Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tools for Oral Cancer Detection
Non-invasive diagnostic tools for detecting oral cancer have seen significant advancements, offering potential for early detection and improved patient outcomes.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Here are some of the most promising methods:
Salivary Biomarkers
Salivary diagnostics involve analyzing specific biomarkers present in saliva, which can indicate the presence of oral cancer. Key salivary biomarkers include:
- Cytokines: Proteins such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) are linked to oral cancer. Elevated levels in saliva can indicate cancerous changes.
- Proteins: Biomarkers like cancer antigen 125 (CA125), cytokeratin 19 fragment (Cyfra 21-1), and tissue polypeptide antigen have shown increased levels in patients with oral cancer.
- Genetic Markers: Genetic alterations, such as hypermethylation of the NID2 and HOXA9 promoters and mutations in genes like CUL3 and ZFP36L2, can be detected using PCR and next-generation sequencing (NGS).
Liquid Biopsy
Liquid Biopsy
Liquid biopsy techniques, particularly those involving the analysis of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in saliva, are emerging as a powerful tool for oral cancer detection. EVs can carry biomarkers such as RNA, proteins, and metabolites that reflect the disease state. Techniques include ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, and microfluidics.
Light-Based Diagnostic Tools for Oral Cancer Detection
Light-based diagnostic tools for detecting oral cancer offer non-invasive, real-time solutions for identifying cancerous and precancerous lesions. Here are some of the primary techniques used:
Autofluorescence Imaging
Autofluorescence imaging detects changes in the natural fluorescence emitted by tissues when exposed to specific wavelengths of light. Healthy tissues and cancerous tissues fluoresce differently, allowing for the identification of abnormal areas.
- Procedure: The oral cavity is exposed to blue or violet light. Healthy tissues emit a green autofluorescence, while dysplastic or cancerous tissues appear dark or maroon due to altered fluorescence properties.
- Advantages: Non-invasive, real-time detection, enhances visualization of early-stage lesions.
- Limitations: False positives can occur due to inflammation or other benign conditions.
Narrow Band Imaging (NBI)
Narrow Band Imaging enhances the visualization of mucosal structures and blood vessels by using specific light wavelengths (blue and green).
- Procedure: Uses a special filter to narrow the light spectrum, enhancing the contrast between blood vessels and surrounding tissues. Abnormal vasculature associated with cancer can be more easily identified.
- Advantages: Enhanced detection of vascular changes, non-invasive, improves visualization of subtle lesions.
- Limitations: Requires specialized equipment, may not distinguish all types of lesions.
Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS)
Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy measures the light reflected by tissues to detect changes in tissue composition and structure.
- Procedure: A light source illuminates the tissue, and a sensor measures the reflected light. Differences in reflectance spectra can indicate the presence of abnormal tissues.
- Advantages: Non-invasive, quantitative analysis, can detect biochemical and morphological changes.
- Limitations: Interpretation of results can be complex, affected by tissue heterogeneity.
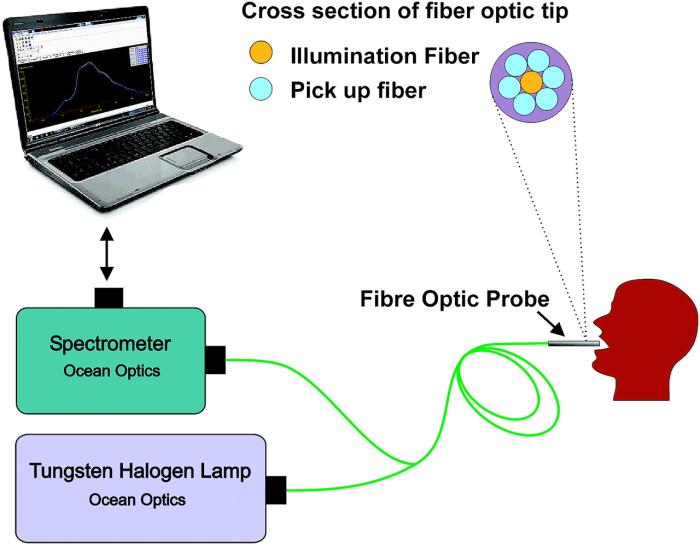
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman Spectroscopy utilizes the scattering of light to provide a molecular fingerprint of tissues, identifying cancerous changes.
- Procedure: A laser light is directed at the tissue, and the scattered light is analyzed to identify specific molecular vibrations indicative of cancerous changes.
- Advantages: High specificity, non-invasive, can provide detailed molecular information.
- Limitations: Requires sophisticated equipment, time-consuming data analysis.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of tissues using light waves.
- Procedure: Light waves are directed at the tissue, and the reflected light is used to create detailed images of tissue structures up to a few millimeters in depth.
- Advantages: High-resolution images, non-invasive, useful for assessing tissue architecture.
- Limitations: Limited depth of penetration, requires specialized equipment.
Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging (FLIM)
Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging measures the decay time of fluorescence from tissues to differentiate between normal and abnormal tissues.
- Procedure: Tissues are excited with a laser, and the time it takes for the fluorescence to decay is measured. Cancerous tissues often have different fluorescence lifetimes compared to normal tissues.
- Advantages: Non-invasive, provides additional contrast based on fluorescence decay properties.
- Limitations: Requires specialized equipment, can be affected by various tissue factors.
Known more about Cost of Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tools for Oral Cancer Detection
Molecular Techniques
Molecular diagnostics involve analyzing genetic and epigenetic changes associated with oral cancer. These techniques include:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): Used to amplify and detect specific DNA sequences associated with oral cancer.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Allows for comprehensive genome analysis, identifying multiple genetic mutations and alterations that contribute to cancer development.
Clinical Utility and Future Prospects
The integration of these non-invasive diagnostic tools into clinical practice holds great promise for improving the early detection and management of oral cancer. Salivary diagnostics, liquid biopsies, advanced imaging, and molecular techniques provide complementary approaches that can be used together to increase diagnostic accuracy and reduce the need for invasive procedures. Regular advancements in these technologies and further research will continue to enhance their sensitivity, specificity, and overall clinical utility.
Discover the Best Oncologists and Cancer Hospitals in India
When it comes to cancer treatment, finding the right specialist and hospital can make a significant difference in the outcome. In this blog, we have compiled a list of the top oncologists and cancer hospitals across major cities in India, ensuring that you have access to the best care available.
Top Oncologists in Major Cities
For those seeking expert oncologists, we have identified the best specialists in key cities:
Leading Cancer Hospitals
In addition to finding the right specialist, choosing the right hospital is crucial for comprehensive cancer care. Here are the top hospitals in major cities:
Get more indepth information on Cancer treatments and their costs
Conclusion
Finding the right oncologist and hospital is the first step in your cancer treatment journey. Explore the links above to learn more about the top specialists and hospitals in your area.