Understanding the anatomy of the buttocks is crucial for successful surgical outcomes in procedures such as buttock augmentation and lifts. The buttocks are composed of several layers—skin, fat, muscle, and fascia—that must be carefully navigated during surgery to achieve both aesthetic and functional goals. Knowledge of these anatomical structures helps surgeons enhance the natural contours while ensuring patient safety, particularly in minimizing complications such as nerve damage or poor circulation. By appreciating the intricate anatomy of the buttocks, surgeons can create results that are both visually pleasing and durable.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
Layers of the Buttocks: Skin, Fat, and Muscle
The buttocks consist of three primary layers: skin, fat, and muscle, each playing a distinct role in the structure and appearance of the area. The outermost layer, the skin, varies in thickness and elasticity, influencing how the buttocks appear after surgical procedures. Beneath the skin lies a layer of subcutaneous fat, which contributes to the shape and fullness of the buttocks. Finally, the gluteal muscles, primarily the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus, provide the foundational structure and movement capability. Understanding how these layers interact allows surgeons to effectively sculpt the buttocks while maintaining a natural look.
The Gluteal Muscles: Structure and Function
The gluteal muscles are a group of three muscles that define the shape and function of the buttocks. The gluteus maximus, the largest and most superficial muscle, is responsible for the bulk of the buttock's shape and its primary movements, such as hip extension and outward rotation. The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, located beneath the maximus, contribute to stability and lateral movement of the hip. In buttock surgery, understanding the structure and role of these muscles is vital for both enhancing contour and preserving muscle function, as implants or fat grafts are often placed either above or within the muscle layers.
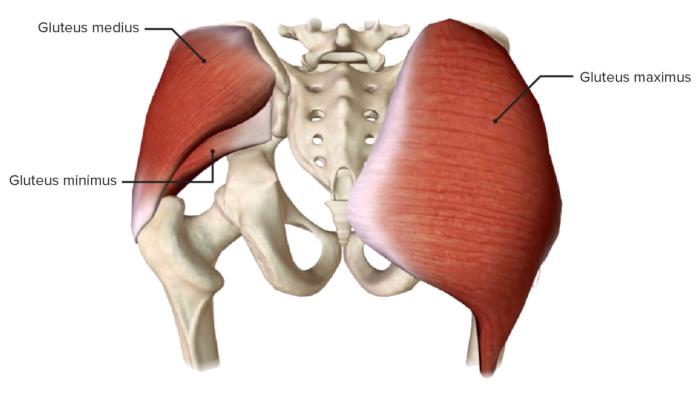
Fat Distribution in the Buttocks: Aesthetic Considerations
Fat distribution plays a key role in the aesthetic appearance of the buttocks, influencing its shape, symmetry, and overall volume. Variations in fat deposits among individuals can result in different buttock shapes, ranging from round to square or heart-shaped. During procedures like fat grafting or liposuction, surgeons carefully consider how fat is distributed to create a balanced and natural-looking outcome. Factors such as genetics, age, and hormonal changes affect fat accumulation, and understanding these patterns allows surgeons to tailor the procedure to each patient's unique body type.
The Role of Fascia in Supporting Buttock Contours
Fascia, the connective tissue that surrounds muscles, plays an important role in maintaining the shape and structure of the buttocks. The deep fascia, particularly in the gluteal region, supports the overlying fat and skin, helping to create a smooth contour. In surgical procedures, maintaining the integrity of the fascia is crucial to achieving long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing results. Damage or weakening of the fascia can lead to complications like sagging or uneven contours. By understanding the role of fascia, surgeons can better preserve or enhance the natural support structures of the buttocks.
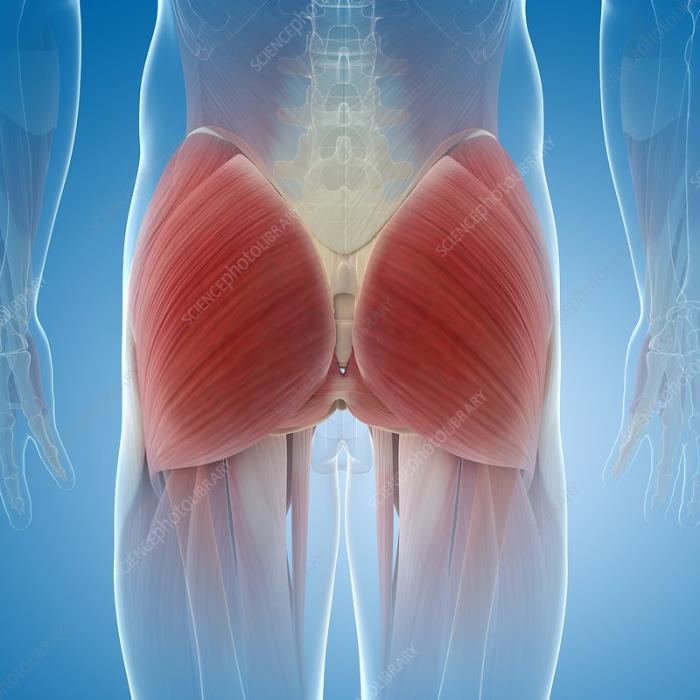
Vascular Anatomy: Key Considerations for Safe Surgery
A thorough understanding of the vascular anatomy of the buttocks is essential for ensuring patient safety during surgery. The gluteal region is supplied by several important blood vessels, including the superior and inferior gluteal arteries, which provide circulation to the skin, fat, and muscles. Any disruption to these blood vessels during surgery can lead to complications such as tissue necrosis or excessive bleeding. Surgeons must carefully navigate around these vascular structures to avoid complications and promote optimal healing. Precise knowledge of the vascular network ensures that procedures like fat grafting or implant placement are performed safely and effectively.
Nerve Supply to the Buttocks: Avoiding Complications
Understanding the nerve supply to the buttocks is crucial in avoiding complications during augmentation. The gluteal region is innervated primarily by the superior and inferior gluteal nerves, and careful surgical planning is required to avoid damage to these nerves, which could lead to numbness, muscle weakness, or chronic pain. Surgeons must have an in-depth knowledge of the anatomy to minimize risks and ensure optimal function post-surgery.
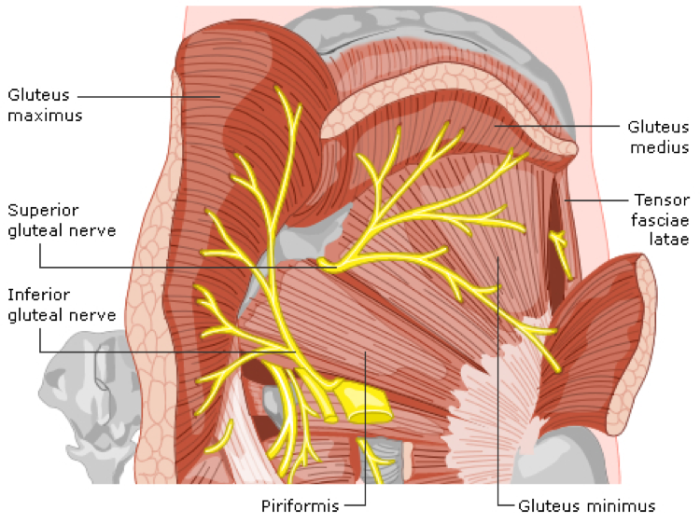
The Importance of Muscle Attachments in Buttock Augmentation
The gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus muscles are key to the shape and function of the buttocks. Preserving these muscle attachments is essential for maintaining stability and strength in the buttocks. Disruption of these attachments can lead to functional deficits or altered appearance. Augmentation techniques must be carefully tailored to ensure muscle integrity and achieve aesthetically pleasing results.
Understanding Skin Elasticity and Its Impact on Surgical Outcomes
Skin elasticity plays a significant role in determining the outcome of buttock augmentation. Patients with more elastic skin may achieve smoother, more natural results, while those with reduced elasticity, often due to aging or weight fluctuations, may experience sagging or irregular contours. Surgeons assess skin elasticity pre-operatively to plan for the best approach, and may recommend skin-tightening procedures in combination with augmentation for optimal results.
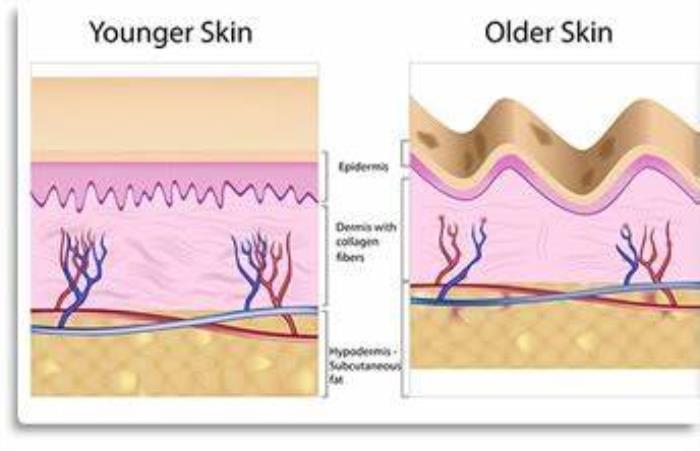
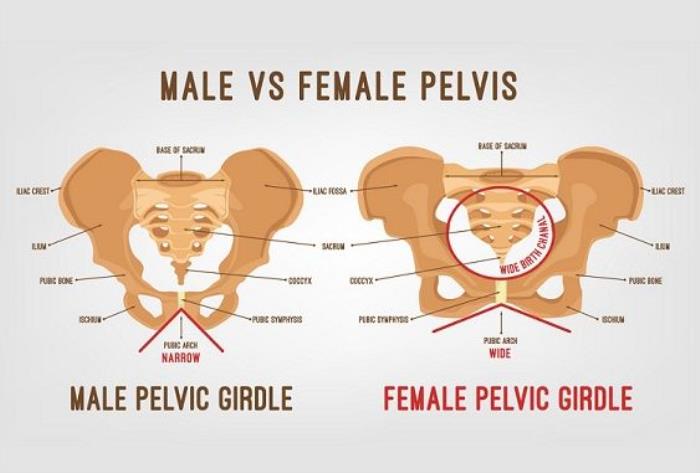
How Bone Structure Affects Buttock Shape and Augmentation
The underlying bone structure, including the pelvis and sacrum, greatly influences the shape of the buttocks. A patient’s pelvic width, sacral angle, and hip structure can dictate the amount of projection and the overall contour of the buttocks. Tailoring surgical techniques to each individual’s unique bone anatomy helps in creating balanced and proportionate results.
Differences in Male and Female Buttock Anatomy
There are notable differences between male and female buttock anatomy that affect augmentation techniques. Women typically have wider hips and more pronounced gluteal projection, while men tend to have narrower hips and flatter buttocks. Surgeons must account for these differences to ensure natural-looking, gender-appropriate results. Male patients may prefer more muscular definitions, while female patients often desire a rounder, fuller appearance.
Gluteal Fold: Defining the Lower Border of the Buttocks
The gluteal fold, the crease where the buttock meets the thigh, is an important aesthetic landmark. It defines the lower boundary of the buttocks, and maintaining or reshaping this fold is crucial during augmentation. Surgeons work carefully to enhance or preserve the natural gluteal fold to avoid an unnatural appearance and ensure aesthetically balanced results.
The Impact of Weight Loss on Buttock Anatomy
Significant weight loss can lead to changes in the anatomy of the buttocks, including loss of volume, skin laxity, and sagging. These changes may make the buttocks appear flatter or deflated. Patients who have undergone major weight loss may require more extensive augmentation procedures, such as fat grafting or skin excision, to restore volume and contour.
Surgical Techniques Tailored to Buttock Anatomy
Different surgical techniques, such as fat grafting or implants, are tailored to the patient’s unique anatomy to achieve the desired results. Factors such as muscle mass, skin elasticity, and bone structure all play a role in selecting the appropriate technique. Personalized surgical plans are key to achieving natural-looking and long-lasting outcomes.
Balancing Volume and Proportion in Buttock Augmentation
Achieving the right balance between volume and proportion is essential for aesthetically pleasing buttock augmentation. Surgeons must take into account the patient's body type, existing fat distribution, and overall proportions to ensure the results enhance the natural silhouette. Over-augmentation can lead to unnatural results, while under-augmentation may not meet the patient’s expectations.
Anatomy of the Buttocks in Fat Grafting Procedures
Fat grafting procedures involve harvesting fat from other areas of the body and injecting it into the buttocks to enhance volume. Understanding the anatomy of the buttocks is critical in determining where to place the fat to achieve smooth, natural contours. Fat must be injected at different layers to ensure even distribution, while avoiding vital structures like blood vessels and nerves.
Enhancing Buttock Projection: Muscle vs. Fat Augmentation
Buttock projection can be enhanced through muscle augmentation (such as with gluteal implants) or fat augmentation (via fat grafting). Muscle augmentation offers a firmer, more defined look, while fat augmentation provides a softer, more natural appearance. Depending on the patient's desired outcome, the surgeon may recommend one or a combination of both methods to achieve the best results.
Avoiding Surgical Risks: An Anatomical Approach
A thorough understanding of buttock anatomy allows surgeons to avoid common risks associated with augmentation, such as nerve damage, implant displacement, or fat embolism. Pre-operative planning based on the patient's anatomy is key to reducing complications and ensuring safe, successful results.
Patient-Specific Anatomy: Customized Surgical Plans
Each patient’s anatomy is unique, and successful buttock augmentation depends on creating a customized surgical plan. By considering factors such as muscle mass, fat distribution, skin elasticity, and bone structure, surgeons can personalize the procedure to achieve the best possible outcome for each individual.
Conclusion: The Role of Anatomy in Achieving Optimal Buttock Surgery Results
Understanding the anatomy of the buttocks is fundamental to the success of augmentation procedures. By taking into account factors like nerve supply, muscle attachments, skin elasticity, and bone structure, surgeons can create customized, safe, and effective plans that deliver natural-looking, long-lasting results.
Exploring Non-Surgical Alternatives to Buttock Augmentation
Discover a range of non-surgical options for enhancing buttock appearance. This section highlights techniques such as dermal fillers, fat transfer, and other innovative methods that can provide subtle volume and contour without the need for invasive surgery, along with their benefits and potential results.
Exploring the Relationship Between Genetics and Buttock Shape
Learn about the influence of genetics on buttock shape and overall body composition. This section discusses how hereditary factors can affect fat distribution, muscle tone, and the natural contour of the buttocks, helping you understand your body better and what options may be available for enhancement.
Best Buttock Augmentation Surgery in India
The Best Buttock Augmentation Surgery in India offers patients a way to enhance the shape and size of their buttocks using advanced surgical techniques, providing natural-looking and long-lasting results.
Best Buttock Augmentation Hospitals in India
The Best Buttock Augmentation Hospitals in India feature modern facilities and experienced surgeons, ensuring comprehensive care from consultation to recovery, tailored to each patient's needs.
Buttock Augmentation Surgery Cost in India
The Buttock Augmentation Surgery Cost in India is competitive and transparent, offering affordable options while maintaining high standards of safety and patient care.
Best Buttock Augmentation Surgeons in India
The Best Buttock Augmentation Surgeons in India are skilled professionals with extensive experience in body contouring, delivering personalized treatment plans for optimal aesthetic results.
FAQ:
What muscles are involved in buttock augmentation surgery?
The gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus muscles are key in buttock augmentation. These muscles provide structure and shape to the buttocks, and their integrity is essential for both function and aesthetic outcomes.
How does fat distribution affect the shape of the buttocks?
Fat distribution plays a major role in buttock shape. Individuals with more fat in the gluteal region tend to have fuller, rounder buttocks, while those with less fat may have flatter buttocks. Fat grafting can be used to enhance volume and contour.
Why is it important to understand vascular anatomy in buttock surgery?
Understanding vascular anatomy is critical to avoid complications such as fat embolism, which can occur if fat is injected into blood vessels. Proper placement of fat or implants ensures safe outcomes and reduces the risk of serious complications.
How do surgeons account for nerve supply during buttock augmentation?
Surgeons carefully map out the nerve supply to avoid damaging important nerves, such as the superior and inferior gluteal nerves. This helps prevent issues like numbness, weakness, or chronic pain following surgery.
Can weight loss change the anatomy of the buttocks?
Yes, significant weight loss can lead to loss of volume and changes in skin elasticity, which can affect the shape and appearance of the buttocks. Augmentation procedures can help restore volume and improve contour following weight loss.
Recent advancements in buttock implant materials have focused on enhancing safety, durability, and aesthetic outcomes. Modern implants are often made from highly cross-linked, stable silicone gel that mimics the feel of natural muscle and has a resistant shell to withstand heavy loads. Innovations also include the use of ultrasonic liposuction and ultrasound-guided fat grafting in combination with submuscular silicone implants to achieve more natural and safe gluteal enhancements. These improvements aim to provide patients with long-lasting results and a more comfortable experience. Exploring the Latest Innovations in Buttock Implant Materials
Genetics significantly influence the shape and size of your buttocks. Factors such as muscle distribution, fat storage patterns, and pelvic structure are largely determined by genetic makeup. Ethnic background also plays a role, with certain buttock shapes more prevalent in specific populations. While lifestyle choices like diet and exercise can enhance muscle tone and overall appearance, the fundamental structure of your buttocks is inherited. Exploring the Relationship Between Genetics and Buttock Shape
For those seeking to enhance their buttocks without undergoing surgery, there are several non-surgical options available. Injectable dermal fillers, such as Sculptra, can add volume and stimulate collagen production for a smoother, fuller appearance. Another option is Emsculpt, a device that uses high-intensity electromagnetic energy to tone and build muscle in the buttocks area. Additionally, CoolTone is a muscle-toning device that is gaining popularity. These non-surgical alternatives offer minimal downtime and reduced risks compared to traditional surgical methods, making them attractive options for those looking to achieve natural-looking results. Exploring Non-Surgical Alternatives to Buttock Augmentation