Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart condition that affects the normal circulation of blood in a newborn. It occurs when the ductus arteriosus, a temporary fetal blood vessel connecting the pulmonary artery to the aorta, fails to close after birth. PDA can lead to various health complications, particularly affecting the heart and lungs, if left untreated. Understanding PDA is essential for recognizing early signs, managing symptoms, and determining the most appropriate course of treatment.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
What Is Patent Ductus Arteriosus? An Overview
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is an abnormal persistence of the ductus arteriosus, which normally closes soon after birth. This ductus arteriosus is a necessary part of fetal circulation, allowing blood to bypass the lungs, as oxygenation occurs through the placenta. When PDA persists, however, oxygen-rich blood from the aorta can flow back into the pulmonary artery, overloading the lungs and heart. This condition can vary in severity, from being relatively asymptomatic to causing significant health issues that may require medical or surgical intervention.
Normal Fetal Circulation and the Role of the Ductus Arteriosus
In fetal development, the ductus arteriosus plays a critical role by allowing most of the blood from the heart’s right ventricle to bypass the lungs and flow directly into the aorta. Since the fetus does not breathe air, the lungs are not used for oxygenation, and this bypass aids efficient circulation through the placenta. Normally, after birth, this vessel closes within a few days as the newborn begins to breathe independently, redirecting blood flow to the lungs for oxygen exchange.
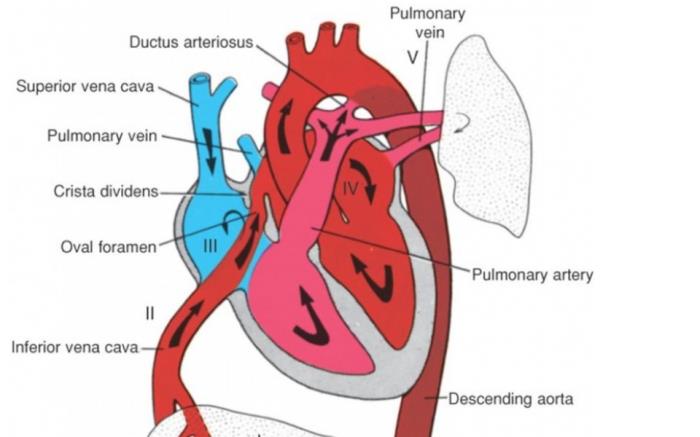
How PDA Occurs: Failure of Ductus Arteriosus Closure
PDA occurs when the ductus arteriosus fails to close naturally after birth, resulting in a persistent open channel between the aorta and pulmonary artery. This incomplete closure causes a left-to-right shunt, where oxygenated blood flows back into the lungs rather than moving through the body, leading to excessive blood flow to the lungs. This ongoing circulation imbalance can strain the heart and increase pulmonary blood pressure, potentially leading to respiratory distress, growth delays, and heart complications.
Key Factors Contributing to PDA Development
The development of PDA is influenced by several factors, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental and physiological conditions. While the exact cause of PDA is not always clear, research suggests that a combination of factors may increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Understanding these factors helps in identifying at-risk newborns and implementing early monitoring and intervention if needed.
Genetic Predisposition: Hereditary Links to PDA
Genetics play a significant role in the likelihood of developing PDA. Children with a family history of congenital heart defects are more susceptible to PDA, suggesting a hereditary component to the condition. Additionally, certain genetic syndromes, like Down syndrome, are associated with a higher incidence of PDA. Genetic counseling and early screening can help families with a history of congenital heart conditions take proactive steps in monitoring newborn heart health.
Prematurity as a Major Risk Factor for PDA
Prematurity is one of the most significant risk factors for PDA. Babies born before full term (before 37 weeks) are more likely to have PDA, as their underdeveloped bodies may struggle to prompt the natural closure of the ductus arteriosus. This is particularly common in very premature infants, whose circulatory systems are not yet fully mature. Premature infants with PDA often require specialized medical care and may benefit from pharmacological or interventional treatments to promote ductus arteriosus closure, helping to avoid complications associated with the condition.
Maternal Health Conditions and Their Influence on PDA
Maternal health during pregnancy can significantly affect the likelihood of congenital heart conditions, including patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Conditions like diabetes or rubella can increase the risk of PDA in infants. Monitoring and managing maternal health conditions are crucial steps in minimizing the risk of PDA.
The Impact of Maternal Infections During Pregnancy
Infections contracted during pregnancy, particularly rubella, can contribute to the development of PDA. Such infections affect fetal development, especially in the early weeks, and increase the likelihood of heart defects. Preventing infections through vaccinations and hygiene practices can help reduce these risks.
Environmental Factors: Exposure Risks Leading to PDA
Environmental factors, such as exposure to harmful chemicals or drugs during pregnancy, may increase the risk of PDA. Smoking, alcohol consumption, or exposure to environmental toxins can affect fetal heart development. Avoiding such risk factors is important for promoting healthy prenatal development.
Gender Differences: Why PDA Is More Common in Females
PDA is more frequently observed in female infants than in male infants. The exact cause of this gender difference is not entirely understood, but hormonal or genetic factors may play a role. Recognizing this increased risk can help healthcare providers take additional screening precautions for female infants.
Low Birth Weight and Its Connection to PDA
Low birth weight, often associated with premature birth, is closely linked to an increased risk of PDA. Premature infants are more likely to have underdeveloped cardiovascular systems, making it harder for the ductus arteriosus to close naturally. Careful monitoring of low-birth-weight infants can help identify PDA early.
Link Between High Altitudes and PDA Incidence
High-altitude environments may contribute to an increased incidence of PDA. The reduced oxygen levels at high altitudes can impact fetal development, potentially affecting the closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth. Families living at high altitudes may consider consulting healthcare providers for additional screening if PDA risk is a concern.
The Role of Prostaglandins in PDA Development
Prostaglandins are chemicals that help maintain the openness of the ductus arteriosus in the womb. After birth, prostaglandin levels decrease, leading to the natural closure of the ductus arteriosus. In some cases, high prostaglandin levels post-birth prevent closure, resulting in PDA. Understanding prostaglandin roles can aid in medical approaches to manage PDA.
Diagnosing PDA: Early Signs and Screening Tests
PDA can be diagnosed through routine screening, often before symptoms even arise. Diagnostic methods include echocardiograms and chest X-rays. Recognizing early signs, like rapid breathing or difficulty feeding, and conducting timely screening are key to managing PDA effectively.
Long-Term Complications If PDA Is Left Untreated
If left untreated, PDA can lead to serious complications, such as heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and even growth delays. Early treatment minimizes these risks and improves the quality of life for children with PDA. Timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent these potential long-term health challenges.
Common Misconceptions About the Causes of PDA
Many misconceptions surround the causes of PDA, such as believing it is solely hereditary or only affects premature infants. While genetics and prematurity are risk factors, other variables like environmental exposure, maternal health, and altitude also contribute to PDA risk. Awareness of these diverse causes helps clarify the condition.
How Early Detection and Intervention Can Help
Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for managing PDA and preventing complications. Treatments range from medication to surgical options, depending on the severity of PDA. Addressing the condition early allows for more effective treatment and better overall outcomes.
Preventive Measures for At-Risk Infants
For infants at higher risk of PDA, preventive measures include regular monitoring and healthy prenatal practices. Healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle adjustments for expecting mothers, such as avoiding smoking and alcohol and getting vaccinated against infections that increase PDA risk.
Post-Surgery Recovery Time for Patent Ductus Arteriosus Device Closure
Understand the recovery time after PDA device closure. This section details the expected duration for healing, factors influencing recovery, and the importance of follow-up care to ensure optimal results after the procedure.
The Role of Pediatric Cardiology in Managing Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Learn about the significant role pediatric cardiologists play in the diagnosis and management of PDA. This section covers the specific expertise required for treating this condition in infants and children and highlights the importance of early intervention.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing PDA Causes
Understanding the diverse causes and risk factors of PDA is essential for effective prevention, early detection, and treatment. Maternal health, environmental exposure, genetics, and birth conditions all play a role in PDA development. By addressing these factors, families and healthcare providers can work together to manage PDA proactively.
Best PDA Device Closure in India
The Best PDA Device Closure in India offers a minimally invasive solution to close the patent ductus arteriosus, helping prevent complications and improve heart function in affected patients.
Best PDA Device Closure Hospitals in India
The best pda device closure hospitals in india are equipped with advanced technology and expert pediatric cardiology teams, ensuring comprehensive care for successful outcomes.
PDA Device Closure Cost in India
The pda device closure cost in india is affordable, offering patients accessible pricing and high standards of care across specialized hospitals.
Best PDA Device Closure Surgeons in India
The Best PDA Device Closure Surgeons in India are experts in pediatric heart procedures, providing skilled and compassionate care tailored to each patient’s needs.
FAQ
What causes patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in infants?
PDA can be caused by a variety of factors, including prematurity, maternal health conditions, and environmental exposures during pregnancy.
Is PDA hereditary?
PDA can have a genetic component, but it is not solely hereditary; multiple risk factors contribute to its development.
Why is PDA more common in premature babies?
Premature babies often have underdeveloped cardiovascular systems, making it more difficult for the ductus arteriosus to close naturally after birth.
Can environmental factors during pregnancy lead to PDA?
Yes, environmental factors like smoking, alcohol, and exposure to certain toxins can increase the risk of PDA.
How can PDA be detected and treated early?
PDA can be detected through screenings like echocardiograms. Early treatment options include medication, catheter-based procedures, and surgery, depending on the case.
Explore the Best Heart Care Resources in India
Find some of the top cardiologist, surgeons and the best heart hospitals in India
Best Heart Hospitals in India
Choosing the right hospital is crucial for successful heart treatments. If you want to explore trusted options, check the list of Best Heart Hospitals in India offering world-class facilities, advanced cardiac care units, and experienced teams for both simple and complex procedures.
Best Cardiologists in India
Finding the right cardiologist can make a huge difference in early diagnosis and long-term heart health. If you are looking for the Best Cardiologists in India, see this curated list of experts who specialize in preventive care, interventional cardiology, and complex heart disease management. Check the full list Best Cardiologists in India.
Best Cardiac Surgeons in India
If you are planning for heart surgery and need top-level expertise, we recommend exploring the Best Cardiac Surgeons in India. These surgeons have a proven record in performing bypass surgeries, valve replacements, and minimally invasive heart operations with excellent outcomes.
Get more indepth information on Cardiology treatments and their costs.
Conclusion
Your cardiology health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top cardiac hospitals and cardiac surgeons in India.
The closure of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) using a device has become a common procedure, offering significant benefits over traditional surgery. Over time, this procedure can lead to improved heart function, as it reduces the abnormal blood flow between the aorta and pulmonary artery1. However, it's important to monitor heart function through regular follow-up echocardiograms, as some patients may experience complications such as left ventricular dysfunction or residual shunts. Long-term studies have shown that most patients experience positive outcomes, with improved cardiac performance and reduced symptoms. PDA Device Closure and Its Impact on Heart Function Over Time
Early detection and treatment of Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) in children can significantly improve health outcomes. Timely intervention helps prevent complications such as pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, and growth delays. Early treatment often involves less invasive methods, reducing the need for surgical intervention and promoting better overall heart function and development. Regular monitoring and appropriate management can lead to healthier, more active lives for children with PDA The Benefits of Early PDA Detection and Treatment in Children
Catheterization plays a crucial role in the minimally invasive closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). This procedure, known as transcatheter PDA closure, involves threading a catheter through a blood vessel to the site of the PDA. A device or coil is then deployed to close the ductus arteriosus, restoring normal blood flow. This method offers several advantages over traditional surgery, including reduced recovery time, less pain, and lower risk of complications. Regular follow-up is essential to monitor the success of the closure and ensure proper heart function Understanding the Role of Catheterization in PDA Device Closure