The gut microbiota refers to the diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, residing in the gastrointestinal tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining overall health by influencing digestion, metabolism, and immune function.
Recent research has highlighted the significance of gut microbiota in various health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, and gastrointestinal disorders. Understanding the gut microbiota's composition and function can provide insights into potential therapeutic interventions for improving health outcomes.
What is Gut Microbiota?
Gut microbiota is the complex ecosystem of microorganisms that inhabit the intestines, primarily in the large intestine. It consists of trillions of microbes, with thousands of different species, that work symbiotically with the host to break down food, synthesize essential vitamins, and protect against pathogens.
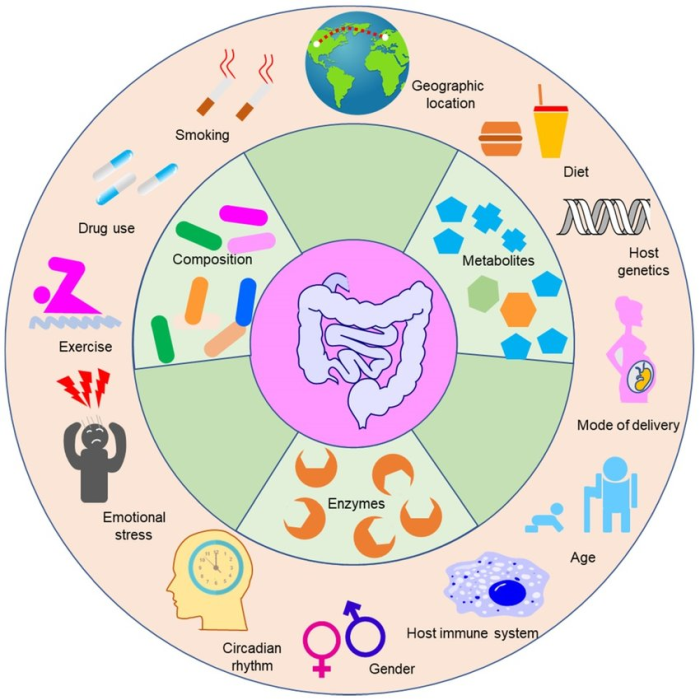
The balance and diversity of these microbial populations are essential for optimal digestive health and metabolic processes. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, age, and antibiotic use can significantly influence the composition and functionality of the gut microbiota.
The Connection Between Gut Microbiota and Obesity
Emerging research has established a strong connection between gut microbiota composition and obesity. Certain microbial populations are associated with increased energy extraction from food and fat storage, contributing to weight gain.
For example, individuals with obesity often exhibit a higher ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes, two major bacterial phyla in the gut, compared to lean individuals. This imbalance may promote an environment conducive to obesity by influencing appetite regulation, fat storage, and metabolic processes.
Consequently, modulating gut microbiota through dietary changes or probiotics presents a promising avenue for obesity management.
How Weight Loss Surgery Affects Gut Microbiota Composition
Weight loss surgery, particularly procedures like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, significantly alters gut microbiota composition. Post-surgery, patients often experience a decrease in harmful bacteria and an increase in beneficial strains, which can enhance metabolic health and promote weight loss.
The changes in gut microbiota are thought to result from factors such as reduced food intake, altered nutrient absorption, and changes in the gastrointestinal environment. These microbial shifts may play a critical role in the success of weight loss surgery by influencing appetite regulation and energy metabolism.
The Role of Gut Microbiota in Nutrient Absorption Post-Surgery
Gut microbiota also plays a vital role in nutrient absorption after weight loss surgery. The composition of gut bacteria can influence the efficiency of nutrient extraction from food, affecting vitamin and mineral status in patients.
For example, beneficial microbes can enhance the absorption of essential nutrients like vitamins B12 and D, while a diverse microbiota can help mitigate malabsorption issues commonly seen after bariatric procedures.
Understanding the interplay between gut microbiota and nutrient absorption is crucial for optimizing post-surgical dietary strategies and preventing deficiencies in patients following weight loss surgery.
Changes in Gut Hormones After Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss surgeries, such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy, lead to significant changes in gut hormone levels. These surgeries alter the anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract, influencing the secretion of hormones involved in appetite regulation and glucose metabolism.

For example, RYGB significantly increases levels of peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which promote satiety and insulin sensitivity. Conversely, levels of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, typically decrease after surgery, contributing to reduced appetite and weight loss.
The Impact of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Gut Microbiota
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has a profound impact on gut microbiota composition. Studies have shown that the surgery can lead to increased microbial diversity, which is often associated with improved metabolic health.
The alterations in gut anatomy and the subsequent changes in nutrient absorption can shift the balance of beneficial bacteria, enhancing the presence of microbiota that support weight loss and metabolic function. This microbiota shift plays a critical role in post-operative outcomes, influencing not just weight loss but also the risk of developing obesity-related comorbidities.
How Gastric Banding Influences Gut Bacteria Diversity
Gastric banding also affects gut bacteria diversity, albeit through a different mechanism compared to more invasive surgeries like RYGB. The presence of the adjustable band restricts food intake, leading to changes in dietary habits that can affect gut microbiota.
While the impact on microbial diversity is generally less pronounced than with RYGB, studies indicate that patients may still experience beneficial shifts in their gut bacteria, which can contribute to weight management and improved metabolic health over time.
The Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Microbial Health
Sleeve gastrectomy is known to significantly alter gut microbiota, promoting a microbiome that favors weight loss and metabolic health. The surgery reduces the size of the stomach and changes the hormonal environment, which together can shift the microbial composition.
Patients often exhibit an increase in beneficial bacteria and a decrease in pathogenic strains, potentially leading to better nutrient absorption and a reduction in inflammation. This shift is thought to contribute to the long-term success of weight loss and the management of obesity-related conditions.
The Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health
Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in metabolic health, influencing energy homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut bacteria, has been linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
After weight loss surgery, the improved diversity and composition of gut microbiota are associated with enhanced metabolic outcomes, making gut health a vital component of post-surgical recovery and long-term success in weight management.
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Supporting Gut Health Post-Surgery
Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into the post-surgical diet can support gut health after weight loss surgery. Probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria, can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome, while prebiotics, found in fiber-rich foods, serve as food for these bacteria, promoting their growth.
Together, these elements can improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and contribute to better overall health outcomes in weight loss surgery patients.
Understanding Dysbiosis: Imbalances in Gut Microbiota
Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiota, which can occur after weight loss surgery due to changes in diet, nutrient absorption, and gut hormone levels. This imbalance can lead to various health issues, including increased inflammation and metabolic disorders.
Monitoring and addressing dysbiosis through dietary changes, probiotics, and other interventions is essential for optimizing health outcomes after surgery.
How Gut Microbiota Influences Weight Loss Outcomes
The composition and diversity of gut microbiota can significantly influence weight loss outcomes following bariatric surgery. Certain microbial profiles are associated with more effective weight loss and improved metabolic health.
The mechanisms behind this influence include the modulation of energy extraction from food, regulation of appetite-related hormones, and impact on inflammation. Understanding these relationships can help tailor post-operative care and dietary recommendations for better results.
The Link Between Gut Microbiota and Inflammation
Gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in regulating inflammation in the body. Imbalances in gut bacteria can lead to increased systemic inflammation, which is linked to obesity and related metabolic disorders.
After weight loss surgery, improvements in gut microbiota composition can help reduce inflammation levels, contributing to better overall health and reducing the risk of comorbidities associated with obesity.
The Potential Role of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Weight Loss Surgery
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is an emerging area of interest in the context of weight loss surgery. By transferring healthy gut bacteria from a donor to a recipient, FMT aims to restore a balanced microbiome and potentially improve metabolic health and weight loss outcomes.
Preliminary studies suggest that FMT may help enhance the benefits of bariatric surgery, although further research is needed to establish its effectiveness and safety in this context.
Dietary Implications for Maintaining Healthy Gut Microbiota
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota after weight loss surgery requires a well-balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes serve as excellent sources of prebiotics, which nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
Additionally, incorporating fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi can provide probiotics that promote microbial diversity. Staying hydrated and avoiding highly processed foods, excess sugars, and artificial sweeteners are also crucial for supporting gut health.
Tailoring dietary choices to include these elements can significantly enhance the microbiota composition and overall health outcomes post-surgery.
Monitoring Gut Health After Weight Loss Surgery
Monitoring gut health after weight loss surgery is essential for ensuring long-term success and minimizing complications. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can include assessments of gastrointestinal symptoms, dietary habits, and laboratory tests to evaluate nutrient levels and microbiota composition.
Patients should be aware of signs of dysbiosis, such as bloating, digestive discomfort, or changes in bowel habits. Keeping a food diary can help identify foods that may impact gut health, while periodic consultations can guide dietary adjustments and the incorporation of supplements as needed.
Future Research Directions: Gut Microbiota and Weight Loss Surgery
Future research into gut microbiota and weight loss surgery will likely focus on understanding the complex relationships between microbial composition, dietary influences, and metabolic health. Studies may explore the efficacy of specific probiotics or prebiotic supplements in enhancing outcomes for bariatric patients.
Additionally, investigating the genetic and environmental factors that shape gut microbiota could lead to personalized approaches for post-surgical care. Exploring the potential of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) as a therapeutic tool in this context may also provide insights into optimizing gut health and weight loss results.
Patient Testimonials: Experiences with Gut Health After Surgery
Patient testimonials can provide valuable insights into the impact of weight loss surgery on gut health. Many patients report significant improvements in digestion, reduced gastrointestinal issues, and enhanced overall well-being following surgery.
Positive dietary changes, such as increased fiber intake and the incorporation of probiotics, often correlate with these improvements. Sharing these experiences can empower new patients to prioritize gut health as part of their recovery journey, highlighting the importance of following dietary recommendations and staying engaged with healthcare providers for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion: Embracing the Role of Gut Microbiota in Weight Loss Surgery
In conclusion, understanding the role of gut microbiota in weight loss surgery is crucial for achieving successful outcomes. The changes in gut health post-surgery can significantly influence weight loss, metabolic health, and overall well-being.
By prioritizing a balanced diet, monitoring gut health, and staying informed about emerging research, patients can enhance their recovery and enjoy the long-term benefits of weight loss surgery. Embracing these dietary implications and strategies will support a healthier gut microbiome, ultimately leading to improved health and quality of life.
How RYGB Surgery Can Lead to Increased Energy Levels
Discover how Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass surgery can boost your energy levels. This section explains the physiological changes that occur after surgery, including improved nutrient absorption and weight loss, which can contribute to enhanced overall vitality and well-being.
Exploring the Different Techniques of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Gain insight into the various techniques used in Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, including traditional and minimally invasive approaches. This section provides an overview of the surgical methods, their benefits, and how they can affect recovery and weight loss outcomes.
Best RYGB Surgery in India
The Best RYGB Surgery in India provides an effective solution for long-term weight loss by reducing stomach size and rerouting the digestive system to limit calorie absorption.
Best RYGB Hospitals in India
The Best RYGB Hospitals in India feature cutting-edge technology and experienced medical teams, ensuring patients receive comprehensive pre-operative and post-operative care for lasting results.
RYGB Surgery Cost in India
The RYGB Surgery Cost in India is competitively priced, offering transparent and affordable treatment plans without compromising on quality or safety standards.
Best RYGB Surgeons in India
The Best RYGB Surgeons in India are leaders in bariatric surgery, providing personalized surgical solutions and expert care to help patients achieve their weight loss goals.
FAQ
How does gut microbiota affect weight loss after surgery?
Gut microbiota influences weight loss by affecting nutrient absorption, metabolism, and the regulation of appetite-related hormones. A balanced microbiome promotes efficient digestion and metabolic processes, which can enhance weight loss outcomes.
Can I improve my gut microbiota after weight loss surgery?
Yes, you can improve your gut microbiota by consuming a diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics. Incorporating fermented foods and maintaining a diverse diet can promote a healthy microbial balance.
What role do probiotics play in gut health post-surgery?
Probiotics help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome after surgery. They can enhance digestion, reduce gastrointestinal symptoms, and support immune function, contributing to overall health.
How do changes in gut microbiota impact my recovery?
Changes in gut microbiota can affect recovery by influencing nutrient absorption, inflammation levels, and digestive health. A balanced microbiome is essential for optimal recovery and long-term success after weight loss surgery.
Is it possible for gut microbiota to influence my appetite after surgery?
Yes, gut microbiota can influence appetite by modulating hormone secretion, such as ghrelin and peptide YY, which regulate hunger and satiety. A healthy gut microbiome can help stabilize these hormone levels, supporting appetite control after surgery.