Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is a critical medical procedure used to treat various hematological disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia. The procedure involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells, which can restore the body’s ability to produce blood cells. BMT can be performed using stem cells from the patient (autologous transplant) or from a donor (allogeneic transplant). The success of an allogeneic transplant heavily relies on the compatibility of the donor and recipient, particularly through human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Understanding HLA and Its Importance
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) are molecules found on the surface of cells that play a vital role in the immune system. They help the body distinguish between its own cells and foreign invaders. HLA molecules are categorized into two main classes: Class I and Class II. The compatibility of HLA between the donor and recipient is crucial in preventing transplant rejection, where the recipient’s immune system attacks the transplanted cells. A close match can significantly improve the chances of a successful transplant and reduce the risk of complications such as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
HLA Matching Process in Transplantation
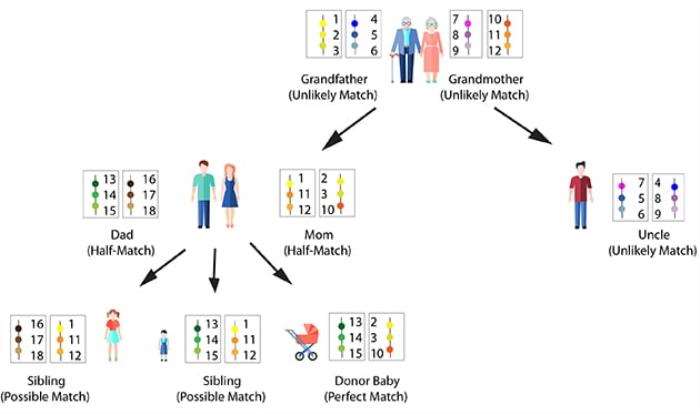
The HLA matching process involves several steps. Initially, a blood sample is taken from the patient and potential donors to determine their HLA typing. This typing identifies the specific HLA alleles present in each individual. The ideal scenario is to find a donor with an HLA profile that matches the recipient’s as closely as possible, typically requiring a match of at least six out of eight HLA markers. The more HLA markers that match, the lower the risk of complications and the better the overall prognosis for the transplant.
Types of HLA Antigens
HLA antigens are classified into several categories, with the most important being HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DR. These antigens are critical in the context of bone marrow transplantation. HLA-A and HLA-B are primarily involved in presenting foreign antigens to T-cells, while HLA-DR plays a significant role in activating the immune response. A mismatch in any of these antigens can lead to an increased risk of transplant rejection and complications post-transplant. Therefore, understanding the types of HLA antigens is essential for healthcare professionals involved in BMT.
Impact of HLA Mismatch on Transplant Outcomes
Studies have shown that HLA mismatches can adversely affect transplant outcomes. A higher degree of mismatch is associated with increased rates of transplant rejection, a higher incidence of GVHD, and poorer overall survival rates. In contrast, a well-matched donor can lead to a more favorable outcome, with improved engraftment rates and reduced complications. Therefore, achieving a high level of HLA matching is a priority in the donor selection process, influencing both short-term and long-term success of the transplantation.
Significance of HLA Typing Prior to Transplantation
HLA typing is a crucial step in the pre-transplant evaluation process. It involves determining the specific HLA alleles present in both the donor and recipient. This typing is performed using techniques such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and sequencing. Accurate HLA typing ensures that the selected donor has the best possible match, minimizing the risk of complications. Additionally, it aids in the identification of suitable unrelated donors from registries, which is particularly important when a matched sibling is not available.
Challenges in Finding Matched Donors
Finding a suitable matched donor can be challenging, particularly for patients from ethnic minority groups. The diversity of HLA alleles among different populations means that individuals may have unique combinations that are less common in the general donor pool. This disparity can lead to difficulties in locating a match, necessitating the need for extensive donor registries that include a diverse range of ethnic backgrounds. Efforts to increase donor registration and awareness are essential to improve the chances of finding a compatible donor for all patients in need of BMT.
Role of Cord Blood in HLA Matching
Cord blood stem cells have emerged as an alternative source for transplantation, particularly when a matched donor is not available. Cord blood has a unique advantage due to its relatively lower HLA matching requirements compared to adult donors. This flexibility is attributed to the naïve nature of the immune cells in cord blood, which can tolerate a certain degree of immunological mismatch. However, the quantity of stem cells available in cord blood units can be a limiting factor, especially for adult patients. Thus, the use of cord blood is a valuable option in the context of HLA matching.
Recent Advances in HLA Matching Techniques
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the HLA matching process. New techniques such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow for more accurate and comprehensive HLA typing. These methods can identify rare alleles and provide a more detailed understanding of the HLA profile. Furthermore, the development of computational algorithms aids in predicting the likelihood of transplant success based on HLA compatibility. These innovations enhance the precision of donor selection, ultimately improving patient outcomes in bone marrow transplantation.
Understanding Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a significant complication that can occur after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. It arises when the donor’s immune cells recognize the recipient’s tissues as foreign and mount an immune response against them. The risk of GVHD is closely related to the degree of HLA mismatch. A well-matched donor can reduce the incidence and severity of GVHD, which can manifest as skin rashes, liver dysfunction, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Understanding the mechanisms of GVHD is essential for clinicians to manage and mitigate its effects.
Strategies to Minimize HLA Mismatch Risks
To reduce the risks associated with HLA mismatch, several strategies can be employed. These include selecting donors with the highest possible HLA compatibility, using pharmacological interventions to suppress the immune response, and employing pre-transplant conditioning regimens that prepare the recipient's immune system. Additionally, post-transplant monitoring for signs of rejection or GVHD is crucial for timely intervention. Utilizing these strategies can enhance the likelihood of a successful transplant and improve patient outcomes.
Psychosocial Considerations in Bone Marrow Transplantation
The journey of bone marrow transplantation extends beyond the medical aspects, encompassing significant psychosocial challenges. Patients may experience anxiety, fear of rejection, and uncertainty about their prognosis. Support systems, including counseling and support groups, play a vital role in helping patients cope with these emotional challenges. Additionally, educating patients about the importance of HLA matching and the transplantation process can empower them to engage actively in their care, fostering a sense of control during a challenging time.
Long-Term Outcomes and Follow-Up Care
Long-term follow-up care is essential for patients who have undergone bone marrow transplantation. Regular monitoring for potential late effects of treatment, such as secondary malignancies, organ dysfunction, and chronic GVHD, is critical. The success of the transplant is often assessed through blood tests and imaging studies to evaluate engraftment and overall health. Furthermore, ongoing support for psychological and social well-being is vital in ensuring that patients can reintegrate into their daily lives and maintain their quality of life post-transplant.
Ethical Considerations in HLA Matching
The process of HLA matching and donor selection raises several ethical considerations. Issues such as informed consent, donor anonymity, and the potential for exploitation in unrelated donor situations must be addressed. Additionally, disparities in access to transplantation services based on socioeconomic status or ethnicity highlight the need for equitable healthcare practices. Ethical frameworks must guide healthcare professionals in navigating these complexities to ensure fair and just treatment for all patients in need of bone marrow transplantation.
Global Perspectives on HLA Matching and Transplantation
Globally, the approach to HLA matching and bone marrow transplantation varies based on healthcare infrastructure, availability of donor registries, and cultural factors. Countries with well-established transplant programs often have extensive donor databases, improving the chances of finding suitable matches. In contrast, regions with limited resources may face challenges in accessing transplantation services. Collaborative efforts among international organizations aim to enhance donor registries and promote awareness of the importance of HLA matching, ultimately benefiting patients worldwide.
Future Directions in HLA Matching Research
Research in HLA matching and bone marrow transplantation continues to evolve, focusing on improving donor-recipient compatibility and enhancing transplant outcomes. Emerging studies are exploring the role of genomic profiling in predicting transplant success and identifying novel HLA alleles. Furthermore, advancements in immunotherapy and targeted therapies may offer new avenues for managing complications associated with HLA mismatches. Continued research is crucial for refining transplantation techniques and ensuring that patients receive the most effective and personalized care possible.
Conclusion on HLA Matching in Bone Marrow Transplantation
In conclusion, HLA matching plays a pivotal role in the success of bone marrow transplantation. The compatibility of HLA antigens between donor and recipient significantly influences transplant outcomes, including the risk of rejection and the incidence of complications such as GVHD. As advancements in HLA typing and donor selection continue to improve, the prospects for patients requiring BMT are becoming increasingly favorable. Ongoing research and ethical considerations will ensure that the field of transplantation evolves to meet the needs of diverse patient populations effectively.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant in India
The Best Bone Marrow Transplant in India provides a vital treatment option for blood disorders and cancers, offering renewed hope through advanced medical techniques and high success rates.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Bone Marrow Transplant Hospitals in India are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and experienced hematologists, ensuring safe procedures and comprehensive patient care.
Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in India
The Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in India is affordable and competitive, providing access to quality care with transparent pricing for international and domestic patients.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant Specialists in India
The Best Bone Marrow Transplant Specialists in India are highly skilled in performing successful transplants, offering personalized care and advanced therapies tailored to individual patient needs.
FAQs about HLA Matching in Bone Marrow Transplantation
What is HLA matching?
HLA matching refers to the process of comparing the HLA antigens of a donor and a recipient to ensure compatibility for bone marrow transplantation. A closer match reduces the risk of complications and improves transplant success rates.
Why is HLA matching important?
HLA matching is crucial because it helps prevent transplant rejection and reduces the risk of GVHD. A well-matched donor can lead to better overall outcomes for the patient.
How is HLA typing performed?
HLA typing is performed using blood samples from the donor and recipient, employing techniques such as PCR and sequencing to identify specific HLA alleles.
What happens if there is an HLA mismatch?
An HLA mismatch can lead to a higher risk of transplant rejection and complications such as GVHD. Careful monitoring and management strategies are essential in these cases.
Can cord blood be used if there is an HLA mismatch?
Yes, cord blood stem cells can be used even if there is an HLA mismatch, as they require a lower degree of compatibility compared to adult donors. However, the quantity of stem cells available may be a limiting factor.
Non-profit organizations are crucial in promoting bone marrow donation through education, simplifying the donation process, and enhancing patient outcomes. Their global efforts increase donor diversity and support essential research and advocacy. The Role of Non-Profit Organizations in Promoting Bone Marrow Donation
Explore the differences between Bone Marrow Transplant and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplant, including procedures, risks, and outcomes to make informed healthcare decisions. Bone Marrow vs. Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplant: What’s the Difference?
Bone marrow regeneration post-transplant varies, typically taking weeks to a year, influenced by transplant type, patient health, and complications. How Long Does It Take for Bone Marrow to Regenerate After a Transplant?