Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects millions of people globally, characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. It occurs due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain and can be triggered by a variety of causes. From genetic predisposition to brain injuries, and even environmental factors, the causes of epilepsy are vast and diverse. Understanding these epilepsy risk factors can help individuals and families recognize early warning signs, seek timely medical intervention, and explore preventive measures to lower the chances of seizure occurrences.

What is Epilepsy? A Comprehensive Overview
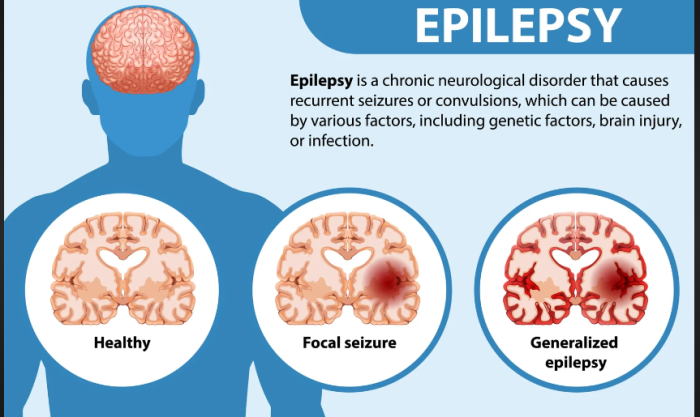
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition defined by recurrent seizures, which are caused by abnormal electrical discharges in the brain. These seizures vary in intensity and type, affecting physical sensations, behaviors, and consciousness. It is one of the most common neurological disorders worldwide and can begin at any age, although it typically manifests in early childhood or after the age of 60.
How the Brain’s Electrical Activity Triggers Epileptic Seizures
In epileptic seizures, brain cells (neurons) send erratic signals that cause bursts of uncontrolled electrical activity. This disruption can affect different parts of the brain, leading to various types of seizures, including generalized and focal seizures. Understanding these electrical malfunctions helps in identifying specific treatment options.
Genetic Causes of Epilepsy: Is It Inherited?
Some forms of epilepsy are linked to genetic mutations passed down from parents. While epilepsy can be inherited, not all cases are due to genetics. Mutations in certain genes, particularly those involved in brain development and function, can increase susceptibility to epilepsy. Genetic testing can help identify the risk in families with a history of epilepsy.
How Birth Trauma Can Lead to Epilepsy
Birth trauma, such as oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) or head injuries during delivery, can lead to epilepsy. These injuries cause damage to the brain, creating abnormal neural activity that may result in seizures later in life. Early medical interventions can reduce the risk, but in some cases, epilepsy develops years after the initial trauma.
The Role of Brain Injuries in Epilepsy Development
A severe head injury is a significant risk factor for epilepsy, especially if the injury causes bleeding or scarring in the brain. Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) can lead to post-traumatic epilepsy, where seizures occur after the injury has healed. Prompt medical treatment and monitoring are crucial for preventing or managing seizure activity.
Stroke and Epilepsy: Understanding the Connection
Stroke, which results from a disruption in blood flow to the brain, is a leading cause of epilepsy in adults over 60. The brain damage caused by a stroke often leads to epileptic seizures, as the affected brain tissue becomes prone to abnormal electrical activity. Rehabilitation and medication can help manage the condition.
The Impact of Infections on Epilepsy Risk
Infections like meningitis, encephalitis, or even brain abscesses can trigger epilepsy by causing inflammation or damage to brain tissue. These infections are often followed by seizures, which can become chronic. Early treatment of infections can prevent long-term complications like epilepsy.
Epilepsy in Children: Early Signs and Causes
In children, epilepsy is often caused by genetic factors, brain malformations, or birth injuries. Early signs include unusual staring spells, sudden jerking movements, or loss of consciousness. Detecting these signs early and consulting a doctor can lead to timely interventions, reducing the frequency and severity of seizures.

Can Tumors Cause Epilepsy? Understanding the Link
Brain tumors can press on surrounding brain tissues, causing abnormal electrical activity that results in seizures. Epileptic seizures are often one of the first symptoms of a brain tumor, particularly in adults who develop epilepsy later in life. Surgery to remove the tumor may help in controlling or eliminating seizures.
Brain Diseases That Increase Epilepsy Risk
Certain brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease, can increase the risk of epilepsy in older adults. The neurodegenerative nature of these diseases disrupts normal brain activity, leading to a higher likelihood of seizures. Managing the primary disease can often reduce seizure occurrences.
The Impact of Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia on Epilepsy
Patients with Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia are at increased risk of developing epilepsy due to brain cell deterioration. The loss of cognitive function and neuronal health creates conditions for unregulated electrical discharges, resulting in seizures. Proper dementia management may help mitigate epilepsy risk.
How Alcoholism Can Trigger Epileptic Seizures
Alcoholism is a significant risk factor for epilepsy. Heavy drinking can damage brain cells, lower seizure thresholds, and lead to alcohol withdrawal seizures. Additionally, sudden cessation of alcohol consumption after prolonged use can trigger life-threatening seizures, making proper medical detox essential.
Epilepsy and Substance Abuse: Understanding the Risks
The use of recreational drugs, particularly stimulants and hallucinogens, can provoke seizures. Substance abuse not only increases the risk of seizures but can also exacerbate epilepsy in those already diagnosed. Seeking treatment for addiction is critical to prevent the onset or worsening of epilepsy.
Common Symptoms of Epilepsy: Recognizing the Signs Early
Discover the early signs of epilepsy, such as recurrent seizures, abnormal behavior, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt medical attention, preventing further complications.
When is Epilepsy Surgery Required? Understanding the Criteria
Explore the criteria for epilepsy surgery, which includes drug-resistant epilepsy, frequent seizures despite treatment, and poor quality of life. Surgery is considered when non-surgical methods fail to control seizures, and it involves careful assessment by a medical team.
Best Epilepsy Surgery Treatment in India
The Best Epilepsy Surgery Treatment in India is performed by expert neurologists who use advanced techniques to ensure optimal outcomes for patients, offering a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual health needs.
Best Epilepsy Surgery Hospitals in India
The Best Epilepsy Surgery Hospitals in India are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and facilities, providing top-notch care, including pre-surgery consultations, surgical expertise, and post-operative recovery support to ensure a smooth patient journey.
Epilepsy Surgery Cost in India
When considering the Epilepsy Surgery Cost in India, patients benefit from affordable and transparent pricing at leading hospitals, which offer cost-effective treatment options without compromising the quality of care.
Best Epilepsy Surgery Doctors in India
The Best Epilepsy Surgery Doctors in India are highly experienced in performing the surgery, utilizing a patient-centric approach that ensures personalized care, precise surgical techniques, and dedicated follow-up care to enhance recovery.
The Role of Autoimmune Disorders in Epilepsy
Autoimmune conditions, such as lupus or multiple sclerosis, can attack the brain’s tissues and increase the risk of seizures. This type of epilepsy, called autoimmune epilepsy, occurs when the immune system creates inflammation or damages nerve cells in the brain, causing seizures.
Hormonal Changes and Epilepsy: How the Two are Connected
For some women, fluctuations in hormones, particularly during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause, can trigger epileptic seizures. This form of epilepsy, known as catamenial epilepsy, is linked to changes in estrogen and progesterone levels, which influence brain activity.
How Sleep Disorders Can Increase the Risk of Epileptic Seizures
Sleep disorders, like insomnia or sleep apnea, can increase the likelihood of epilepsy by depriving the brain of restorative sleep. Sleep deprivation lowers the brain’s threshold for seizures, making it easier for electrical disruptions to trigger seizures. Maintaining proper sleep hygiene is essential for seizure management.
The Impact of Emotional Stress on Epilepsy Development
Chronic emotional stress can lead to epilepsy in some individuals by increasing the frequency of electrical discharges in the brain. Stress-induced epilepsy often presents as psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES), where stress mimics the symptoms of epilepsy. Proper stress management can reduce seizure episodes.
How Environmental Factors Trigger Epileptic Seizures
Certain environmental factors, such as bright flashing lights, loud sounds, or extreme temperatures, can trigger seizures in individuals with reflex epilepsy. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is crucial for preventing seizure occurrences in susceptible individuals.
The Role of Nutrition in Managing Epilepsy
A well-balanced diet can play a significant role in managing epilepsy, particularly in children. The ketogenic diet, which is high in fats and low in carbohydrates, has been shown to reduce seizure frequency in some individuals. Proper nutritional support, including supplements, can enhance overall brain health and improve outcomes.
Understanding Epilepsy After Brain Surgery
Following brain surgery, some patients may develop epilepsy as a side effect of the procedure. This is particularly common after surgeries that involve removing tumors or treating other neurological conditions. Post-surgical epilepsy can often be managed through medication or additional procedures to control seizures.
Types of Epilepsy Surgeries: Which Is Right for You?
For patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, various surgical options are available, including lobectomy, lesionectomy, and corpus callosotomy. Each surgery targets different parts of the brain where seizures originate. Choosing the right surgery depends on the patient’s specific type of epilepsy and overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Epilepsy: What Are Your Options?
Not all cases of epilepsy require surgery. There are various non-surgical treatments, including anti-seizure medications, the ketogenic diet, and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), which can help manage seizures. Combining these treatments with lifestyle changes can offer significant relief for many patients.
Diagnostic Tests for Epilepsy: How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors use a combination of tests to diagnose epilepsy, including EEGs (electroencephalograms), MRIs, CT scans, and blood tests. These tests help to identify the cause of seizures, the type of epilepsy, and the best treatment options available for each patient.
The Role of Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Treatment
Advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and PET scans, are used to pinpoint the location of seizure activity in the brain. These images guide doctors in planning epilepsy treatments, including surgeries, by providing detailed maps of the brain’s structure and function.
How Epilepsy Affects Quality of Life
Living with epilepsy can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Challenges include the physical limitations caused by seizures, medication side effects, and emotional stress. However, with the right treatment and support, many individuals with epilepsy lead fulfilling lives. Early intervention and comprehensive care are key.
Differences in Epilepsy Management Between Children and Adults
Managing epilepsy varies between children and adults. Children may require special consideration regarding medication doses, growth, and development, while adults may face additional challenges related to aging, other medical conditions, or lifestyle. Tailored treatment plans are essential for optimal care.
The Future of Epilepsy Treatment: What to Expect
Advancements in epilepsy treatment are ongoing, with new therapies like gene therapy, advanced brain stimulation, and personalized medicine showing promise. The future of epilepsy care is geared toward more effective, less invasive treatments that improve seizure control and enhance quality of life.
FAQs
What is the success rate of epilepsy surgery?
The success rate of epilepsy surgery depends on the type of surgery and the location of the seizure focus. In cases where the seizure origin is well-defined, success rates can be as high as 70-80% in significantly reducing or completely stopping seizures.
Is epilepsy curable?
While epilepsy is not always curable, it is manageable through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery. Many individuals with epilepsy lead seizure-free lives with the right treatment plan.
Can epilepsy be triggered by stress?
Yes, stress is a common trigger for seizures in people with epilepsy. Chronic stress can increase the frequency and intensity of seizures, making stress management an important aspect of epilepsy treatment.
What is the ketogenic diet and how does it help with epilepsy?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has been shown to reduce the frequency of seizures in some individuals, particularly children. The diet helps the brain use ketones for energy, which may reduce seizure activity.
Can epilepsy develop later in life?
Yes, while epilepsy often begins in childhood, it can also develop later in life due to factors such as brain injuries, strokes, or neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. In older adults, epilepsy is commonly linked to these underlying conditions.
How is epilepsy diagnosed?
Epilepsy is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, neurological exams, and tests like EEGs and MRIs. These tools help doctors identify abnormal brain activity and determine the type of epilepsy a patient may have.
What are the different types of seizures?
There are two main types of seizures: generalized seizures, which affect the entire brain, and focal seizures, which affect just one part of the brain. Each type can present with different symptoms and require different treatments.
What medications are used to treat epilepsy?
A variety of anti-seizure medications (also called anticonvulsants) are used to control seizures. These medications work by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain. The choice of medication depends on the type of epilepsy and the patient’s overall health.
How can I support someone with epilepsy?
Supporting someone with epilepsy involves understanding their condition, knowing what to do in the event of a seizure, and being aware of their treatment needs. Providing emotional support and reducing stigma around epilepsy are also essential for improving quality of life.
What should I do if I witness someone having a seizure?
If you witness someone having a seizure, stay calm and help them to a safe position. Do not restrain them, but ensure that they are not in danger of injuring themselves. After the seizure, allow them to rest and seek medical attention if necessary.
Discover the Best Neurosurgery Hospitals and Neurosurgeons in India
When it comes to brain and spine care, choosing the right hospital and specialist is essential. We�ve highlighted the top neurosurgery hospitals and neurosurgeons across India to ensure you receive the best care available.
Top Neurosurgery Hospitals in India
Find the leading centers for brain and spine care:
Best Neurosurgeons in India
Meet the top specialists in brain and spine surgery:
Conclusion
Your brain and spine health deserve the best care. Explore the links above to learn more about the top neurosurgery hospitals and neurosurgeons in India.
Related Resources
At ArogyaJivan, we strive to provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information to help you make informed decisions about your healthcare. Whether you are searching for the Best Doctors in India or the Top 5 Doctors in India, our resources are tailored to guide you through your medical journey. Additionally, our comprehensive guides on the Best Hospitals in India and the Top 5 Hospitals in India will assist you in choosing the right healthcare facility for your needs. Explore these resources to ensure you receive the best possible care.