Introduction to Chronic Pancreatitis and Its Impact on Health
Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive inflammatory disease of the pancreas that leads to permanent damage and impaired function. It is primarily characterized by abdominal pain, malabsorption, and diabetes, often due to the destruction of pancreatic tissue. Over time, the condition can severely affect digestion and insulin production, leading to life-altering symptoms. The inflammation in chronic pancreatitis causes the pancreas to become scarred, reducing its ability to produce essential digestive enzymes and insulin. This condition significantly impacts a patient’s quality of life, as ongoing pain and digestive issues can become debilitating. Effective management often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Understanding Pancreas Transplant: A Lifeline for Chronic Pancreatitis Patients
Pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a diseased or damaged pancreas with a healthy donor pancreas. For patients with chronic pancreatitis, this transplant offers the potential to resolve severe complications, particularly those related to pancreatic insufficiency and diabetes. Pancreas transplantation is considered when other treatments have failed, especially in patients suffering from recurrent pain, debilitating symptoms, and insulin dependence. The procedure not only helps restore normal digestive function but can also eliminate or significantly reduce the need for insulin therapy in diabetic patients. Given the complexity and risks, it is typically recommended when the patient's quality of life is severely compromised.
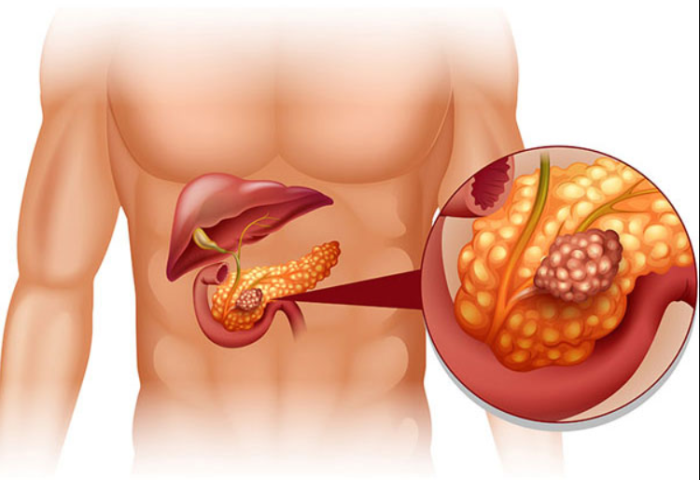
Why Pancreas Transplantation Is Considered for Chronic Pancreatitis
Pancreas transplantation is considered a viable option for patients with chronic pancreatitis who experience significant deterioration in pancreatic function. It is particularly beneficial for those with pancreatic insufficiency and those who develop diabetes as a result of the disease. Chronic pain, difficulty managing blood sugar levels, and the inability to properly digest food often leave these patients with limited options for treatment. In such cases, a pancreas transplant offers a potential cure by replacing the diseased pancreas with a healthy one, restoring both insulin production and digestive function. The procedure has been shown to improve the overall quality of life and reduce or eliminate the need for insulin injections in diabetic patients.
What Is Chronic Pancreatitis? Key Symptoms and Diagnosis
Chronic pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition of the pancreas that progresses over time, often leading to irreversible damage. Common symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and unexplained weight loss. As the pancreas loses its ability to function, patients may experience malabsorption, resulting in nutritional deficiencies, and the development of diabetes due to the loss of insulin-producing cells. Diagnosing chronic pancreatitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRIs, and laboratory tests to assess pancreatic function. The disease may also be diagnosed by measuring enzyme levels in the blood, with high levels of lipase and amylase suggesting pancreatic damage.
The Evolution of Pancreas Transplantation for Pancreatitis Treatment
Pancreas transplantation as a treatment for chronic pancreatitis has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, the procedure was limited to patients with type 1 diabetes, but advances in surgical techniques and immunosuppressive therapy have expanded its use to individuals with chronic pancreatitis who also suffer from pancreatic insufficiency and diabetes. Early challenges with rejection and post-transplant complications have led to improved protocols for donor matching, organ preservation, and post-transplant care. The success rates of pancreas transplants have steadily improved, with many patients experiencing long-term benefits such as pain relief, improved nutritional absorption, and a reduced need for insulin.
When Is Pancreas Transplantation the Right Choice for Chronic Pancreatitis?
Pancreas transplantation is considered when a patient’s chronic pancreatitis has led to significant complications that cannot be controlled by other medical treatments. It is particularly considered for individuals suffering from debilitating pain, malnutrition, and diabetes that are no longer manageable with insulin or enzyme therapy. The right timing for a transplant is when other treatments have been exhausted, and the patient’s quality of life is severely compromised. However, transplant surgery is not suitable for every patient, as the procedure requires careful evaluation of the patient's overall health, including their ability to manage the rigorous immunosuppressive therapy required post-transplant.
Assessing Eligibility for Pancreas Transplant in Chronic Pancreatitis
Eligibility for a pancreas transplant is determined based on various factors, including the severity of chronic pancreatitis, overall health, and the presence of associated conditions like diabetes. Ideal candidates are typically those who have significant pancreatic dysfunction, persistent pain, and severe complications that have not responded to conventional treatments. Other considerations include the patient’s ability to tolerate long-term immunosuppressive medications and their potential for post-surgical recovery. Pre-transplant assessments often involve comprehensive evaluations of cardiovascular health, kidney function, and mental health to ensure the patient is physically and psychologically prepared for the procedure.
The Role of Pancreas Transplant in Managing Diabetes Caused by Pancreatitis
In chronic pancreatitis, damage to the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas can lead to the development of diabetes. Pancreas transplantation plays a crucial role in managing this form of diabetes, as it can restore normal insulin production and eliminate the need for exogenous insulin therapy. After a successful transplant, most patients see an improvement or even a complete reversal of their diabetic symptoms. This can significantly enhance their quality of life, as managing blood glucose levels becomes easier, and the associated risks of long-term diabetes complications are reduced. Pancreas transplant offers a unique solution for diabetic patients who suffer from chronic pancreatitis and have difficulty managing their blood sugar.
Types of Pancreas Transplant: Whole, Islet, or Combined
There are three main types of pancreas transplants: whole pancreas transplant, islet cell transplant, and combined kidney-pancreas transplant. The whole pancreas transplant involves replacing the entire pancreas, including both its endocrine and exocrine functions, which restores insulin production and digestion. Islet cell transplant, on the other hand, involves isolating and transplanting only the insulin-producing islet cells from a donor pancreas. This procedure is typically done when the patient does not have severe digestive issues. In some cases, a combined kidney-pancreas transplant is performed for patients with end-stage renal disease due to diabetes. The choice of transplant type depends on the patient's specific needs and the severity of their condition.
Surgical Techniques in Pancreas Transplantation: What to Expect
Pancreas transplantation involves a highly complex surgical procedure where the diseased pancreas is removed and replaced with a donor pancreas. The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and involves an incision in the abdomen to access the pancreas. In some cases, the procedure may be done in conjunction with a kidney transplant if the patient has kidney failure. After the pancreas is transplanted, the new organ is connected to the digestive tract and blood vessels. Post-surgical recovery typically involves a hospital stay of several weeks, followed by a long-term follow-up to monitor for complications such as organ rejection or infections.
Risks and Complications of Pancreas Transplantation
Like all major surgeries, pancreas transplantation carries risks, including organ rejection, infection, and bleeding. Post-transplant complications such as pancreas failure or delayed graft function can also occur. Patients must adhere to a strict regimen of immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection, which also increases the risk of infections and certain cancers. Additionally, there is a risk of graft-versus-host disease if the transplanted tissue reacts against the patient’s cells. Long-term complications can include chronic rejection or the gradual failure of the transplant over time, necessitating further medical interventions or additional transplants.
Innovative Advancements in Pancreas Transplant for Chronic Pancreatitis
Recent advancements in pancreas transplant technology have improved both the success rates and patient outcomes. New surgical techniques, better immunosuppressive drugs, and refined donor matching processes have made transplants safer and more effective. Additionally, research into tissue engineering and stem cell therapies holds promise for future treatments that may reduce the need for whole organ transplants. These innovations are expected to enhance the long-term success of pancreas transplants and reduce the risks associated with the procedure.
The Role of Stem Cells in Pancreas Transplant and Chronic Pancreatitis Treatment
Stem cell research has shown great potential in treating chronic pancreatitis and improving the success of pancreas transplants. By using stem cells to regenerate damaged pancreatic tissue, researchers hope to develop treatments that can repair the pancreas without the need for a full transplant. In some experimental approaches, stem cells may be used to generate insulin-producing cells that can be transplanted into patients, potentially offering a less invasive alternative to traditional pancreas transplants.
Evaluating Success Rates of Pancreas Transplant in Chronic Pancreatitis
The success rates of pancreas transplants for chronic pancreatitis vary depending on multiple factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. On average, around 80-85% of patients experience long-term function of their transplanted pancreas, and many no longer require insulin therapy. Success rates are higher in patients who undergo combined kidney-pancreas transplants, as the kidney transplant often provides a more favorable environment for the pancreas to function. However, as with any transplant, there are risks involved, and outcomes can differ based on individual circumstances.
Alternatives to Pancreas Transplant: When Other Treatments Are Preferred
While pancreas transplantation is an effective option for many patients with chronic pancreatitis, it is not always the first choice. Other treatments such as enzyme replacement therapy, pain management, and insulin therapy are often used to manage the disease. In cases where a patient’s pancreatitis has not caused severe dysfunction or complications, these non-surgical treatments can provide relief. For patients with end-stage renal disease, a combined kidney-pancreas transplant might be considered as an alternative to a single organ transplant. The decision to opt for pancreas transplant surgery depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
Pancreas Transplantation and Pain Relief for Chronic Pancreatitis Sufferers
One of the most significant benefits of pancreas transplantation for chronic pancreatitis patients is the potential for pain relief. Chronic pancreatitis is often accompanied by severe abdominal pain, which can be debilitating and resistant to other treatments. By replacing the damaged pancreas with a healthy donor organ, many patients experience a complete resolution or significant reduction in pain. The transplant also improves the function of the digestive system, which can further reduce discomfort associated with malabsorption and nutritional deficiencies.
Psychological and Emotional Support for Patients Undergoing Pancreas Transplant
Undergoing a pancreas transplant can be an emotionally challenging process, requiring patients to adjust to new routines, medications, and potential long-term changes in their health. Psychological support is essential to help patients cope with the stress of surgery and the uncertainty that comes with the transplant process. Mental health professionals can help patients manage anxiety, depression, and other emotional concerns during their recovery. Support groups and counseling also offer a valuable network for patients to share experiences and receive emotional support.
The Future of Pancreas Transplant: Advancements and Research Directions
The future of pancreas transplantation looks promising, with advancements in surgical techniques, immunosuppressive therapies, and organ preservation methods continuously improving outcomes. Researchers are exploring alternative approaches such as xenotransplantation (using animal organs) and stem cell-based therapies that may eventually eliminate the need for full organ transplants. Ongoing studies aim to enhance the durability and success rates of pancreas transplants, potentially providing better solutions for chronic pancreatitis patients in the coming years.
How Pancreas Transplant Impacts the Management of Digestive Disorders
For patients with chronic pancreatitis, a pancreas transplant can significantly improve the management of digestive disorders. By restoring the pancreas’s exocrine function, the transplant enables the production of enzymes necessary for digesting food. This improvement in digestive function reduces symptoms such as malabsorption, diarrhea, and weight loss. Patients often experience better nutrient absorption and overall gastrointestinal health post-transplant, leading to enhanced energy levels and improved nutritional status.
How to Prepare for a Pancreas Transplant: What Patients Need to Know
Preparing for a pancreas transplant involves thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging studies, and psychological assessments. Patients are educated on the surgery, the risks involved, and the post-surgical care they will need. It is important to follow specific guidelines before the procedure, such as avoiding certain medications, quitting smoking, and adhering to dietary recommendations. Understanding the process and following medical advice can help patients achieve the best possible outcomes.
The Ethical Considerations of Pancreas Transplant for Chronic Pancreatitis
Pancreas transplantation raises ethical questions, particularly regarding organ allocation and the use of donor organs. With limited organ availability, patients must be evaluated based on their medical need, potential benefits from the transplant, and overall prognosis. Ethical considerations also extend to the risks involved in the surgery, such as the possibility of rejection and the long-term need for immunosuppressive medications. These factors require careful consideration by the transplant team to ensure that the procedure is appropriate for the patient.
Challenges in Pancreas Transplantation for Chronic Pancreatitis Patients
Pancreas transplantation for chronic pancreatitis patients presents numerous challenges, including the complexity of the surgery, the risk of organ rejection, and the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy. The availability of suitable donor organs is another significant challenge, as pancreas donations are rare compared to other organs. Post-transplant complications such as infection, rejection, and surgical failure can occur, requiring ongoing care and monitoring. These challenges underscore the importance of careful patient selection and rigorous post-transplant care.
Pancreas Transplant as a Treatment Option for Young Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis
Pancreas transplantation can be an important treatment option for younger patients with chronic pancreatitis who have severe symptoms and complications. Early intervention with a pancreas transplant can prevent further damage to the pancreas and improve the patient’s long-term quality of life. Younger patients may benefit from the procedure as they typically have a better chance of successful outcomes and longer transplant survival. However, they must also be prepared for the lifelong commitment to immunosuppressive medications and regular follow-up care.
Cost Considerations in Pancreas Transplant for Chronic Pancreatitis
The cost of pancreas transplantation for chronic pancreatitis patients is significant, with the surgery itself, hospital stay, and post-transplant care contributing to the overall expenses. Additionally, patients require lifelong immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection, which can add to the financial burden. Health insurance coverage and government programs may help offset some of the costs, but patients should be prepared for substantial out-of-pocket expenses. Financial counseling is often recommended for those considering transplant surgery.
Post-Transplant Care: What to Expect After Pancreas Transplantation
Post-transplant care for pancreas transplant patients involves strict monitoring to ensure that the new organ is functioning well and that there are no signs of rejection or complications. Patients must take immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection, which increases the risk of infection. Regular follow-up visits with the transplant team are essential for adjusting medications, monitoring pancreatic function, and addressing any side effects. Patients are also closely monitored for blood sugar levels and other potential complications.
Key Stages of Post-Surgery Recovery After a Pancreas Transplant
Recovery after a pancreas transplant is crucial to ensure the graft's longevity and optimal function. Learn about the post-surgery recovery process, including monitoring for rejection, managing medications, and resuming daily activities safely.
The Essential Roles of the Pancreas in Maintaining Body Functions
The pancreas plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation, making it indispensable for overall health. Explore how the pancreas supports key bodily functions and why its health is critical to your well-being.
Impact of Pancreas Transplant on Long-Term Health and Prognosis
Pancreas transplantation can have a profound impact on a patient’s long-term health and prognosis. For many patients, the procedure improves overall quality of life by eliminating chronic pain, improving digestive function, and stabilizing blood sugar levels. Studies show that long-term survival rates for pancreas transplant recipients are high, with many patients living for several years after the transplant. However, long-term health requires continuous management, including immunosuppressive therapy and monitoring for potential complications such as infection or organ rejection.
Rejection and Monitoring After a Pancreas Transplant
Organ rejection is one of the most significant risks following pancreas transplantation. To prevent rejection, patients must adhere to a lifelong regimen of immunosuppressive medications, which help to suppress the body's immune response. Regular follow-up visits with the transplant team are critical to monitor for signs of rejection, such as changes in organ function or lab test results. In some cases, rejection episodes can be managed with medication adjustments, but severe rejection may require additional interventions or even a second transplant.
Best Pancreas Transplant in India
The Best Pancreas Transplant in India is performed by skilled transplant surgeons who utilize advanced techniques to restore pancreatic function, providing patients with a tailored treatment plan to improve their quality of life and manage diabetes effectively.
Best Pancreas Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Hospitals for Pancreas Transplant in India are equipped with state-of-the-art transplant facilities and multidisciplinary care teams, ensuring comprehensive pre- and post-transplant care to support a smooth recovery process.
Pancreas Transplant Cost in India
When considering the Pancreas Transplant Cost in India, patients benefit from transparent, affordable pricing at leading transplant centers, which offer high-quality, cost-effective options for managing complex pancreatic conditions.
Best Pancreas Transplant Doctors in India
The Best Pancreas Transplant Doctors in India are highly experienced in performing complex transplants, providing personalized care and dedicated follow-up support to maximize transplant success and patient recovery.
Quality of Life After Pancreas Transplantation
For many patients with chronic pancreatitis, a successful pancreas transplant leads to significant improvements in quality of life. Pain relief, better digestion, and improved blood sugar control are the primary benefits of the procedure. Patients often experience a return to normal activities, as the debilitating symptoms of chronic pancreatitis are alleviated. However, the responsibility of adhering to lifelong medications and regular monitoring is a key aspect of post-transplant life. Despite these ongoing requirements, many patients report a significant boost in their physical and emotional well-being.
Living with a Pancreas Transplant: Lifelong Care and Management
Living with a pancreas transplant requires lifelong care and management to ensure the success of the procedure and prevent complications. Patients must continue to take immunosuppressive medications to avoid organ rejection, and they must also follow strict medical guidelines regarding diet, exercise, and lifestyle. Regular follow-ups with the transplant team are essential for monitoring organ function, adjusting medications, and addressing any health concerns that may arise. With careful management, many patients enjoy a long and healthy life following their transplant.
FAQs About the Role of Pancreas Transplant in Treating Chronic Pancreatitis
1. What is a pancreas transplant?
A pancreas transplant is a surgical procedure where a diseased pancreas is replaced with a healthy donor pancreas. This procedure is often done for patients with chronic pancreatitis or diabetes.
2. Who is eligible for a pancreas transplant?
Eligibility for a pancreas transplant depends on the severity of chronic pancreatitis, the patient's overall health, and their response to other treatments. A comprehensive evaluation is needed to determine eligibility.
3. What are the risks of pancreas transplant surgery?
Risks of pancreas transplant surgery include organ rejection, infection, bleeding, and complications related to immunosuppressive medications. Close monitoring is essential after the surgery to minimize these risks.
4. How long does recovery take after a pancreas transplant?
Recovery after a pancreas transplant typically requires a hospital stay of several weeks. Patients must also follow up with their transplant team regularly to monitor progress and manage any complications.
5. Can a pancreas transplant cure chronic pancreatitis?
While a pancreas transplant does not cure chronic pancreatitis, it can significantly relieve symptoms, including chronic pain, digestive issues, and diabetes, leading to an improved quality of life.
6. How does a pancreas transplant help manage diabetes?
A pancreas transplant helps manage diabetes by restoring the body’s ability to produce insulin, thus eliminating the need for insulin injections and improving blood sugar control.
7. What is the success rate of pancreas transplants?
The success rate of pancreas transplants is generally high, with approximately 80-85% of patients experiencing long-term function and improved quality of life.
8. What are the alternatives to pancreas transplant for chronic pancreatitis?
Alternatives to pancreas transplants include enzyme replacement therapy, insulin therapy, pain management, and lifestyle changes to manage the symptoms of chronic pancreatitis.
9. How does a pancreas transplant improve quality of life?
A pancreas transplant can improve quality of life by relieving pain, restoring digestive function, and eliminating the need for insulin therapy, allowing patients to return to normal activities.
10. Are there any long-term complications after a pancreas transplant?
Long-term complications can include organ rejection, infections, and the need for ongoing immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection and maintain organ function.
Explore common post-surgery complications such as infections, blood clots, and delayed healing. Learn about preventive strategies, early signs to watch for, and effective management techniques to ensure a smoother recovery. A Guide to Post Surgery Complications and How to Manage Them
Learn about the risks associated with pancreas transplant surgery, including organ rejection, infections, and surgical complications. Discover how careful monitoring and post-surgery care help manage these risks and ensure better outcomes. Understanding the Risks of Pancreas Transplant Surgery
Discover innovative non-surgical treatments for pancreas health, including advanced medications, lifestyle modifications, and regenerative therapies. Learn how these approaches help manage pancreatic disorders and improve long-term health. Exploring Non-Surgical Innovations for Pancreas Health