Pacemakers are sophisticated devices designed to manage abnormal heart rhythms, ensuring the heart beats consistently and efficiently. They come in two primary types: external and implantable. Each type serves specific medical needs and offers distinct features. Understanding the technology behind these devices helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options tailored to individual heart conditions.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
What Are External Pacemakers?
External pacemakers are temporary devices used to regulate heart rhythms in critical situations. They are placed outside the body and connected to the heart using wires threaded through a vein or attached directly during surgery. These pacemakers are typically used in hospitals for short-term purposes, such as stabilizing patients after surgery or during emergencies, until a permanent solution can be implemented.
What Are Implantable Pacemakers?
Implantable pacemakers are long-term devices surgically placed under the skin, usually near the collarbone. These devices continuously monitor and regulate the heart’s rhythm, delivering electrical impulses as needed. Implantable pacemakers are designed to treat chronic conditions like bradycardia or heart block, providing a durable solution that restores normal heart function and significantly improves quality of life.
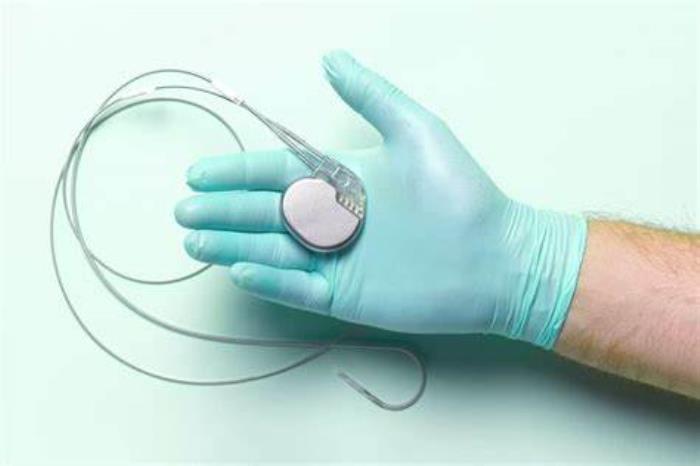
Key Functions of External vs. Implantable Pacemakers
While both types of pacemakers serve to regulate heart rhythms, their functions differ based on the patient’s needs. External pacemakers provide immediate, short-term pacing, often in critical care settings, with adjustments made by medical staff. Implantable pacemakers, on the other hand, are programmed to autonomously detect and correct arrhythmias over an extended period, requiring minimal patient involvement after implantation.
When Is an External Pacemaker Recommended?
External pacemakers are recommended in situations requiring temporary heart rhythm management. These include acute arrhythmias, post-operative stabilization, or as a bridge to permanent pacemaker implantation. They are also used during diagnostic procedures to evaluate the heart’s response to pacing and in emergencies when immediate intervention is necessary.
When Is an Implantable Pacemaker Necessary?
Implantable pacemakers are necessary for individuals with chronic heart rhythm disorders, such as persistent bradycardia, tachy-brady syndrome, or advanced atrioventricular block. They are also indicated for patients at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. Implantable pacemakers provide a reliable, long-term solution to maintain heart function and prevent complications like fainting, fatigue, or heart failure.
Differences in Power Sources and Battery Life
External pacemakers are powered by external batteries that can be replaced as needed, making them suitable for temporary use. Implantable pacemakers, however, rely on internal batteries with a lifespan of 5 to 15 years, depending on the device's usage and settings. When the battery depletes, a minor surgical procedure is required to replace the pacemaker generator, ensuring uninterrupted functionality. This distinction highlights the adaptability of each device to specific clinical needs.
Placement and Installation: External vs. Implantable
External pacemakers are typically placed outside the body and connected to the heart via wires, often used temporarily after surgery or during emergencies. Implantable pacemakers, on the other hand, are surgically inserted under the skin and connected to the heart with leads, designed for long-term use to manage chronic arrhythmias.
Comparing the Durability of External and Implantable Pacemakers
Implantable pacemakers are built for longevity, often lasting 5–15 years before requiring battery replacement. External pacemakers, however, are intended for short-term use and may not offer the same durability or reliability in long-term scenarios.
The Role of External Pacemakers in Temporary Cardiac Support
External pacemakers are critical in temporary cardiac support, such as after surgery, during acute arrhythmias, or in emergency cases where long-term implantation is not immediately feasible. They provide a bridge until the patient stabilizes or an implantable device can be installed.
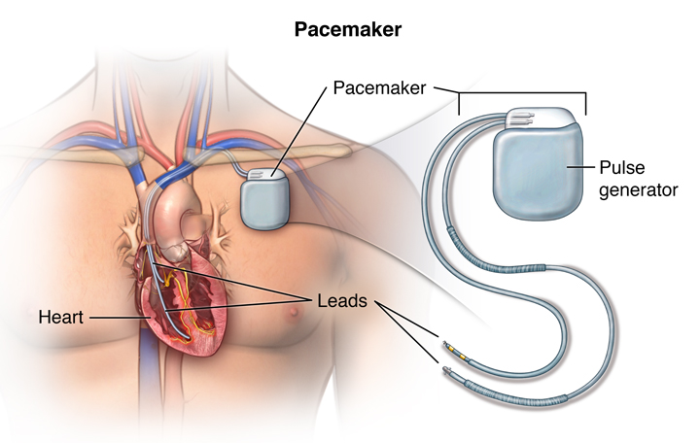
Longevity and Maintenance of Implantable Pacemakers
Implantable pacemakers require periodic monitoring to ensure proper function and battery health. While the device itself is durable, leads may occasionally need replacement due to wear or complications.
Patient Comfort: External vs. Implantable Devices
Implantable pacemakers are generally more comfortable for patients in the long run, as they are hidden under the skin and do not interfere with daily activities. External pacemakers can be cumbersome, as they involve visible wires and require careful handling to avoid disconnection or infection.
Cost Differences Between External and Implantable Pacemakers
External pacemakers tend to have lower upfront costs but may become expensive if used over an extended period. Implantable pacemakers involve higher initial expenses, including surgery, but are more cost-effective for long-term cardiac management.
Advantages of Implantable Pacemakers for Long-Term Care
Implantable pacemakers provide consistent and reliable heart rhythm management, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient quality of life. They also eliminate the need for frequent adjustments and the inconvenience of external devices.
Risks and Complications Associated with External Pacemakers
External pacemakers carry risks such as infection at the connection sites, wire dislodgement, and interference with mobility. Prolonged use increases the likelihood of complications and discomfort for the patient.
Risks and Complications Associated with Implantable Pacemakers
Implantable pacemakers come with surgical risks, such as infection, bleeding, or lead displacement. Over time, the device or its leads may require replacement, posing additional procedural risks.
Advances in Technology for Both Types of Pacemakers
Modern external pacemakers are more compact and efficient, while implantable pacemakers feature innovations like MRI compatibility, wireless connectivity, and improved battery life. These advancements enhance safety and convenience for both types of devices.
How to Choose Between External and Implantable Options
The choice between external and implantable pacemakers depends on the patient’s condition, the duration of required pacing, and the associated risks. Doctors typically recommend external pacemakers for temporary use and implantable devices for chronic conditions requiring long-term management.
Pacemaker Maintenance: How Often Should You Get Checked?
Find out how often to get your pacemaker checked and the importance of regular maintenance to ensure proper function and avoid complications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Pacemaker for Your Needs
Choosing between an external and implantable pacemaker involves evaluating factors such as the condition's duration, patient lifestyle, and overall health. Consulting with a cardiac specialist is crucial to making an informed decision that optimizes heart health and quality of life.
Best Pacemaker Implantation Surgery in India
The Best Pacemaker Implantation Surgery in India offers a life-saving solution for patients with irregular heartbeats, helping to regulate heart rhythm and improve overall health.
Best Pacemaker Implantation Surgeons in India
The Best Pacemaker Implantation Surgeons in India are experienced in cardiac device implantation, delivering personalized care to help patients manage heart rhythm issues effectively.
FAQ
What are the main differences between external and implantable pacemakers?
External pacemakers are temporary devices used outside the body, while implantable pacemakers are permanent devices placed under the skin for long-term rhythm management.
Are external pacemakers only for temporary use?
Yes, external pacemakers are typically used for short-term support during emergencies or recovery after surgery.
How long can an implantable pacemaker last before replacement is needed?
Implantable pacemakers usually last 5–15 years, depending on the battery life and frequency of use.
What are the risks of using an external pacemaker for an extended period?
Prolonged use of external pacemakers increases the risk of infection, wire dislodgement, and limited patient mobility.
Which type of pacemaker is more cost-effective in the long run?
Implantable pacemakers are generally more cost-effective for long-term management of heart rhythm disorders due to their durability and reliability.
Explore the Best Heart Care Resources in India
Find some of the top cardiologist, surgeons and the best heart hospitals in India
Best Heart Hospitals in India
Choosing the right hospital is crucial for successful heart treatments. If you want to explore trusted options, check the list of Best Heart Hospitals in India offering world-class facilities, advanced cardiac care units, and experienced teams for both simple and complex procedures.
Best Cardiologists in India
Finding the right cardiologist can make a huge difference in early diagnosis and long-term heart health. If you are looking for the Best Cardiologists in India, see this curated list of experts who specialize in preventive care, interventional cardiology, and complex heart disease management. Check the full list Best Cardiologists in India.
Best Cardiac Surgeons in India
If you are planning for heart surgery and need top-level expertise, we recommend exploring the Best Cardiac Surgeons in India. These surgeons have a proven record in performing bypass surgeries, valve replacements, and minimally invasive heart operations with excellent outcomes.
Get more indepth information on Cardiology treatments and their costs.
Conclusion
Your cardiology health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top cardiac hospitals and cardiac surgeons in India.
Updated for 2025 – Discover the best hospitals in India for pacemaker implantation surgery, including top choices, advanced techniques, and cost-effective options. Pacemaker Implantation Surgery Cost in India
Discover the best hospitals in India for pacemaker implantation surgery, including top choices, advanced techniques, and cost-effective options. Best Pacemaker Implantation Surgery Hospitals in India
Heart rhythm disorders, or arrhythmias, can necessitate the use of a pacemaker to help regulate the heartbeat. Common causes include conditions such as bradycardia, where the heart rate is too slow, heart block, which occurs when electrical signals are partially or completely blocked, and atrial fibrillation (AFib), an irregular heart rate leading to poor blood flow. Other causes include sick sinus syndrome, malfunctions of the heart’s natural pacemaker, congenital heart defects affecting the heart's electrical system, and recovery after cardiac arrest. These conditions can be influenced by factors such as heart disease, aging, medications, and genetic predispositions. Causes of Heart Rhythm Disorders That May Require a Pacemaker