Cardiomyopathy is a progressive condition that affects the heart muscle's ability to pump blood effectively. It can lead to debilitating symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling, significantly impairing quality of life. In advanced stages, cardiomyopathy may result in severe heart failure, necessitating aggressive interventions such as heart transplantation. Understanding the progression and management of cardiomyopathy is crucial for timely and effective treatment planning.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
What Is Severe Cardiomyopathy?
Severe cardiomyopathy occurs when the heart muscle becomes so weakened or stiffened that it can no longer maintain adequate blood circulation. This advanced stage often leads to complications like arrhythmias, fluid retention, and organ damage, making it life-threatening without advanced medical interventions.
When Is Heart Transplantation Recommended for Cardiomyopathy Patients?
Heart transplantation is considered when other treatments fail to manage symptoms or improve heart function. It is typically recommended for patients with end-stage heart failure due to cardiomyopathy, where survival and quality of life can be significantly improved with a new heart.
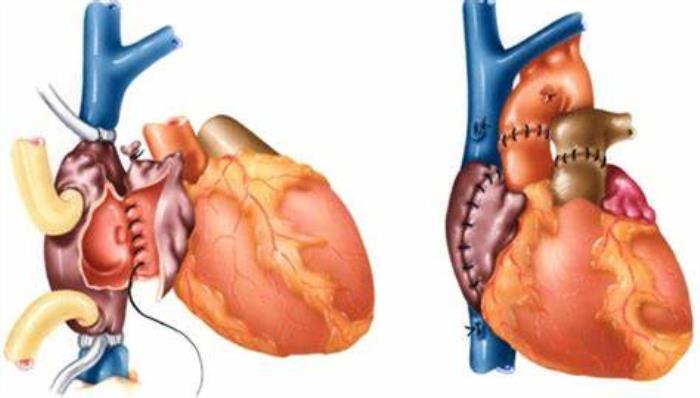
Types of Cardiomyopathy That May Lead to Heart Transplantation
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM): Characterized by an enlarged, weakened heart muscle.
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): A condition causing thickened heart walls, leading to restricted blood flow.
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: Marked by stiff heart walls, impairing the heart's ability to fill properly.
The Pre-Transplant Evaluation Process for Cardiomyopathy Patients
Patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine their eligibility for heart transplantation. This process includes assessing heart function, overall health, and the presence of comorbidities that may affect surgical outcomes. Psychological evaluations and lifestyle factors are also considered to ensure readiness for the rigorous post-transplant regimen.
The Role of Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs) Before Transplantation
LVADs are mechanical pumps that help maintain blood flow in patients with severe heart failure awaiting transplantation. These devices improve quality of life and bridge patients to transplant by stabilizing their condition and supporting organ function.
Managing Advanced Heart Failure Symptoms Prior to Transplant Surgery
Effective management of symptoms, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention, is essential to optimize patient health before surgery. This may include medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications, along with careful monitoring by a specialized heart failure team.
Challenges of Matching Donor Hearts for Cardiomyopathy Patients
Matching donor hearts for cardiomyopathy patients involves evaluating compatibility based on blood type, size, and immunological factors. Limited donor availability and the urgency of severe cases can make the process complex and time-sensitive.
Surgical Considerations for Cardiomyopathy-Related Heart Transplants
Heart transplants in cardiomyopathy patients often require special attention to factors like prior device implants (e.g., LVADs) or structural changes in the heart caused by the disease.
How Immunosuppressive Therapy Supports Recovery After Transplantation
Immunosuppressive therapy prevents rejection by suppressing the immune response, enabling the transplanted heart to function effectively. These therapies are tailored to minimize risks like infection or cancer.
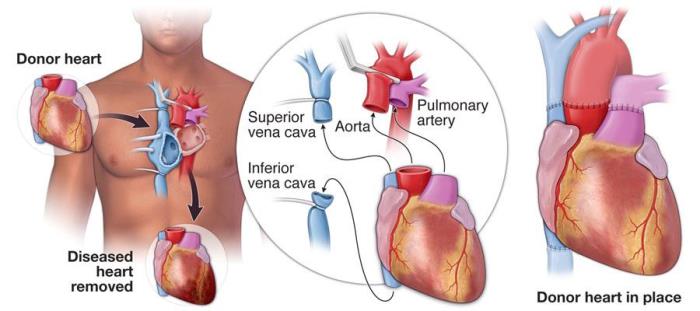
Long-Term Outcomes of Heart Transplantation for Cardiomyopathy Patients
Heart transplant recipients with severe cardiomyopathy often experience significant improvements in survival rates and quality of life. Long-term outcomes depend on adherence to medical care and lifestyle changes.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Cardiomyopathy Post-Transplant Recovery
Rehabilitation programs focus on improving physical endurance, restoring strength, and managing lifestyle changes post-transplant, which are essential for recovery and long-term health.
Managing Comorbidities After Heart Transplantation for Cardiomyopathy
Patients with pre-existing conditions like diabetes or hypertension require close monitoring and management to ensure overall health and reduce complications post-transplant.
Psychological Support for Patients Transitioning to Life Post-Transplant
Adapting to life with a transplanted heart can be emotionally challenging. Counseling and support groups help patients manage anxiety, depression, and the stress of ongoing medical care.
Advances in Transplant Surgery for Severe Cardiomyopathy Cases
Innovative techniques, such as minimally invasive approaches and improved donor heart preservation methods, are making heart transplants safer and more accessible for severe cardiomyopathy patients.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring for Rejection in Cardiomyopathy Patients
Frequent follow-ups with echocardiograms, biopsies, and blood tests help detect signs of rejection early, allowing timely intervention and preserving heart function.
How Heart Transplants Improve Quality of Life in Cardiomyopathy Cases
Heart transplantation offers cardiomyopathy patients relief from debilitating symptoms like fatigue and breathlessness, enabling them to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Success Stories: Life After Heart Transplantation for Severe Cardiomyopathy
Many patients thrive post-transplant, regaining their independence and achieving milestones they previously thought unattainable, demonstrating the transformative impact of heart transplants.
The Role of Family and Caregivers in Supporting Transplant Patients
Family members and caregivers play a crucial role in the recovery process by providing emotional support, assisting with medical routines, and ensuring adherence to post-transplant care plans.
Heart Transplantation and the Risk of Post-Transplant Cancer
Learn about the risk of post-transplant cancer. This blog addresses the potential increased risk of cancer after heart transplantation, caused by immunosuppressive medications and other factors, and the measures taken to monitor and reduce this risk.
Conclusion: Heart Transplantation as a Lifesaving Option for Severe Cardiomyopathy
For patients with severe cardiomyopathy, heart transplantation offers a second chance at life. While challenges exist, advancements in medical care and support systems have made transplants a reliable solution for improving both survival and quality of life.
Best Heart Transplant in India
The Best Heart Transplant in India offers a life-saving solution for patients with end-stage heart failure, using advanced surgical techniques and comprehensive post-transplant care.
Best Heart Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Heart Transplant Hospitals in India provide state-of-the-art facilities, skilled transplant specialists, and multidisciplinary teams for seamless patient care and recovery.
Heart Transplant Cost in India
The Heart Transplant Cost in India is structured to offer affordability while ensuring access to world-class transplant services and comprehensive care packages.
Best Heart Transplant Surgeons in India
The Best Heart Transplant Surgeons in India have extensive experience in performing complex transplants, ensuring precise techniques and personalized patient care for optimal outcomes.
FAQs
What is severe cardiomyopathy, and how does it affect the heart?
Severe cardiomyopathy involves significant weakening or stiffening of the heart muscles, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively and leading to symptoms like breathlessness and fatigue.
When is a heart transplant considered for cardiomyopathy?
A heart transplant is considered when severe cardiomyopathy symptoms cannot be managed with medications or assistive devices, and the patient’s condition poses a high risk of heart failure.
What are the survival rates for cardiomyopathy patients after a heart transplant?
Survival rates vary but generally exceed 85% at one year post-transplant and 70% at five years, with ongoing care playing a key role in long-term success.
How are donor hearts matched for cardiomyopathy patients?
Donor hearts are matched based on factors like blood type, body size, and tissue compatibility to minimize rejection risks and optimize function.
What role do assist devices play before a heart transplant for cardiomyopathy?
Devices like Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs) support heart function temporarily, helping patients survive until a suitable donor heart becomes available.
To be considered for heart transplant surgery in India, patients must meet specific criteria. These include having end-stage heart disease that is not responding to other treatments, being within the age range of 18 to 60 years (sometimes up to 69 years), and being in good general health without major conditions like cancer or kidney disease. Additionally, patients must have a strong support system in place for post-operative care and recovery. The Eligibility Criteria for Heart Transplant Surgery in India
Cardiac rehabilitation is a critical component of recovery after a heart transplant. It helps patients regain strength, improve mobility, and speed up recovery. These programs typically include medically supervised exercise, nutrition counseling, health education, and psychological support. Engaging in cardiac rehabilitation can significantly enhance the quality of life and long-term health outcomes for heart transplant recipients. The Role of Cardiac Rehabilitation After a Heart Transplant
Post-transplant rehabilitation programs are vital for improving the recovery and long-term health of transplant recipients. These programs help patients regain strength, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being. They typically include medically supervised exercise, nutrition counseling, health education, and psychological support. Engaging in these programs can significantly reduce the risk of complications, promote a healthier lifestyle, and improve the quality of life for transplant patients. The Importance of Post-Transplant Rehabilitation Programs