Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart condition characterized by an opening in the septum, the wall that separates the heart's upper chambers (atria). This abnormality allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to mix with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium, disrupting the normal flow of blood through the heart and lungs. Understanding ASD is crucial for recognizing its impact on heart function and the potential complications it can cause if left untreated.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
What Is ASD and How Does It Affect the Heart?
ASD is a structural defect that creates an abnormal pathway for blood flow within the heart. In a healthy heart, the septum prevents mixing between the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. However, with an ASD, this barrier is compromised, leading to inefficiencies in circulation. The increased workload on the heart can cause significant strain, especially over time, making early diagnosis and intervention essential.
The Role of the Heart's Septum and Its Importance in Blood Flow
The heart's septum plays a critical role in maintaining efficient blood circulation by separating oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This separation ensures that blood flows correctly through the heart and lungs, delivering adequate oxygen to the body. An ASD disrupts this balance, allowing blood to bypass its intended path, which can impair the heart's ability to function optimally.
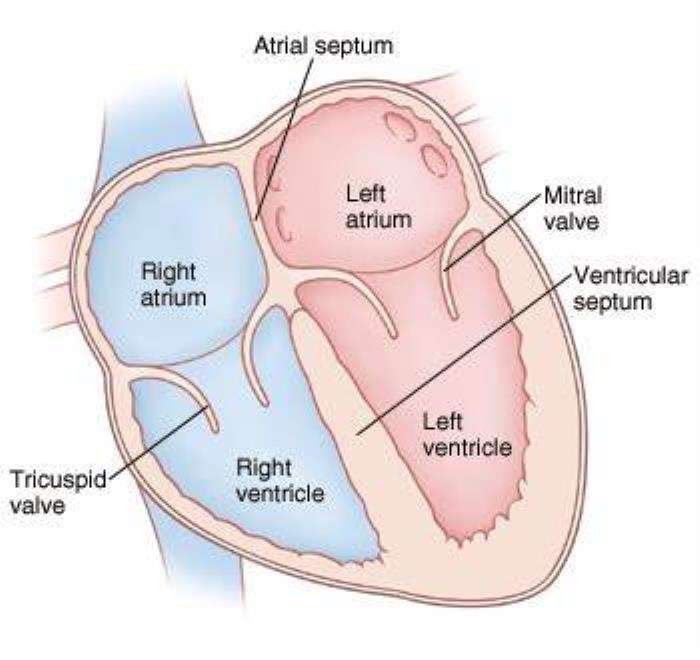
How ASD Impacts Heart Function: An Overview
The abnormal blood flow caused by ASD forces the heart to work harder to compensate for the inefficiency. Over time, this can lead to enlargement of the right atrium and ventricle due to increased volume and pressure. If left untreated, these changes can progress, potentially leading to complications such as arrhythmias, heart failure, and pulmonary hypertension.
Increased Blood Flow to the Lungs: A Key Effect of ASD
One of the primary consequences of ASD is an increase in blood flow to the lungs. The extra blood volume from the left atrium to the right atrium is pumped into the pulmonary arteries, creating added pressure on the lungs' blood vessels. Over time, this can damage the pulmonary circulation, leading to respiratory difficulties and other complications.
Enlarged Heart Chambers: A Long-Term Complication of ASD
Prolonged exposure to increased blood volume can cause the heart's right-sided chambers to enlarge. This enlargement, known as dilation, puts additional stress on the heart's structure and function, potentially leading to issues such as heart rhythm disturbances and reduced pumping efficiency.
The Risk of Pulmonary Hypertension Due to ASD
Pulmonary hypertension, or increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, is a serious complication of untreated ASD. The continuous overflow of blood into the lungs can cause permanent damage to the pulmonary vessels, raising pressure levels and straining the right side of the heart. Addressing ASD early through medical or surgical intervention is critical to preventing this life-threatening condition.
Arrhythmias and Other Electrical Complications Caused by ASD
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) can disrupt the heart's normal electrical activity, leading to arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. This occurs because the extra blood flow between the atria can cause the heart to enlarge and stretch its electrical pathways, creating irregular heart rhythms. Untreated ASD increases the risk of stroke and other complications associated with arrhythmias.
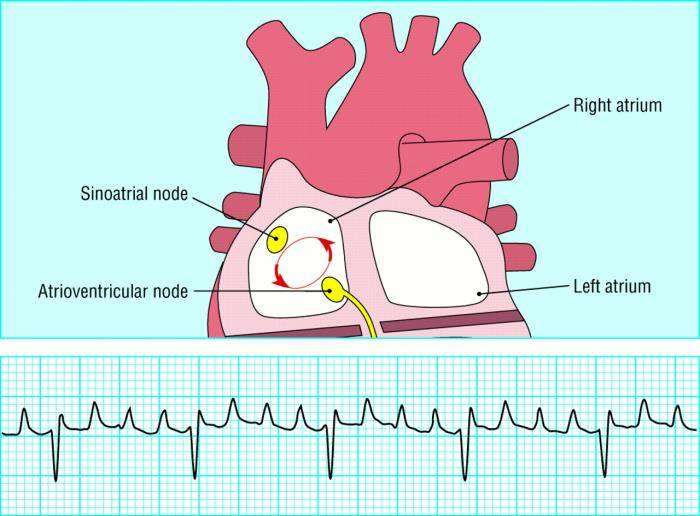
The Effect of ASD on Oxygen Levels in the Body
ASD can allow oxygen-rich blood to mix with oxygen-poor blood, reducing the overall oxygen levels delivered to the body. This inefficiency can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and reduced exercise capacity. In severe cases, this condition, known as hypoxemia, may result in cyanosis—a bluish tint to the skin caused by low oxygen levels.
How ASD Impacts Overall Physical Health
The persistent left-to-right shunting of blood in ASD increases the workload on the right side of the heart and the lungs, potentially leading to pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, or reduced stamina. Over time, this can significantly impair the overall physical health and quality of life of individuals with untreated ASD.
Developmental Concerns for Children with ASD
Children with ASD may experience delayed growth and development due to reduced oxygen delivery to tissues and organs. They may also face difficulties in physical activities and have a higher risk of respiratory infections, which can further impact their overall development.
ASD and Fatigue: Why Energy Levels Are Affected
Fatigue is a common symptom of ASD because the heart and lungs have to work harder to compensate for the abnormal blood flow. This extra effort drains energy, leaving individuals feeling exhausted even with minimal physical exertion.
The Psychological Impact of Living with an Untreated ASD
Living with an untreated ASD can lead to anxiety and depression, especially as symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, or exercise intolerance begin to affect daily life. Children with noticeable symptoms may feel isolated or restricted, impacting their mental health and self-esteem.
Potential Complications of Untreated ASD in Adults
In adults, untreated ASD can lead to severe complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, stroke, and arrhythmias. Eisenmenger syndrome, a condition where the shunting of blood reverses direction, can develop in advanced cases, resulting in severe oxygen deprivation and cyanosis.
Advances in Diagnostic Techniques for Assessing ASD
Modern diagnostic techniques like echocardiography, transesophageal echocardiography, and cardiac MRI have made it easier to detect and assess the size and location of an ASD. These tools provide detailed images and help physicians determine the most appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for ASD and Their Impact on Heart Function
Treatment options for ASD include minimally invasive procedures such as transcatheter device closure or surgical repair. Closing the defect normalizes blood flow, alleviates symptoms, and prevents future complications. For many patients, these treatments significantly improve heart function and quality of life.
The Role of Medications in Managing ASD Symptoms
While medications cannot close an ASD, they are used to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Diuretics help reduce fluid buildup, beta-blockers or antiarrhythmics control arrhythmias, and anticoagulants lower the risk of stroke in patients with arrhythmias.
Long-Term Outlook for Patients After ASD Repair
The long-term outlook for patients who undergo ASD repair is excellent, particularly when the defect is detected and treated early. Most individuals lead normal lives with minimal restrictions on physical activity. However, regular follow-up is essential to monitor for rare complications such as residual shunting or arrhythmias.
Importance of Early Detection in Preventing Complications of ASD
Early detection and treatment of ASD can prevent many complications, including heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and stroke. Routine screenings and timely medical intervention are critical, particularly for children with symptoms or a family history of congenital heart defects.
The Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Surgery for ASD Closure
Discover the advantages of robotic-assisted surgery for ASD closure. Robotic surgery offers improved precision, smaller incisions, and quicker recovery times. This article explores how this innovative approach enhances outcomes for patients undergoing Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure and how it contributes to faster, less invasive treatment.
The Role of Blood Thinners After ASD Closure Surgery
Learn about how blood thinners are used after ASD closure surgery. Post-surgical anticoagulation therapy is often necessary to prevent blood clots, which can lead to complications. This article explains the role of blood thinners in recovery and how they help ensure a safe healing process following ASD closure surgery.
Conclusion: Managing ASD for a Healthy Heart and Life
Proper management of ASD through early detection, advanced diagnostic techniques, and timely treatment can prevent serious complications and significantly improve heart health and overall well-being. Patients and families should work closely with healthcare providers to ensure optimal outcomes and a better quality of life.
Best ASD Closure Surgery in India
The Best ASD Closure Surgery in India is a procedure designed to close a hole in the heart’s atrial septum, improving blood flow and overall cardiac health in patients with atrial septal defects.
Best ASD Closure Surgery Hospitals in India
The best asd closure surgery hospitals in india provide advanced facilities and specialized cardiac teams, ensuring comprehensive care from initial assessment to post-surgical recovery.
ASD Closure Surgery Cost in India
The asd closure surgery cost in india is affordable and transparent, offering patients high-quality care and a range of options to suit their needs.
Best ASD Closure Surgeons in India
The Best ASD Closure Surgeons in India are experts in congenital heart procedures, providing personalized care and a high success rate for patients with atrial septal defects.
FAQ
What is the primary impact of ASD on heart function?
ASD causes abnormal blood flow between the atria, increasing the workload on the right side of the heart and potentially leading to complications like heart enlargement, pulmonary hypertension, and arrhythmias.
Can ASD lead to permanent damage to the heart or lungs?
If left untreated, ASD can cause permanent damage, including heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and irreversible changes in lung vasculature, which may severely impact overall health.
How does ASD affect children differently than adults?
In children, ASD can cause delayed growth, frequent respiratory infections, and reduced exercise tolerance. In adults, untreated ASD often leads to complications such as arrhythmias, stroke, and pulmonary hypertension.
What are the long-term health risks of untreated ASD?
Untreated ASD can lead to serious complications, including heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, stroke, and Eisenmenger syndrome, which is a life-threatening condition.
How does repairing an ASD improve heart health and overall well-being?
Repairing an ASD restores normal blood flow, alleviates symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath, and prevents future complications, greatly improving heart health and overall quality of life.
Explore the Best Heart Care Resources in India
Find some of the top cardiologist, surgeons and the best heart hospitals in India
Best Heart Hospitals in India
Choosing the right hospital is crucial for successful heart treatments. If you want to explore trusted options, check the list of Best Heart Hospitals in India offering world-class facilities, advanced cardiac care units, and experienced teams for both simple and complex procedures.
Best Cardiologists in India
Finding the right cardiologist can make a huge difference in early diagnosis and long-term heart health. If you are looking for the Best Cardiologists in India, see this curated list of experts who specialize in preventive care, interventional cardiology, and complex heart disease management. Check the full list Best Cardiologists in India.
Best Cardiac Surgeons in India
If you are planning for heart surgery and need top-level expertise, we recommend exploring the Best Cardiac Surgeons in India. These surgeons have a proven record in performing bypass surgeries, valve replacements, and minimally invasive heart operations with excellent outcomes.
Get more indepth information on Cardiology treatments and their costs.
Conclusion
Your cardiology health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top cardiac hospitals and cardiac surgeons in India.
An atrial septal defect (ASD) can affect physical activity and exercise choices due to the strain it places on the heart. Individuals with ASD may experience symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and decreased exercise tolerance. While moderate exercise is generally beneficial and recommended, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level of activity. Low-intensity activities such as brisk walking, swimming, and cycling are often well-tolerated. Regular physical activity can help improve cardiovascular health and overall well-being. The Impact of ASD on Physical Activity and Exercise Choices
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure devices are critical for repairing the hole in the septum that separates the upper chambers of the heart. The main types include the Amplatzer Septal Occluder, Amplatzer Cribriform Occluder, Gore Cardioform Septal Occluder, and STARFlex Septal Closure System. Each device is tailored to specific defect characteristics and is typically implanted using minimally invasive catheter-based procedures, leading to reduced recovery times and improved outcomes for patients. Understanding the Different Types of ASD Closure Devices
Early screening for atrial septal defects (ASD) is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention. Detecting ASD early can prevent complications such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and arrhythmias. Early treatment can improve long-term outcomes, reduce symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue, and enhance overall quality of life. Regular check-ups and imaging tests are essential for monitoring the condition and ensuring appropriate care. The Benefits of Early Screening for Atrial Septal Defects