Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD) is a significant complication that can arise following intestinal transplants. This condition occurs when the donor's immune cells recognize the recipient's tissues as foreign and mount an immune response against them. The severity of GVHD can vary, affecting the quality of life and overall outcomes for transplant recipients. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and management strategies is essential for both patients and healthcare providers involved in transplant care.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Pathophysiology of Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The pathophysiology of GVHD involves the activation of donor T-cells that attack the recipient's tissues. This immune response is primarily mediated by the recognition of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. In the case of intestine transplants, the intestinal mucosa is particularly vulnerable, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and malabsorption. Understanding this pathophysiological mechanism is crucial for developing targeted therapies and preventive strategies.
Risk Factors for Developing Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing GVHD after an intestine transplant. These include the degree of HLA mismatch between donor and recipient, the age of the recipient, and the presence of pre-existing conditions such as autoimmune diseases. Additionally, the use of certain immunosuppressive therapies can influence the risk. Identifying these factors can help clinicians personalize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
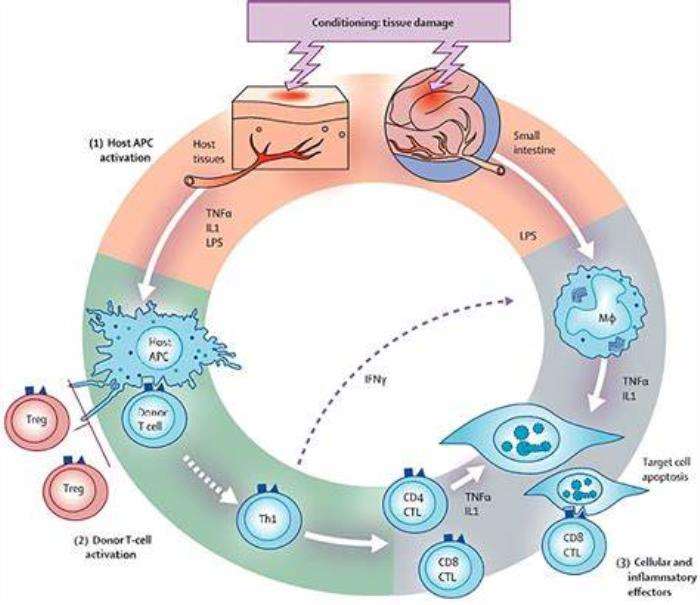
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations of Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The symptoms of GVHD can vary widely and may include gastrointestinal manifestations like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Extraintestinal symptoms may also occur, such as skin rashes, liver dysfunction, and respiratory issues. Early recognition of these clinical manifestations is vital for prompt intervention and management, which can significantly affect patient prognosis.
Diagnosis of Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Transplant Recipients
Diagnosing GVHD involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers typically assess the patient's history, symptoms, and perform physical examinations. Biopsy of affected tissues, particularly from the intestinal tract or skin, may provide definitive evidence of GVHD. Additionally, laboratory tests to evaluate liver function and other organ systems can help in assessing the severity of the disease.
Management Strategies for Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The management of GVHD primarily focuses on immunosuppression to mitigate the donor immune response. Commonly used therapies include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antimetabolites. In severe cases, more aggressive treatments such as extracorporeal photopheresis or biologic agents may be considered. The choice of therapy should be tailored to the individual patient's condition and response.
Preventive Measures Against Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Preventing GVHD is a critical aspect of post-transplant care. Strategies include careful donor-recipient matching to minimize HLA mismatches and the use of prophylactic immunosuppressive regimens. Regular monitoring for early signs of GVHD can facilitate timely intervention, potentially improving outcomes and reducing the severity of symptoms.
Role of Immunosuppressive Therapy in Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Immunosuppressive therapy plays a pivotal role in managing GVHD by dampening the immune response of the transplanted cells. Common agents include tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and sirolimus. The goal is to achieve a delicate balance between preventing GVHD and maintaining enough immune function to protect against infections. Regular monitoring of drug levels and side effects is essential for optimizing treatment.
Long-Term Outcomes for Patients with Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The long-term outcomes for patients who develop GVHD can vary significantly. Factors such as the extent of organ involvement, response to treatment, and overall health of the patient play a crucial role. Some patients may experience chronic symptoms that affect their quality of life, while others may achieve remission. Ongoing follow-up and supportive care are essential for managing long-term complications.
Psychosocial Impact of Graft-Versus-Host Disease
The psychosocial impact of GVHD on patients and their families can be profound. The chronic nature of the disease, coupled with its symptoms, can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, and depression. Supportive counseling and involvement in support groups can provide valuable resources for coping with the challenges associated with GVHD, enhancing the overall well-being of patients.
Research Advances in Graft-Versus-Host Disease Management
Recent research has focused on understanding the mechanisms of GVHD and developing novel therapeutic approaches. Advances in cellular therapies, such as regulatory T-cells, and new immunomodulatory agents show promise in reducing the incidence and severity of GVHD. Ongoing clinical trials are critical for evaluating the effectiveness and safety of these emerging therapies.
Importance of Multidisciplinary Care in Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Multidisciplinary care is essential for managing GVHD effectively. A team approach involving transplant surgeons, gastroenterologists, immunologists, and mental health professionals ensures comprehensive management of the condition. This collaborative model facilitates the integration of medical, nutritional, and psychological support, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
Role of Nutrition in Managing Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Nutrition plays a significant role in the management of GVHD. Patients may experience malabsorption and dietary restrictions due to gastrointestinal symptoms. A tailored nutrition plan that addresses individual dietary needs, along with nutritional supplementation, can help maintain body weight, support immune function, and improve overall health. Collaboration with a registered dietitian is beneficial for optimizing nutritional status.
Impact of Graft-Versus-Host Disease on Quality of Life
The impact of GVHD on a patient's quality of life can be substantial. Chronic symptoms can hinder daily activities and social interactions. Addressing these concerns through comprehensive care, including symptom management, psychological support, and lifestyle modifications, is crucial for improving the overall quality of life for affected individuals.
Potential Complications Associated with Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Complications arising from GVHD can include infections, organ dysfunction, and secondary malignancies. The immunosuppressive therapies used to manage GVHD can further predispose patients to infections. Regular monitoring and preventive measures, such as vaccinations and prophylactic antibiotics, are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure better health outcomes.
Future Directions in Graft-Versus-Host Disease Research
Future research in GVHD aims to enhance our understanding of its pathogenesis and improve treatment modalities. Investigating biomarkers for early detection, exploring novel immunotherapeutic agents, and developing personalized medicine approaches are critical areas of focus. These advancements could lead to improved prevention strategies and more effective management of GVHD in transplant recipients.
Educational Resources for Patients and Families Affected by Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Access to reliable educational resources is vital for patients and families affected by GVHD. Organizations such as the American Society of Hematology and National Marrow Donor Program provide valuable information on disease management, support networks, and coping strategies. Empowering patients with knowledge can enhance their ability to engage in their care and make informed decisions.
Understanding Intestine Transplantation for Complex Digestive Disorders
Gain insights into intestine transplantation as a solution for complex digestive disorders. Learn about its benefits, procedures, and success rates.
Clinical Trials and Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Participation in clinical trials offers patients access to cutting-edge therapies for managing GVHD. These trials are crucial for evaluating new treatments and improving existing protocols. Patients should discuss the potential benefits and risks of participating in clinical trials with their healthcare providers to make informed choices regarding their treatment options.
Best Intestine Transplant in India
The Best Intestine Transplant in India offers a vital treatment option for patients with severe intestinal failure, combining advanced surgical techniques and comprehensive post-transplant care.
Best Intestine Transplant Hospitals in India
The Best Intestine Transplant Hospitals in India are equipped with cutting-edge technology and multidisciplinary teams, ensuring seamless patient care and successful transplant outcomes.
Intestine Transplant Cost in India
The Intestine Transplant Cost in India is competitively priced, providing access to world-class treatment with transparent pricing and comprehensive care packages.
Best Intestine Transplant Surgeons in India
The Best Intestine Transplant Surgeons in India are highly skilled and experienced, ensuring precise surgical interventions and personalized patient care for optimal recovery and long-term success.
FAQs on Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Intestine Transplants
What causes Graft-Versus-Host Disease?
GVHD is caused by the donor's immune cells attacking the recipient's tissues, particularly when there is a mismatch in HLA antigens. This immune response can lead to various symptoms, primarily affecting the skin, liver, and gastrointestinal tract.
How is Graft-Versus-Host Disease treated?
Treatment for GVHD typically involves immunosuppressive medications such as corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antimetabolites. In severe cases, additional therapies like extracorporeal photopheresis may be utilized.
Can Graft-Versus-Host Disease be prevented?
While it may not be entirely preventable, the risk of GVHD can be reduced through careful donor-recipient matching and the use of prophylactic immunosuppressive regimens. Regular monitoring for early signs of GVHD is also crucial.
What is the prognosis for patients with Graft-Versus-Host Disease?
The prognosis for patients with GVHD varies based on the severity of the disease and the response to treatment. Some patients may achieve remission, while others may experience chronic symptoms that require ongoing management.
Updated for 2025 – Discover the best hospitals in India for intestine transplant procedures, including top choices, advanced techniques, and cost-effective options. Intestine Transplant Cost in India
Discover the best hospitals in India for intestine transplant procedures, including top choices, advanced techniques, and cost-effective options. Intestine Transplant in India
Explore the latest alternatives to intestine transplantation, including innovative therapies, emerging treatments, and patient success stories. Discover how advancements in medical science are providing new hope for managing intestinal disorders without the need for transplantation. Intestine Transplant Alternatives: Emerging Therapies and Innovations