Reconstruction Surgery After Oral Cancer in India
Reconstruction surgery after oral cancer is crucial for restoring function and appearance following tumor removal. The specific options and outcomes can vary based on the extent of the cancer, the location within the oral cavity, and individual patient factors. Facial reconstructive surgery addresses deformities resulting from trauma, tumor removal, congenital conditions like cleft lip and palate, and craniofacial anomalies. These deformities can profoundly impact psychological well-being due to the face's prominence in social interactions. Reconstructive surgery restores function and aesthetics, boosting confidence by correcting abnormal facial structures. Here are some key points:
Learn more about Best Oral or Mouth Cancer Treatment in India
Options for Reconstruction Surgery after Oral or Mouth Cancer in India:
- Primary Closure: In cases where the defect is small, the surgeon may be able to close the wound directly. This is often possible for small lesions or early-stage cancers.
- Local Flaps (Rhomboid Flap): Tissue adjacent to the defect is mobilized and rotated or moved to cover the surgical site. Local flaps are useful for moderate-sized defects and help maintain vascular supply. Known more in detail.
- Regional Flaps (Melolabial Flap or nasolabial flap): Tissue is taken from a nearby area with a common blood supply to reconstruct larger defects. Examples include the nasolabial flap (cheek) or temporalis muscle flap.Known more in detail.
- Microvascular Free Tissue Transfer: In cases of extensive defects, tissue is harvested from distant sites (often from the forearm, leg, or abdomen) along with its blood supply (artery and vein) and transferred to the oral cavity. This is complex but offers excellent functional and cosmetic outcomes. Known more in detail.
Reconstruction Surgery based Hospital, Cost and Success Rate in India
| Type of Reconstruction Surgery |
Approximate Cost (INR) |
Hospitals (Delhi) |
Doctors (Delhi) |
Hospitals (Mumbai) |
Doctors (Mumbai) |
Success Rate (%) |
| Primary Closure |
1,50,000 - 2,50,000 |
AIIMS, Delhi
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Alok Thakar, Dr. Anil Agarwal
Dr. T. Raja, Dr. M. G. Bhat
Dr. Amit Javed, Dr. Sanjay Gupta
|
Tata Memorial Hospital
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Pankaj Chaturvedi, Dr. Anil D'Cruz
Dr. Sanjay Sharma, Dr. Hemant Malhotra
Dr. Vishal Rao, Dr. Bharat Shah
|
95-98% |
| Local Flaps (Rhomboid Flap) |
2,00,000 - 3,50,000 |
AIIMS, Delhi
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Alok Thakar, Dr. Anil Agarwal
Dr. T. Raja, Dr. M. G. Bhat
Dr. Amit Javed, Dr. Sanjay Gupta
|
Tata Memorial Hospital
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Pankaj Chaturvedi, Dr. Anil D'Cruz
Dr. Sanjay Sharma, Dr. Hemant Malhotra
Dr. Vishal Rao, Dr. Bharat Shah
|
90-95% |
| Regional Flaps (Melolabial Flap) |
2,50,000 - 4,00,000 |
AIIMS, Delhi
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Alok Thakar, Dr. Anil Agarwal
Dr. T. Raja, Dr. M. G. Bhat
Dr. Amit Javed, Dr. Sanjay Gupta
|
Tata Memorial Hospital
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Pankaj Chaturvedi, Dr. Anil D'Cruz
Dr. Sanjay Sharma, Dr. Hemant Malhotra
Dr. Vishal Rao, Dr. Bharat Shah
|
85-90% |
| Microvascular Free Tissue Transfer |
3,50,000 - 5,00,000 |
AIIMS, Delhi
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Alok Thakar, Dr. Anil Agarwal
Dr. T. Raja, Dr. M. G. Bhat
Dr. Amit Javed, Dr. Sanjay Gupta
|
Tata Memorial Hospital
Apollo Hospitals
Fortis Healthcare
|
Dr. Pankaj Chaturvedi, Dr. Anil D'Cruz
Dr. Sanjay Sharma, Dr. Hemant Malhotra
Dr. Vishal Rao, Dr. Bharat Shah
|
80-90% |
Outcomes and Considerations:
- Functionality: Reconstruction aims to restore speech, swallowing, and chewing functions. The choice of reconstruction method affects outcomes; for example, free tissue transfer can provide better functional results compared to local flaps for large defects.
- Cosmesis: Reconstruction also focuses on restoring facial aesthetics and minimizing disfigurement. Surgeons aim to achieve symmetry and natural contours to the extent possible.
- Complications: Potential risks include infection, flap failure (particularly with free tissue transfer), and impaired wound healing. Close post-operative monitoring and care are crucial.
- Rehabilitation: Patients often require speech therapy and physiotherapy post-surgery to regain optimal function.
- Long-term Monitoring: Regular follow-up is essential to monitor for cancer recurrence and to address any long-term functional or cosmetic concerns.
Decision-making Process:
The choice of reconstruction method is individualized based on factors such as:
- Size and location of the defect
- Patient's overall health and ability to tolerate surgery
- Patient preferences regarding cosmetic outcomes and recovery time
Prognosis:
- Early detection and treatment generally lead to better outcomes.
- The success of reconstruction depends on the surgeon's expertise, the extent of the cancer, and the patient's response to treatment.
Facial Reconstructive Surgery in India
Facial reconstructive surgery addresses deformities resulting from trauma, tumor removal, congenital conditions like cleft lip and palate, and craniofacial anomalies. These deformities can profoundly impact psychological well-being due to the face's prominence in social interactions. Reconstructive surgery restores function and aesthetics, boosting confidence by correcting abnormal facial structures.
Reconstructive Jaw Surgery in India
In India, Performed by Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, reconstructive jaw surgery corrects skeletal and dental irregularities such as jaw misalignment. It improves chewing, speaking, and breathing. For patients missing parts of the jaw after tumor removal, techniques like bone grafts from the patient, deceased donors, or advanced growth factor applications (stem cells, platelet-rich plasma, bone morphogenetic protein) are utilized.
Reconstructive Surgery for Cleft Lip and Palate in India
In India, Reconstructive surgery is critical for aesthetic enhancement and functional restoration in individuals with cleft lip and palate. Early intervention, starting from three months for cleft lip and between seven to eighteen months for cleft palate, addresses speech and feeding difficulties. As patients mature, additional procedures like orthognathic surgery, upper lip plasty, rhinoplasty, and orthodontic treatments correct remaining deformities.
Reconstructive Surgery After Skin Cancer Removal in India
In India, Skin cancer on the face, nose, lips, and ears often requires wide tissue excision, occasionally necessitating organ removal. Reconstruction aims to restore appearance and function, employing local or distant tissues like bone and cartilage. Multiple surgeries may be necessary for optimal results, highlighting the importance of a skilled maxillofacial surgeon.
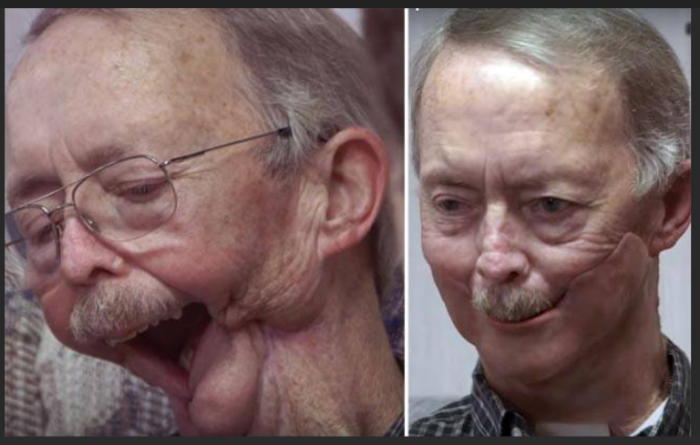
Reconstruction Surgery After Oral Cancer Using Rhomboid Flap
Reconstruction surgery after oral or mouth cancer is vital for restoring functionality and aesthetics following tumor removal. The rhomboid flap, also known as the Limberg flap, is one of the versatile local flaps used in this context. It is especially useful for covering defects in the head and neck region, including the oral cavity.
Key Features and Procedure
Design
The rhomboid flap is designed as a parallelogram with angles typically of 60 and 120 degrees. This shape allows for an optimal tension-free closure of the defect.
Procedure
- Incision: A rhomboid-shaped incision is made around the defect left after tumor removal.
- Flap Outline: An adjacent area of healthy skin is outlined with a similar rhomboid shape.
- Elevation and Transposition: The flap is elevated and transposed to cover the defect, maintaining its blood supply.
- Closure: The donor site, where the flap was harvested, is closed primarily without significant tension, minimizing the risk of necrosis or wound dehiscence.
Applications in Oral Cancer Reconstruction
- Defect Coverage: Effective for covering defects in the oral cavity resulting from the excision of cancerous tissues.
- Versatility: Can be adapted to various sizes and locations within the oral cavity, making it suitable for different types of defects.
Advantages
- Reliable Blood Supply: Due to the short pedicle and local tissue use, the flap maintains a robust blood supply, essential for healing.
- Aesthetic Outcomes: Provides good cosmetic results with minimal distortion of surrounding tissues.
- Functionality: Helps restore the structure and function of the oral cavity, crucial for speech, chewing, and swallowing.
Considerations and Limitations
- Tissue Match: Best suited for areas where the donor site's skin matches the defect site in color, texture, and thickness.
- Tension-Free Closure: Ensuring a tension-free closure is critical to prevent complications.
- Donor Site Scar: The donor site will have a scar, which should be considered, especially in aesthetically sensitive areas.
Melolabial Flap Oral or Mouth Cavity Reconstruction
The melolabial flap, also known as the nasolabial flap, is a reliable and versatile option for reconstructing defects in the oral cavity, particularly after tumor resection. This flap is based on the rich vascular supply from the facial artery and its branches, making it a dependable choice for head and neck reconstruction.
Key Features and Procedure
Design and Anatomy
- Location: The melolabial flap is harvested from the nasolabial fold, an area extending from the side of the nose to the corner of the mouth.
- Vascular Supply: It relies on the branches of the facial artery, providing a robust blood supply essential for healing and graft viability.
Procedure
- Incision and Flap Design: The incision is designed along the nasolabial fold, which allows for optimal aesthetic outcomes as the scar blends into the natural crease of the face.
- Flap Elevation: The flap is elevated, ensuring the inclusion of sufficient subcutaneous tissue to maintain vascular integrity.
- Transposition: The flap is then transposed to cover the defect in the oral cavity. This can involve simple advancement, rotation, or interpolation depending on the defect's size and location.
- Donor Site Closure: The donor site is closed primarily, often resulting in a cosmetically acceptable scar due to its location along a natural facial crease.
Applications in Oral Cavity Reconstruction
- Small to Medium Defects: Ideal for reconstructing small to medium-sized defects within the oral cavity, particularly those affecting the lip, floor of the mouth, and buccal mucosa.
- Versatility: Can be used for both intraoral and perioral defects, making it a versatile option in head and neck reconstructive surgery.
Advantages
- Reliable Blood Supply: The rich vascular network of the facial artery ensures a high success rate for flap survival.
- Cosmetic Outcomes: The scar is well-hidden within the nasolabial fold, leading to favorable aesthetic results.
- Functionality: The flap provides good tissue match in terms of color and texture, crucial for restoring both appearance and function in the oral cavity.
Considerations and Limitations
- Size of Defect: Best suited for small to medium defects; larger defects may require alternative or additional reconstruction techniques.
- Donor Site Morbidity: Generally minimal, but careful surgical technique is required to ensure optimal cosmetic results.
- Patient Factors: Factors such as skin elasticity and patient age can affect the outcome and should be considered during planning.
Microvascular Free Tissue Transfer in Oral or Mouth Cancer Reconstruction
Microvascular free tissue transfer, also known as free flap surgery, is a highly specialized technique used in reconstructive surgery following oral cancer removal. This method involves the transplantation of tissue from one part of the body to another, along with its blood supply, to reconstruct defects caused by the excision of oral cancer.
Donor Sites and Tissue Types
- Common Donor Sites: Radial forearm, fibula, iliac crest, and anterolateral thigh are commonly used donor sites. Each site offers different types of tissue (skin, muscle, bone) that can be used based on the reconstruction needs.
- Types of Tissue: Includes bone, skin, muscle, and fat. The choice depends on the defect’s size, location, and the required tissue type for optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes.
Procedure
- Harvesting the Flap: The chosen tissue is carefully harvested along with its supplying artery and vein. This ensures the flap has a good blood supply.
- Preparation of the Recipient Site: The defect area in the oral cavity is prepared to receive the flap. Blood vessels in this area are identified and prepared for anastomosis (connection).
- Microvascular Anastomosis: The surgeon connects the flap’s blood vessels to those at the recipient site under a microscope. This intricate step ensures the flap receives adequate blood supply.
- Shaping and Insetting the Flap: The flap is shaped to fit the defect and secured in place. This may involve some reshaping of the bone or adjustment of the soft tissue for optimal results.
- Closure: The donor site is closed, often using a skin graft if necessary, and the recipient site is monitored for proper blood flow and healing.
Applications in Oral Cancer Reconstruction
- Jaw Reconstruction: Particularly useful in reconstructing the mandible or maxilla after resection. The fibula flap is often used for its strength and ability to be shaped to match the jawbone.
- Tongue and Floor of Mouth: Radial forearm flap is preferred due to its thin, pliable skin, which is ideal for intraoral reconstruction.
- Cheek and Palate: Anterolateral thigh flap provides ample soft tissue for larger defects.
Advantages
- Versatility: Ability to transfer various tissue types (bone, skin, muscle, and fat) tailored to the specific defect.
- Functional Restoration: Enhances functional outcomes like speech, swallowing, and chewing.
- Aesthetic Results: Provides better cosmetic outcomes, preserving facial contours and appearance.
- Reliable Vascular Supply: High success rate due to the robust blood supply ensured by microvascular anastomosis.
Considerations and Limitations
- Technical Expertise: Requires skilled microvascular surgeons due to the complexity of the procedure.
- Operative Time: Longer surgery duration compared to local flap techniques.
- Postoperative Care: Intensive monitoring post-surgery to ensure flap viability and manage complications such as flap failure or infection.
- Patient Factors: Overall health, comorbidities, and ability to tolerate a lengthy surgical procedure must be considered.
Discover the Best Oncologists and Cancer Hospitals in India
When it comes to cancer treatment, finding the right specialist and hospital can make a significant difference in the outcome. In this blog, we have compiled a list of the top oncologists and cancer hospitals across major cities in India, ensuring that you have access to the best care available.
Top Oncologists in Major Cities
For those seeking expert oncologists, we have identified the best specialists in key cities:
Leading Cancer Hospitals
In addition to finding the right specialist, choosing the right hospital is crucial for comprehensive cancer care. Here are the top hospitals in major cities:
Get more indepth information on Cancer treatments and their costs
Conclusion
Finding the right oncologist and hospital is the first step in your cancer treatment journey. Explore the links above to learn more about the top specialists and hospitals in your area.