. This bleeding may result in neurological deficits, depending on its location and severity. Post-operative bleeding is also a concern, especially if blood vessels near the shunt site are damaged during the procedure. Careful surgical technique and close monitoring of the patient’s vital signs and brain imaging after surgery can help identify and manage any bleeding complications promptly, minimizing their impact on the patient’s recovery.
Are There Risks of Neurological Damage Following VP Shunt Surgery?
There is a risk of neurological damage following VP shunt surgery, particularly if complications arise during the procedure. The insertion of the shunt involves passing a catheter through delicate brain tissue, and any trauma or disruption during this process can result in damage to surrounding structures. Neurological symptoms such as weakness, paralysis, speech difficulties, or sensory loss may occur in the event of such damage. While these risks are generally low, they can have long-term implications for the patient's quality of life. To reduce this risk, the surgery should be performed by an experienced neurosurgeon with proper pre-operative planning and intra-operative monitoring.
Can VP Shunt Surgery Cause Seizures in Some Patients?
Seizures can occur in some patients following VP shunt surgery, although they are relatively rare. Seizures may be triggered by several factors, such as brain irritation from the surgical procedure, infection, or electrolyte imbalances that can arise post-operatively. In some cases, the formation of scar tissue or the displacement of the shunt can also contribute to seizure activity. If seizures occur, they may be managed with antiepileptic medications or, in some cases, the revision of the shunt. Close post-operative monitoring, including neurological assessments, can help identify potential triggers for seizures and address them before they lead to significant issues.
How Can Overdrainage of CSF Affect the Patient After Surgery?
Overdrainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a potential complication following VP shunt surgery, and it occurs when the shunt drains CSF too quickly or in excessive amounts. This can lead to a condition known as "slit ventricle syndrome," where the ventricles in the brain become abnormally small, causing headaches, nausea, and, in severe cases, brain herniation. Overdrainage can also cause the brain to collapse or "sink," resulting in further complications such as dizziness, blurred vision, and cognitive issues. Adjustments to the shunt's valve or surgical revision may be required to regulate CSF drainage and alleviate symptoms caused by overdrainage.
What is the Impact of Shunt Overdrainage on Brain Pressure?
Overdrainage of CSF can significantly impact brain pressure, leading to a drop in intracranial pressure. While the shunt is designed to alleviate high pressure caused by excess CSF, improper drainage can cause the brain to become under-pressurized. This state can lead to a variety of symptoms, including headache, dizziness, and visual disturbances. The brain’s ability to adjust to these changes may be compromised, leading to long-term damage if not corrected. Shunt overdrainage can be managed by adjusting the shunt's valve settings or, in some cases, replacing the shunt to ensure that CSF drainage is regulated properly.
How Do Shunt Blockages Occur, and What Are the Risks?
Shunt blockages can occur when debris, blood clots, or tissue obstruct the flow of CSF through the shunt. This can prevent proper drainage of fluid from the brain, causing increased intracranial pressure and a return of symptoms like headaches, vomiting, and cognitive dysfunction. Blockages may happen due to an infection, scar tissue formation, or mechanical issues with the shunt. The risk of blockage is higher in patients who have had their shunts for extended periods. To address a blockage, the shunt may need to be revised or replaced, with the use of imaging tests to locate the obstruction.
How Can Shunt Migration Lead to Complications?
Shunt migration occurs when the catheter or other components of the shunt move out of place. This can result in improper CSF drainage and cause the accumulation of fluid in the brain, leading to symptoms like headaches, nausea, and increased intracranial pressure. In some cases, migration may also cause discomfort or pain due to the displacement of the shunt. To minimize the risk of migration, careful surgical technique and proper post-operative monitoring are essential. If migration occurs, surgical repositioning or replacement of the shunt may be necessary to restore proper function.
What Are the Long-Term Risks Associated with VP Shunt Surgery?
The long-term risks of VP shunt surgery include shunt malfunction, infection, and the recurrence of hydrocephalus. Over time, the shunt may become blocked, displaced, or damaged, leading to a need for shunt revision surgery. Infections can develop at any time after the procedure, requiring long-term antibiotic therapy or surgical intervention. Additionally, there is a risk that hydrocephalus may recur, necessitating further management. Long-term follow-up care is crucial to monitor the shunt's function and address any emerging issues before they cause significant problems.
Can VP Shunt Surgery Lead to Cognitive Decline or Memory Issues?
Cognitive decline or memory issues can occur after VP shunt surgery, although this is rare. These complications may be related to factors such as surgical trauma, infection, or changes in intracranial pressure. If the shunt malfunctions or overdrainage occurs, the brain may experience fluctuations in pressure, which can impact cognitive function. In some cases, the stress of the surgical procedure itself or post-operative recovery could also contribute to temporary memory problems. Regular follow-up care is crucial to monitor for these issues and address them promptly to prevent long-term cognitive decline.
Can VP Shunt Surgery Cause Cognitive Decline or Memory Issues?
Cognitive decline or memory issues can occur after VP shunt surgery, although this is rare. These complications may be related to factors such as surgical trauma, infection, or changes in intracranial pressure. If the shunt malfunctions or overdrainage occurs, the brain may experience fluctuations in pressure, which can impact cognitive function. In some cases, the stress of the surgical procedure itself or post-operative recovery could also contribute to temporary memory problems. Regular follow-up care is crucial to monitor for these issues and address them promptly to prevent long-term cognitive decline.
How Do Shunt Blockages Occur, and What Are the Risks?
Shunt blockages can occur when debris, blood clots, or tissue obstruct the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the shunt. This blockage can prevent the proper drainage of CSF, leading to increased intracranial pressure and a return of symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and cognitive dysfunction. Blockages can happen due to infection, scar tissue, or mechanical issues with the shunt, and they are more likely to develop in the long term. Shunt blockages can be managed by replacing or revising the shunt and ensuring that the blockage is cleared.
How Can Shunt Migration Lead to Complications?
Shunt migration occurs when the catheter or other components of the shunt move out of their intended position. This can prevent the shunt from draining CSF effectively, leading to a recurrence of symptoms like headaches and vomiting. In some cases, shunt migration can also cause pain or discomfort due to the displaced tubing. If migration occurs, a revision surgery may be required to reposition the shunt and restore proper function. Proper surgical technique and post-operative monitoring are essential in minimizing the risk of migration.
What Are the Long-Term Risks Associated with VP Shunt Surgery?
The long-term risks of VP shunt surgery include shunt malfunction, infection, and the potential recurrence of hydrocephalus. Over time, the shunt may become blocked, displaced, or damaged, requiring revision or replacement. Infections can develop at any point after the surgery, sometimes necessitating the removal and replacement of the shunt. Additionally, there is a risk that hydrocephalus may return, requiring ongoing management. Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor the shunt's function and address any emerging issues before they result in significant complications.
Can VP Shunt Surgery Cause Cognitive Decline or Memory Issues?
Cognitive decline or memory issues can occur after VP shunt surgery, although they are rare. These complications may be related to surgical trauma, infection, or fluctuations in intracranial pressure. If the shunt malfunctions, overdrainage or underdrainage can affect brain function, leading to cognitive impairment. Additionally, the stress of the surgery or the underlying condition being treated can contribute to temporary memory problems. Close monitoring and early intervention can help prevent or manage these cognitive challenges.
How Can VP Shunt Surgery Impact Mental Health?
The mental health impact of VP shunt surgery can vary among patients, with some experiencing mood changes, anxiety, or depression after the procedure. The physical changes brought on by hydrocephalus, as well as the stress of undergoing surgery, can contribute to these mental health challenges. In some cases, a return of symptoms, such as headaches or cognitive issues, may further affect the patient's emotional well-being. Providing psychological support, along with regular monitoring of the patient's physical recovery, can help address these concerns and improve long-term outcomes.
Can Shunt Surgery Lead to Developmental Delays in Children?
In children, VP shunt surgery can have a mixed impact on development. While the surgery aims to alleviate hydrocephalus and prevent further brain damage, the underlying condition may still affect cognitive and physical development. Children who undergo VP shunt surgery may experience delays in motor skills, language, or learning, depending on the severity and duration of their hydrocephalus before treatment. Early intervention with therapy and regular monitoring can help children recover lost developmental milestones and improve long-term outcomes.
What Are the Risk Factors for Complications After VP Shunt Surgery?
Several factors can increase the risk of complications after VP shunt surgery, including age, underlying medical conditions, and the presence of infections. Older adults may be at a higher risk for complications due to decreased immune function and the presence of comorbidities. Children with congenital hydrocephalus may face additional challenges related to shunt placement and function. Patients with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are also at a higher risk for infection. Proper pre-operative assessment and post-operative care can help minimize these risks.
What Is the Risk of Developing Hydrocephalus Again After Shunt Surgery?
While VP shunt surgery is designed to manage hydrocephalus, there is a risk that the condition may recur after surgery. This can happen due to shunt malfunction, infection, or changes in the patient's health that affect CSF production or absorption. If hydrocephalus reoccurs, patients may experience symptoms such as headaches, vomiting, and cognitive difficulties. Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider, along with monitoring imaging tests, are essential for identifying and addressing any recurrence of hydrocephalus.
What Are the Potential Risks of Shunt Revision Surgeries?
Shunt revision surgeries are typically required when the original shunt malfunctions, becomes blocked, or causes other complications. However, revision surgeries carry their own risks, such as infection, bleeding, and additional shunt malfunctions. The need for multiple surgeries increases the risk of scarring and damage to surrounding tissues, making subsequent procedures more complicated. Additionally, there is a risk of the new shunt not functioning properly or causing similar complications as the original one. Careful planning and proper surgical technique are essential for minimizing the risks associated with revision surgeries.
Can VP Shunt Surgery Affect the Immune System?
VP shunt surgery itself does not directly affect the immune system; however, post-surgical infections can compromise the body's ability to fight off other illnesses. Patients with compromised immune systems, such as those on immunosuppressive medications, are more susceptible to infections following surgery. The risk of infection can be minimized by following strict hygiene protocols, monitoring for signs of infection, and treating any infections promptly with antibiotics or other necessary interventions. Regular follow-up care is crucial to prevent long-term immune system complications.
How Does Age Impact the Outcome of VP Shunt Surgery?
Age can significantly impact the outcome of VP shunt surgery. In children, early intervention can often lead to better long-term outcomes as the brain is more adaptable and capable of recovering from hydrocephalus-related damage. However, in elderly patients, the risk of complications may be higher due to pre-existing health conditions, a weakened immune system, and slower recovery rates. Older adults may also experience a longer healing process, making them more prone to infections or delayed complications. Age-specific adjustments in treatment plans and close monitoring are essential for optimizing outcomes.
When is VP Shunt Surgery Necessary for Hydrocephalus?
VP shunt surgery is often essential for managing hydrocephalus, particularly when fluid buildup causes significant pressure on the brain. This procedure helps restore normal fluid flow. Learn more about the necessity of VP shunt surgery for hydrocephalus treatment.
Success Rates of Hydrocephalus Surgery in India
Hydrocephalus surgeries, including VP shunts, show high success rates in India due to advanced techniques and experienced surgeons. Timely intervention improves outcomes significantly. Explore the success rates of hydrocephalus surgery and patient recovery statistics in India.
What Is the Role of Imaging in Managing Complications After VP Shunt Surgery?
Imaging plays a critical role in diagnosing and managing complications after VP shunt surgery. Techniques like CT scans and MRI are used to assess the placement of the shunt, monitor CSF drainage, and detect complications such as shunt malfunction, blockages, or fluid buildup. Imaging is also essential for identifying infections, hematomas, or other structural issues that could impact the shunt's effectiveness. Regular imaging assessments help healthcare providers track the progress of the surgery and make timely adjustments to ensure proper function.
How Are Shunt Complications Managed in the Long Term?
Long-term management of shunt complications involves routine monitoring of the shunt’s function and the patient’s overall health. If complications arise, such as malfunction, infection, or overdrainage, interventions may include shunt revision surgeries, antibiotic treatment for infections, or adjustments to the shunt's valve. The patient’s healthcare team may also recommend physical therapy or neurological assessments to help manage symptoms and prevent further deterioration. Consistent follow-up visits and regular diagnostic tests are essential for addressing complications promptly and ensuring optimal long-term outcomes.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Treatment in India
The Best Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Treatment in India is performed by expert neurosurgeons who utilize advanced techniques to ensure optimal outcomes for patients, offering a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual health needs.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery Hospitals in India
The best hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) hospitals in india are equipped with cutting-edge technology and facilities, providing top-notch care, including pre-surgery consultations, surgical expertise, and post-operative recovery support to ensure a smooth patient journey.
Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Cost in India
When considering the hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) cost in india, patients benefit from affordable and transparent pricing at leading hospitals, which offer cost-effective treatment options without compromising the quality of care.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery Doctors in India
The best hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) doctors in india are highly experienced in performing the procedure, utilizing a patient-centric approach that ensures personalized care, precise surgical techniques, and dedicated follow-up care to enhance recovery.
What Are the Signs That a Shunt May Be Malfunctioning?
Signs that a shunt may be malfunctioning include a return of symptoms such as headaches, nausea, vomiting, or a general decline in neurological function. Other signs may include seizures, vision problems, or changes in mental status. These symptoms may indicate that the shunt is either blocked, displaced, or not functioning properly. If any of these signs are noticed, it is crucial to contact a healthcare provider immediately to assess the situation and determine if revision surgery or other interventions are required.
What Is the Prognosis for Patients Who Experience Complications After VP Shunt Surgery?
The prognosis for patients who experience complications after VP shunt surgery depends on the nature and severity of the complication. Many complications, such as shunt blockages or infections, can be treated effectively with medical interventions or additional surgeries. However, some complications, like extensive brain damage or infections that are difficult to treat, may lead to long-term health issues. Early identification and prompt treatment of complications are key to improving the prognosis and minimizing the long-term impact on the patient's quality of life.
FAQs About the Potential Risks and Complications of VP Shunt Surgery
What is VP shunt surgery, and why is it performed?
VP shunt surgery is a procedure that treats hydrocephalus by diverting cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to the abdomen. It helps to reduce intracranial pressure and prevent damage.
How common are complications after VP shunt surgery?
Complications occur in about 30-40% of patients within the first year, but most are manageable with proper care.
What are the immediate risks of VP shunt surgery?
Immediate risks include infection, bleeding, and potential damage to surrounding tissues, especially during catheter insertion.
Can infection occur after VP shunt surgery?
Yes, infections are one of the most common post-surgical complications and can lead to severe outcomes like meningitis if not treated promptly.
How does a VP shunt surgery lead to shunt malfunction?
Malfunctions often occur due to blockages, displacement, or mechanical failure of the shunt system, requiring revision surgeries.
What is the risk of bleeding during or after VP shunt surgery?
While bleeding is rare, it can occur during the insertion of the shunt, leading to increased intracranial pressure or hematomas.
Are there risks of neurological damage following VP shunt surgery?
Neurological damage is a rare but serious risk, often associated with surgical trauma or complications.
Can VP shunt surgery cause seizures in some patients?
Seizures are a possible complication following VP shunt surgery, potentially caused by brain irritation or infection.
How can overdrainage of CSF affect the patient after surgery?
Overdrainage can lead to brain under-pressurization, causing symptoms like dizziness and cognitive issues.
What is the impact of shunt overdrainage on brain pressure?
Overdrainage leads to a drop in intracranial pressure, which may cause complications like brain herniation or visual disturbances.