An Overview of Post-Surgery Complications in Bone Marrow Transplants
Post-surgery complications in bone marrow transplants can vary widely, depending on the patient’s health, the type of transplant, and the body's response. Some complications arise immediately after surgery, while others may develop over time. Key risks include graft versus host disease (GVHD), infections, and immune suppression, which can affect organs like the liver, lungs, and digestive tract. Understanding these complications helps in providing timely intervention and improving long-term outcomes for bone marrow transplant recipients.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Common Post-Surgery Risks in Bone Marrow Transplantation
The most common risks following a bone marrow transplant include infections, GVHD, and organ damage due to the immune system's altered functioning. Infections are particularly dangerous because the immune system is weakened post-transplant, making patients vulnerable to bacterial, fungal, and viral infections. Additionally, GVHD can occur in allogeneic transplants where the donor's immune cells may attack the patient’s tissues. Managing these risks is crucial for recovery and patient safety.
Understanding Graft vs. Host Disease (GVHD) After Bone Marrow Transplants
GVHD is a significant complication of allogeneic bone marrow transplants, where the donor's immune cells recognize the recipient's body as foreign and begin to attack it. This disease can be either acute or chronic, impacting organs such as the liver, skin, and gastrointestinal tract. Acute GVHD usually manifests within 100 days post-transplant, while chronic GVHD may develop later. Preventive medications and careful monitoring can help reduce the risk and severity of GVHD.
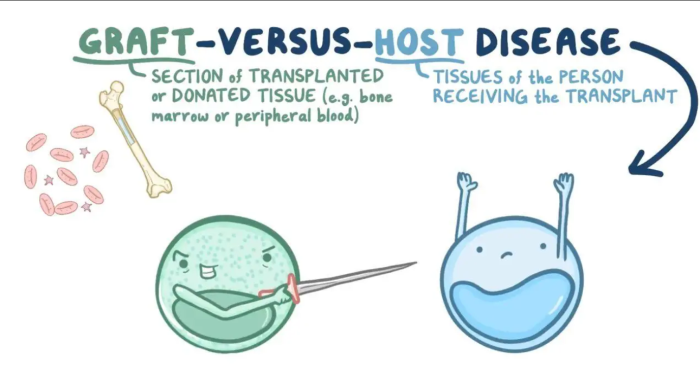
Infections After Bone Marrow Transplant: Causes and Prevention
After a bone marrow transplant, patients have a high risk of infections due to suppressed immune function. Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections are common and can lead to severe complications if untreated. To prevent infections, patients are often prescribed antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal medications, and are advised to follow strict hygiene and isolation practices during recovery. Regular monitoring and early detection are essential to manage infections effectively.
Managing Immune System Suppression After Bone Marrow Transplants
The immune system is intentionally suppressed following a bone marrow transplant to prevent graft rejection or GVHD. However, this suppression makes patients more susceptible to infections and other complications. Managing immune suppression involves balancing medications to prevent rejection while minimizing infection risks. Patients typically undergo regular blood tests and health checks to adjust immune-suppressing medications as needed, based on their recovery progress and infection risks.
Bone Marrow Transplant Complications: Early vs. Late-Stage Risks
Early-stage complications in bone marrow transplants often include acute GVHD, infections, and bleeding, which may appear within days to weeks post-surgery. Late-stage complications, such as chronic GVHD, secondary cancers, and organ damage, can develop months or even years after the transplant. Recognizing and addressing these complications at each stage allows healthcare providers to implement preventative measures and treatments promptly.
Identifying Acute and Chronic GVHD in Bone Marrow Transplant Patients
GVHD can occur as either acute or chronic, with different symptoms and timelines. Acute GVHD generally arises within the first 100 days, affecting the skin, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. Chronic GVHD appears later and can involve multiple organs, including the lungs and eyes, and is often more challenging to treat. Accurate diagnosis and regular monitoring help manage the condition and improve patient outcomes.
When Complications Arise: Post-Transplant Care Essentials
Post-transplant care is critical to managing complications in bone marrow transplant patients. This care includes regular monitoring for GVHD, infections, and signs of organ toxicity. Patients may require additional medications to support the immune system, prevent infections, and manage symptoms of potential complications. Adopting a proactive approach to care and maintaining clear communication with healthcare providers can improve recovery and reduce risks.
Understanding Organ Toxicity Risks After Bone Marrow Transplant Surgery
Organ toxicity can result from high doses of chemotherapy or radiation used before the bone marrow transplant to prepare the body. The liver, kidneys, and lungs are especially vulnerable to damage. Liver toxicity may cause jaundice or liver failure, while lung toxicity can lead to breathing difficulties. Regular organ function tests and early intervention are essential to manage these risks and support patient recovery.
Infection Prevention and Control in Bone Marrow Transplant Recipients
Preventing infection is a priority in the post-transplant period due to the patient’s weakened immune system. Infection control measures may include antibiotic and antiviral medications, isolation practices, and careful monitoring. Patients are often advised to avoid large crowds, maintain hygiene, and follow a balanced diet to support immune function. Infection control helps reduce hospital stays, improve recovery, and decrease mortality rates among bone marrow transplant patients.
Secondary Cancers as a Post-Complication in Bone Marrow Transplants
Patients who have undergone a bone marrow transplant face an increased risk of developing secondary cancers due to prior exposure to chemotherapy and radiation. Common secondary cancers include skin cancers, leukemias, and lymphomas. Regular screenings and early detection are vital for managing and treating these risks promptly.
Risks of Bleeding and Clotting Disorders After Bone Marrow Transplantation
Bleeding and clotting disorders can arise post-transplant due to low platelet counts and disrupted blood cell production. This increases the risk of severe bruising, internal bleeding, and blood clots. Careful monitoring of blood counts and administering blood products as needed are common interventions for managing these risks.
Bone Marrow Transplant Failure: Causes and Next Steps
Transplant failure occurs when the new marrow does not produce sufficient blood cells, which can result from graft rejection, infections, or relapse of the initial disease. Treatment options may include another transplant or supportive care, depending on the patient’s health and prognosis.
The Role of the Immune System in Post-Transplant Complications
The immune system plays a central role in transplant outcomes, balancing between rejecting foreign tissue and defending against infections. Immunosuppressive medications are critical for minimizing complications, though they come with risks like increased susceptibility to infections. Managing immune response is crucial for successful recovery.
Recognizing and Managing Pulmonary Complications Post-Transplant
Pulmonary complications, such as lung infections, pulmonary fibrosis, and bleeding, are common after a bone marrow transplant and can cause long-term respiratory issues. Early identification and prompt treatment are essential for reducing risks of respiratory failure.
Post-Transplant Monitoring: Key Indicators of Complications
Regular monitoring helps identify early signs of complications like GVHD, infections, and organ damage. Blood tests, imaging, and physical exams are standard post-transplant care practices, allowing for timely intervention when complications arise.
The Link Between Graft Failure and Post-Surgery Complications
Graft failure may occur due to immune rejection, insufficient stem cell engraftment, or infection. Graft failure can lead to serious health risks, including increased infection susceptibility and anemia, and often necessitates additional treatments or repeat transplants.
Managing the Psychological Impact of Post-Surgery Complications
The psychological effects of post-transplant complications, such as anxiety, depression, and stress, are common and impact recovery. Support from mental health professionals, counseling, and group support can help patients cope with these challenges.
Understanding Immune Reconstitution and Recovery
Post-transplant, the immune system gradually recovers through a process called immune reconstitution. This process varies in time, and patients may need periodic immunoglobulin supplementation and vaccinations to restore immunity levels fully.
The Role of Nutrition in Bone Marrow Transplant Recovery
Nutrition is vital for supporting immune recovery and overall health post-transplant. A balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals helps rebuild strength, supports immunity, and can reduce infection risks during recovery.
Neurological Issues Post-Surgery: What to Expect
Some patients experience neurological issues such as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and mood swings after a bone marrow transplant. These effects are often temporary and improve with time, though cognitive therapy and mental health support can aid recovery.
Renal and Liver Complications After Bone Marrow Transplants
Renal and liver complications are potential side effects of the medications and treatments involved in bone marrow transplants. Kidney function is monitored closely, as well as liver enzymes, to detect and manage any organ toxicity early.
Gastrointestinal Issues After Transplant Surgery
Gastrointestinal complications, including nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, often result from medication side effects or infections. Patients are advised to follow a diet that reduces stomach irritation, and medications are available to manage these symptoms.
Evaluating Success Rates and Outcomes of Bone Marrow Transplants
Success rates of bone marrow transplants vary based on the condition treated and the patient’s health. Explore the factors influencing transplant success rates and the potential outcomes that can lead to a full recovery and improved quality of life.
The Role of Stem Cells in Bone Marrow Transplant Success
Stem cells are fundamental to the success of a bone marrow transplant, as they help rebuild the patient’s blood and immune system. Discover how stem cells contribute to successful transplants and improve recovery by restoring healthy cellular function.
Dealing With Fatigue and Physical Weakness
Fatigue and physical weakness are common due to the body’s recovery demands. Physical therapy and gradual reintroduction of daily activities can aid in rebuilding strength over time.
Vaccinations and Immunization Needs After Bone Marrow Transplant
Reimmunization is often necessary for transplant patients due to lost immunity post-surgery. Patients receive vaccines in a phased approach, prioritizing those for severe infections like influenza and pneumonia.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant in India
The Best Bone Marrow Transplant in India is performed by expert hematologists and transplant specialists who use advanced techniques to treat conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood disorders, offering patients a tailored treatment plan focused on optimal outcomes.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Hospitals for Bone Marrow Transplant in India are equipped with cutting-edge technology and specialized transplant units, providing comprehensive care, from pre-transplant evaluations to post-transplant support, ensuring a successful and smooth recovery process.
Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in India
When considering the Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in India, patients benefit from transparent, affordable pricing at leading hospitals, which offer cost-effective treatment options without compromising quality and care standards.
Best Bone Marrow Transplant Doctors in India
The Best Bone Marrow Transplant Doctors in India are highly skilled in complex transplant procedures, utilizing a patient-centered approach to ensure personalized care, precision, and dedicated follow-up support for long-term recovery.
Late-Onset Complications: What to Watch for Years After Transplant
Late-onset complications include chronic GVHD, secondary cancers, and endocrine disorders. Continuous monitoring helps detect these conditions early, facilitating timely intervention and better long-term management.
Improving Quality of Life Post-Bone Marrow Transplantation
Improving quality of life focuses on both physical and emotional recovery, including regular medical care, mental health support, and healthy lifestyle changes. Family and social support play a vital role in achieving a fulfilling life post-transplant.
FAQs About Recognizing Post-Surgery Complications in Bone Marrow Transplant Patients
What is Graft vs. Host Disease (GVHD) in bone marrow transplants?
GVHD is a condition where donor cells attack the recipient’s body, common in allogeneic transplants, affecting organs like skin and liver.
Why are infections common after bone marrow transplants?
Infections are frequent because the immune system is suppressed post-transplant, making patients more susceptible to bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
What are early complications after bone marrow transplants?
Early complications include infections, acute GVHD, and bleeding due to low blood cell counts.
How does the immune system impact post-transplant recovery?
A suppressed immune system prevents rejection but increases infection risk, so careful management of immune suppression is essential.
What are secondary cancers in bone marrow transplant recipients?
Secondary cancers, such as skin cancer and leukemia, can develop due to prior chemotherapy and radiation exposure.
Why might bone marrow transplants fail?
Transplants may fail due to graft rejection, infection, or disease relapse, requiring additional treatment.
How are bleeding disorders managed after a transplant?
Blood products and platelet monitoring help manage bleeding due to low platelet counts post-transplant.
What are long-term respiratory risks after bone marrow transplants?
Lung infections, fibrosis, and pulmonary complications may develop, requiring close monitoring for early treatment.
Are neurological issues common after a bone marrow transplant?
Cognitive changes, including memory loss and difficulty concentrating, can occur and often benefit from cognitive therapy.
What lifestyle changes improve post-transplant recovery?
Adopting a balanced diet, gradual exercise, and regular follow-ups enhance recovery and long-term health post-transplant.