Overview of Hydrocephalus in Adults
Hydrocephalus in adults occurs when there is an abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain's ventricles, leading to increased intracranial pressure. While hydrocephalus is more commonly associated with infants and children, adults can develop the condition as well, either due to congenital causes or as a result of injury or disease later in life. Adult-onset hydrocephalus can lead to significant neurological impairments if not properly diagnosed and treated. The most prevalent form of hydrocephalus in adults is normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), which typically affects older adults and is characterized by the gradual onset of symptoms like gait disturbances, cognitive decline, and urinary incontinence.
Medical disclaimer: This content is for general awareness and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. For diagnosis or treatment decisions, consult a qualified specialist.
The treatment for adult hydrocephalus often involves the placement of a shunt system to drain excess CSF, though other surgical procedures, such as endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV), may be considered depending on the underlying cause.
Causes and Risk Factors for Adult-Onset Hydrocephalus
Adult-onset hydrocephalus can be caused by several factors, including head trauma, infections such as meningitis, brain tumors, or complications from hemorrhages within the brain. In some cases, hydrocephalus may develop as a consequence of brain surgery or after a stroke, particularly if these events disrupt the normal flow or absorption of CSF. Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a common form of hydrocephalus in older adults and is thought to arise due to changes in CSF dynamics, though the exact cause is not always clear.
Risk factors for developing hydrocephalus in adulthood include advancing age, a history of neurological infections, or previous head injuries. Certain genetic factors may also predispose individuals to hydrocephalus, though these cases are less common in adults compared to children.
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus in Adults: What to Look For
The symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. In normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), the classic triad of symptoms includes difficulty walking, cognitive decline, and urinary incontinence. Gait disturbances, often described as a shuffling or unsteady walk, are typically one of the earliest signs. Cognitive issues, such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating, may mimic dementia, while urinary problems can range from increased urgency to complete incontinence.
Other forms of hydrocephalus may present with symptoms such as headaches, nausea, blurred vision, and balance problems. In severe cases, hydrocephalus can lead to changes in consciousness or seizures. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for preventing permanent neurological damage and improving patient outcomes.
The Importance of Early Detection in Adult Hydrocephalus
Early detection of hydrocephalus in adults is critical for preventing long-term neurological damage and improving quality of life. Many of the symptoms of adult-onset hydrocephalus, particularly in the case of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), can be mistaken for other age-related conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which may reduce the effectiveness of interventions.
Early detection allows for timely surgical intervention, such as the placement of a shunt system to relieve intracranial pressure or an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) to restore normal CSF flow. The earlier the condition is treated, the better the chances of reversing symptoms and preventing further complications. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are also essential to ensure the long-term success of the treatment.
Diagnostic Techniques for Adult Hydrocephalus: MRI, CT, and More
Diagnosing hydrocephalus in adults typically involves the use of advanced imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans. These imaging modalities provide detailed views of the brain’s ventricles, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the extent of CSF buildup and identify any structural abnormalities that may be causing the condition.
MRI is often the preferred diagnostic tool as it provides high-resolution images without radiation exposure, allowing for the detailed visualization of soft tissues. CT scans are also widely used, particularly in emergency settings, as they offer quick and reliable imaging to confirm hydrocephalus. In some cases, lumbar punctures or intracranial pressure monitoring may be conducted to measure CSF pressure and assess the flow dynamics. These diagnostic techniques are crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions over time.
How Untreated Hydrocephalus Affects Brain Function
Untreated hydrocephalus leads to the buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain, causing increased intracranial pressure that can severely affect brain function. This pressure can damage brain tissues, leading to cognitive decline, memory problems, and impaired motor functions. Individuals may experience headaches, difficulty walking, balance issues, and even changes in personality or mood. Over time, untreated hydrocephalus can result in more severe complications like seizures, vision loss, or irreversible brain damage. In adults, the longer hydrocephalus remains untreated, the more difficult it becomes to recover lost neurological functions.
Common Challenges in Diagnosing Hydrocephalus in Adults
Diagnosing hydrocephalus in adults can be challenging because its symptoms often overlap with other neurological conditions, such as dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, or Parkinson’s disease. Common signs like memory loss, difficulty walking, and urinary incontinence can be mistaken for normal aging, delaying accurate diagnosis. Additionally, imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans are crucial for diagnosing hydrocephalus, but these may not always be utilized promptly due to misinterpretation of initial symptoms. The condition known as normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) can further complicate diagnosis since brain pressure readings often appear normal despite CSF buildup.
The Role of Neurological Exams in Early Diagnosis
Neurological exams play a key role in the early diagnosis of hydrocephalus by evaluating motor skills, reflexes, coordination, and cognitive functions. These exams help physicians detect early warning signs such as gait abnormalities, balance issues, and cognitive changes. When combined with neuroimaging tests like MRI or CT scans, neurological exams help identify the extent of CSF buildup and potential brain damage. Early detection through comprehensive neurological assessments is vital for initiating timely treatment and preventing long-term complications associated with hydrocephalus.
Early Treatment Options: Shunt Surgery and Beyond
The most common early treatment option for hydrocephalus is shunt surgery, which involves inserting a flexible tube to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain to another part of the body, typically the abdomen. This helps reduce intracranial pressure and relieves symptoms. In some cases, an alternative procedure called Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) may be performed to create a new pathway for CSF flow. Medications to manage symptoms or reduce fluid production may also be used in conjunction with surgical treatments. Early intervention with these treatments is crucial for improving outcomes and reducing the risk of long-term cognitive and physical impairment.
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) for Adults: Is It an Option?
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) is a viable treatment option for some adults with hydrocephalus, particularly those with obstructive hydrocephalus where CSF flow is blocked. During this minimally invasive procedure, a small hole is created in the floor of the third ventricle, allowing CSF to bypass the obstruction and flow into the brain's natural cavities for absorption. While ETV can be effective in reducing the need for a permanent shunt, it is not suitable for all patients, especially those with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). A thorough evaluation of the patient's condition is essential to determine if ETV is the appropriate treatment.
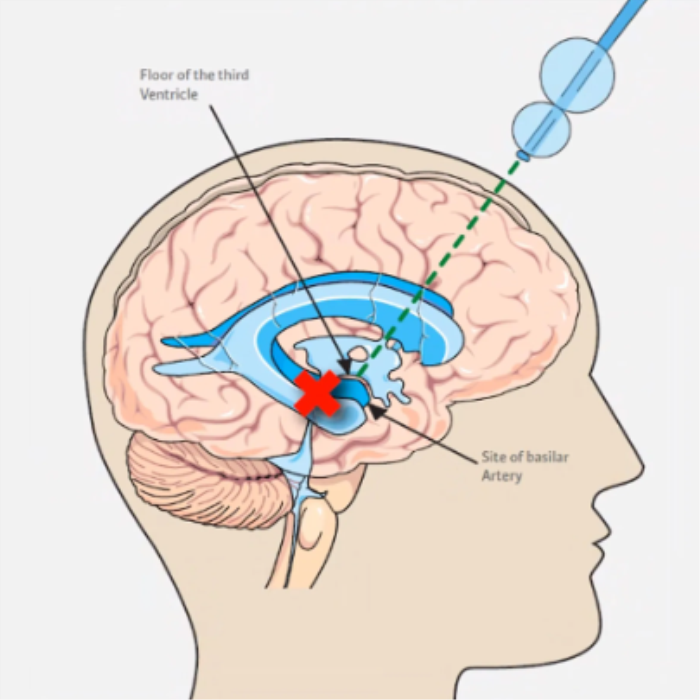
Consequences of Delayed Hydrocephalus Treatment in Adults
Delaying treatment for hydrocephalus in adults can lead to a range of serious consequences. Prolonged pressure on the brain can cause irreversible damage to neural tissues, resulting in significant cognitive decline, memory impairment, and motor dysfunction. In cases of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), delayed treatment can worsen symptoms like difficulty walking and urinary incontinence, which may eventually become permanent. Additionally, the longer hydrocephalus remains untreated, the more challenging it becomes to achieve a full recovery, even after surgical intervention, potentially reducing the patient's overall quality of life.
Improving Quality of Life Through Early Intervention
Early intervention for hydrocephalus can greatly improve a patient's quality of life by preventing or mitigating neurological damage. Surgical options such as shunt placement or Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) can relieve pressure on the brain, alleviating symptoms like headaches, cognitive decline, and mobility issues. Early treatment also improves long-term outcomes by reducing the likelihood of permanent brain damage. Additionally, post-surgical rehabilitation and therapy, including physical therapy and cognitive exercises, help restore lost functions and enable individuals to regain independence and a better quality of life.
Managing Cognitive Decline in Hydrocephalus Patients
Managing cognitive decline in hydrocephalus patients involves a combination of medical treatment, rehabilitation, and supportive therapies. Surgical interventions, such as shunt placement or ETV, can help reduce cognitive symptoms by relieving pressure on the brain. In addition to surgery, cognitive rehabilitation programs focusing on memory, attention, and problem-solving skills are essential for improving mental function. Neurologists may also prescribe medications to address specific cognitive deficits. Moreover, family support and counseling are important for creating a structured environment that promotes cognitive health and helps patients cope with the challenges of living with hydrocephalus.
Post-Surgical Care and Rehabilitation for Adults with Hydrocephalus
Post-surgical care for adults with hydrocephalus involves close monitoring to ensure the shunt or ETV is functioning properly and preventing complications such as infection or shunt malfunction. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping patients regain lost motor and cognitive functions. Physical therapy is often needed to improve balance and mobility, while occupational therapy helps patients relearn daily tasks. Cognitive rehabilitation is also essential for those who experienced memory loss or other cognitive deficits before surgery. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to assess progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Long-term Effects of Hydrocephalus in Adults and How to Mitigate Them
The long-term effects of hydrocephalus in adults can include memory loss, cognitive decline, motor difficulties, and emotional challenges. To mitigate these effects, early intervention with surgical treatment, such as shunt placement or ETV, is critical. In addition, ongoing rehabilitation, including physical, occupational, and cognitive therapy, helps individuals manage symptoms and improve functional outcomes. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor for complications, such as shunt malfunction, and to adjust care as needed. Support from family, counseling, and patient advocacy groups can also play a crucial role in maintaining long-term well-being.
Living with Hydrocephalus: Support and Resources for Adults
Living with hydrocephalus as an adult can present various challenges, but there are numerous support and resources available to help patients manage the condition. Patient advocacy groups, such as the Hydrocephalus Association, provide education, support networks, and assistance in navigating treatment options. These organizations offer community forums, counseling, and peer-to-peer support to help individuals cope emotionally and practically. Rehabilitation services, including physical, occupational, and cognitive therapy, are also essential for improving quality of life. Additionally, patients may benefit from working with social workers and patient navigators who can help access healthcare services, financial aid, and other forms of support.
Innovations in Hydrocephalus Treatment for Adults
Recent innovations in hydrocephalus treatment for adults have focused on improving surgical techniques and long-term management strategies. Advances in shunt technology, such as programmable shunts, allow doctors to adjust the flow of cerebrospinal fluid without additional surgery, improving patient outcomes. Smart shunt systems are also being developed, which use sensors to monitor intracranial pressure in real-time, potentially reducing complications. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) remains a key option for certain patients, offering a minimally invasive alternative to shunt placement. Research into less invasive diagnostic tools and alternative treatments, including pharmacological options, continues to expand the horizons of hydrocephalus care.
Innovations in Hydrocephalus Treatment in India: Advancing Medical Care
Explore the latest innovations in hydrocephalus treatment in India, showcasing how advanced medical technologies are improving patient outcomes and treatment efficiency.
Recognizing Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) in Older Adults
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) is a form of hydrocephalus that predominantly affects older adults, and it can often be misdiagnosed as dementia or Parkinson’s disease. The key symptoms of NPH include difficulty walking (often described as shuffling or unsteady gait), urinary incontinence, and cognitive decline, including memory problems or confusion. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for proper diagnosis, as NPH is one of the few reversible causes of dementia-like symptoms in older adults. Neuroimaging, such as MRI or CT scans, combined with clinical assessments, are used to diagnose NPH, leading to appropriate treatment, typically through shunt surgery.
Why Early Intervention is Critical for Aging Populations with Hydrocephalus
Early intervention is particularly critical for aging populations with hydrocephalus because the longer the condition goes untreated, the more likely it is to cause permanent neurological damage. In older adults, symptoms like cognitive decline and mobility issues can often be attributed to aging, which delays diagnosis. Timely treatment, such as shunt placement or Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV), can prevent further brain damage and significantly improve a patient’s quality of life. Early treatment can also reduce the risk of complications, restore mobility, and improve cognitive function, allowing older adults to maintain independence and avoid further decline.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Treatment in India
The Best Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Treatment in India is performed by expert neurosurgeons who utilize advanced techniques to ensure optimal outcomes for patients, offering a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual health needs.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery Hospitals in India
The best hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) hospitals in india are equipped with cutting-edge technology and facilities, providing top-notch care, including pre-surgery consultations, surgical expertise, and post-operative recovery support to ensure a smooth patient journey.
Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) Cost in India
When considering the hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) cost in india, patients benefit from affordable and transparent pricing at leading hospitals, which offer cost-effective treatment options without compromising the quality of care.
Best Hydrocephalus Surgery Doctors in India
The best hydrocephalus surgery (vp shunt) doctors in india are highly experienced in performing the procedure, utilizing a patient-centric approach that ensures personalized care, precise surgical techniques, and dedicated follow-up care to enhance recovery.
Future Research on Adult Hydrocephalus Treatment
Future research on adult hydrocephalus treatment is focused on developing less invasive diagnostic methods, improving surgical techniques, and enhancing the effectiveness of long-term management strategies. Researchers are exploring genetic factors that may contribute to hydrocephalus, which could lead to earlier and more precise diagnoses. Advances in biomaterials and robotics are being integrated into shunt systems to improve durability and functionality. Additionally, clinical trials are examining the potential for pharmacological therapies to reduce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) production or address underlying causes of CSF blockage. Continued research aims to reduce the need for repeat surgeries and enhance the quality of life for adults with hydrocephalus.
FAQs:
What are the signs of hydrocephalus in adults?
The signs of hydrocephalus in adults include headaches, difficulty walking, memory loss, difficulty concentrating, urinary incontinence, and changes in mood or personality. In some cases, vision problems, nausea, or balance issues may also occur.
Why is early treatment important for hydrocephalus in adults?
Early treatment is crucial for hydrocephalus because it helps prevent permanent brain damage, cognitive decline, and motor dysfunction. Prompt surgical intervention can alleviate symptoms and improve the long-term prognosis, significantly enhancing the patient's quality of life.
What diagnostic methods are used for adult hydrocephalus?
The primary diagnostic methods for hydrocephalus in adults include MRI and CT scans, which provide detailed images of cerebrospinal fluid buildup in the brain. Neurological exams and lumbar punctures may also be used to assess brain function and pressure levels.
What are the risks of delaying treatment for hydrocephalus?
Delaying treatment for hydrocephalus can lead to permanent cognitive impairment, motor dysfunction, and increased intracranial pressure, which can result in irreversible brain damage. Prolonged pressure on the brain may also lead to seizures and vision loss.
What surgical options are available for adults with hydrocephalus?
The main surgical options for adults with hydrocephalus include shunt placement, which diverts excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to another part of the body, and Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV), a minimally invasive procedure that creates a new pathway for CSF flow within the brain.
Can hydrocephalus in adults be cured with early treatment?
While hydrocephalus cannot be completely cured, early treatment through shunt surgery or ETV can successfully manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. With appropriate intervention, patients can lead a relatively normal life and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
How does early treatment improve the quality of life for adult patients?
Early treatment improves the quality of life by relieving symptoms such as headaches, cognitive decline, and mobility issues. By reducing intracranial pressure, it prevents further brain damage and allows patients to regain physical and cognitive functions, enabling greater independence.
What is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) and how is it treated?
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) is a condition that primarily affects older adults and is characterized by difficulty walking, urinary incontinence, and cognitive decline. It is treated through the surgical placement of a shunt to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid, which often leads to significant improvement in symptoms.
What are the long-term effects of untreated hydrocephalus in adults?
Untreated hydrocephalus can lead to severe long-term effects, including permanent cognitive impairment, motor dysfunction, vision problems, and seizures. In extreme cases, it can result in coma or death due to increased intracranial pressure.
Are there innovative treatments for hydrocephalus in adults?
Innovative treatments for hydrocephalus in adults include advances in shunt technology, such as programmable and smart shunts, as well as minimally invasive procedures like Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV). Ongoing research into pharmacological treatments and less invasive diagnostic methods continues to expand the options available for managing the condition.
Discover the Best Neurosurgery Hospitals and Neurosurgeons in India
When it comes to brain and spine care, choosing the right hospital and specialist is essential. We�ve highlighted the top neurosurgery hospitals and neurosurgeons across India to ensure you receive the best care available.
Top Neurosurgery Hospitals in India
Find the leading centers for brain and spine care:
Best Neurosurgeons in India
Meet the top specialists in brain and spine surgery:
Get more indepth information on Neurology treatments and their costs.
Conclusion
Your brain and spine health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top neurosurgery hospitals and neurosurgeons in India.
Discover the best hospitals in India for Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt), including top choices, advanced techniques, and cost-effective options. Hydrocephalus Surgery (VP Shunt) in India
Explore the innovations in Hydrocephalus treatment and discover how India is advancing medical care with cutting-edge technologies and modern surgical techniques. Learn about the best hospitals and specialists leading the way in providing world-class Hydrocephalus treatment in India, and how these innovations are improving patient outcomes and recovery times. Innovative Approaches to Hydrocephalus Treatment in India
Learn about the legal and ethical considerations surrounding hydrocephalus surgery in India. This guide covers patient rights, medical laws, and the ethical responsibilities of healthcare providers when offering hydrocephalus treatment. Understanding Legal and Ethical Aspects of Hydrocephalus Surgery in India